Abstract
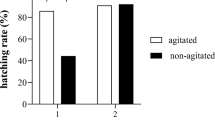
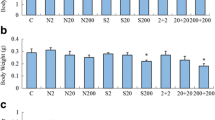
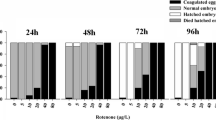
This study describes a long-term test over three generations, using zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio) as the test species and concentrations of 1, 0.2, and 0.04 mg/L 4-chloroaniline (CA) as a model substance. The effect of the compound on the ecologically important parameters reproduction and growth was the focus of interest. Reduction in egg release by fish raised under CA was the most sensitive parameter in the test. Compared to the toxic threshold concentration for growth (0.4 mg/L), egg release was affected by a ten-fold lower concentration (0.04 mg/L). This study demonstrates that a long-term test is still the most appropriate method to assess the chronic toxicity of a substance on fish. A chronic toxicity test is proposed which comprises two generations, with the zebrafish as test species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braunbeck T, Storch V, Bresch H (1990) Species specific reaction of liver ultrastructure in zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio) and trout (Salmo gairdneri) after prolonged exposure to 4-chloroaniline. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:405–418
Bresch H (1982) Investigation of the long-term action of xenobiotics on fish with special regard to reproduction. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 6:102–112
— (1983) Beiträge zur Entwicklung eines Langzeittests am Fisch im Rahmen des Chemikaliengesetzes. Texte 27/83:111–137 Umweltbundesamt, Berlin
— (1984) A simple way of storing numerical and metrical parameters of fish progeny for toxicological studies by photograms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 32:491–496
Bresch H, Markert M, Munk R, Spieser OH (1986) Long-term fish toxicity test using the zebrafish: Effect of group formation and temporary separation by sex on spawning. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 37:606–614
Chorus I (1987) Literaturrecherche und Auswertung zur Notwendigkeit chronischer Tests—insbesondere des Reproduktionstests-am Fisch für die Stufe II nach dem Chemikaliengesetz. Studie I 4.1.-9731617 Umweltbundesamt, Berlin
Dave G, Damgaard B, Grande M, Martelin JE, Rosander B, Viktor T (1987) Ring test of an embryolarval toxicity test with zebra-fish (Brachydanio rerio) using chromium and zinc as toxicants. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:61–71
European Communities (1979) Council directive of 18 September 1979 amending for the sixth time directive 67/548/EEC on the approximation of the laws, regulations and administrative provisions relating to the classification, packaging and labelling of dangerous substances. Official Journal of the European Communities L 259:10–28 (15 October 1979)
Fogels A, Sprague JB (1977) Comparative short-term tolerance of zebrafish, flagfish and rainbow trout to five poisons including potential reference toxicants. Water Res 11:811–817
Korte F, Greim H (1981) Überprüfung der Durchführbarkeit von Prüfvorschriften und der Aussagekraft der Grundstufe des Entwurfs zum Chemg. Gesellschaft für Strahlen- und Umweltforschung München, mbH, Neuherberg. Im Auftrage des Umweltbundesamtes. Forschungsbericht 10704006/01, Umweltbundesamt, Berlin
Laale HW (1977) The biology and use of zebrafish,Brachydanio rerio, in fisheries research. A literature review. J Fish Biol 10:121–173
Landner L, Neilson AH, Sörensen L, Tärnholm A, Viktor T (1985) Short-term test for predicting the potential of xenobiotics to impair reproductive success in fish. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 9:282–293
Malle KG (1984) Die Bedeutung der 129 Stoffe der EG-Liste für den Gewässerschutz. Z Was Abwas Forsch 17:75–81
McKim JM (1977) Evaluation of tests with early life stages of fish for predicting long-term toxicity. J Fish Res Board Can 34:1148–1154
Mount DI (1968) Chronic toxicity of copper to fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas, Rafinesque). Water Res 2:215–223
Munk R (1984) Überprüfung der Durchführbarkeit von Prüfungs-vorschriften und der Aussagekraft der Stufen 1 und 2 des Chemg, BASF AG, Ludwigshafen. Forschungsbericht 10604011/03 Umweltbundesamt, Berlin
Nagel R (1986) Untersuchungen zur Eiproduktion beim Zebrabärbling (Brachydanio rerio, Ham.-Buch.). J Appl Ichthyol 4:173–181
Newsome CS, Piron RD (1982) Aetiology of skeletal deformities in the zebradanio fish (Brachydanio rerio, Hamilton-Buchanan). J Fish Biol 21:231–237
Piron RD (1978) Spontaneous skeletal deformities in the zebradanio (Brachydanio rerio) bred for fish toxicity tests. J Fish Biol 13:79–83
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52:591–611
Scheffé H (1953) A method for judging all contrasts in the analysis of variance. Biometrika 40:87–104
Smith WE (1973) A cyprinodontid fish,Jordanella floridae, as reference animal for rapid chronic bioassays. J Fish Res Board Can 39:329–330
Sprague B (1973) The ABC's of pollutant bioassay using fish. In: Biol. methods for the assessment of water quality. American Society for Testing and Materials, special technical publication No 528:6–30
Suter II GW, Aaron RE, Linder E, Parkhurst DF (1987) Endpoints for responses of fish to chronic toxic exposures. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:793–809
Watanabe T, Ohta M, Kitajima C, Fujita S (1983) Improvement of dietary value of brine shrimpArtemia salina for fish larvae by feeding them on omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty-acids. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 48:1775–1782
Wegemann RCC, De Korte GAL (1981) Aromatic amines in surface waters of the Netherlands. Water Res 15:391–394
Wellens H (1982) Comparison of the sensitivity ofBrachydanio rerio andLeuciscus idus in the study of the toxicity to fish of chemical compounds and wastewaters. Z Was Abwas Forsch 15:49–52
Woltering DM (1984) The growth response in fish chronic and early life stage toxicity tests: a critical review. Aquat Toxicol 5:1–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bresch, H., Beck, H., Ehlermann, D. et al. A long-term toxicity test comprising reproduction and growth of zebrafish with 4-chloroaniiine. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19, 419–427 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054987
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054987