Summary
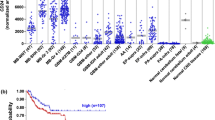
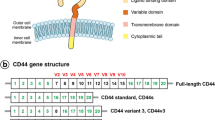
Expression of CD44, particularly of certain splice variants, has been linked to tumor progression and metastatic potential in a number of different animal and human cancers. Although differential expression of CD44 standard epitopes (CD44s) in human brain tumors has been reported, the expression of CD44 variant exon encoded sequences (CD44v) in primary brain tumorsin situ has not been studied in detail. In the present study, the expression of CD44s and CD44v epitopes was analyzed immunohistochemically on frozen sections of primary brain tumors. In addition, the expression of CD44 on cultured glioma cells was investigated by immunofluorescence flow cytometry. The results demonstrate the presence of CD44s epitopes and of CD44 splice variants containing CD44v4, v5 and v10 sequences in various types of brain tumors. A subgroup of highly malignant gliomas showed a strong (focal) expression of CD44v5. CD44v6 was absent in all brain tumors examined. CD44s appeared to be the dominant form of CD44 expressed in primary brain tumors, its expression was not correlated with tumor grade. We envisage that CD44 isoforms, in particular CD44s, may contribute to the invasive character of primary tumors by interacting with hyaluronate, one of the most abundant molecules in the extracellular matrix of the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underbill CB, Seed B: CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61: 1303–1313, 1990
Lesley J, Hyman R, Kincade PW: CD44 and its interaction with the extracellular matrix. Adv Immunol 54: 271–335, 1993
Stamenkovic I, Amiot M, Pesando JM, Seed B: A lymphocyte molecule implicated in lymph node homing is a member of the cartilage link protein family. Cell 56: 1057–1062, 1989
Dougherty GJ, Lansdorp PM, Cooper DL, Humpries RH: Molecular cloning of CD44R1 and CD44R2, two novel isoforms of the human CD44 lymphocyte ‘homing’ receptor expressed by haemopoietic cells. J Exp Med 174: 1–5, 1991
Günthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S, Zöller M, Hausmann I, Matzku M, Wenzel A, Ponta H, Herrlich P: A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell 65: 13–24, 1991
Jackson DG, Buckley J, Bell JI: Multiple variants of the human lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 generated by insertions at a single site in the extracellular domain. J Biol Chem 267: 4732–4739, 1992
Koopman G, Griffioen AW, Ponta H, Herrlich P, van den Berg F, Manten-Horst E, Pals ST: CD44 splice variants: expression on lymphocytes and in neoplasia. Res Immunol 144: 750–754, 1993
Screaton GF, Bell MV, Jackson D, Cornelius FB, Gerth U, Bell J: Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternative spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89: 12160–12164, 1992
Heider KH, Hofmann M, Horst E, van den Berg F, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST: A human homologue of rat metastasisassociated variant of CD44 is expressed in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps. J Cell Biol 120: 227–233, 1993
Koopman G, Heider K-H, Horst E, Adolf GR, van den Berg F, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST: Activated human lymphocytes and aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphomas express a homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44. J Exp Med 177: 897–904, 1993
Jalkanen ST, Bargatze RF, Herron LR, Butcher EC: A lymphoid cell surface glycoprotein involved in endothelial and lymphocyte homing in man. Eur J Immunol 16: 1195–1202, 1986
Haynes BF, Telen MJ, Hale LP, Denning SM: CD44-A molecule involved in leukocyte adherence and T-cell activation. Immunol Today 10: 423–428, 1989
Miyake K, Underhill CB, Lesley J, Kincade PW: Hyaluronate can function as a cell adhesion molecule and CD44 participates in hyaluronate recognition. J Exp Med 172: 69–75, 1990
Rudy W, Hofmann M, Schwartz-Albiez R, Zöller M, Heider KH, Ponta H, Herrlich P: The two major CD44 proteins expressed on a metastatic rat tumor cell line are derived from different splice variants each one individually suffices to confer metastatic behavior. Cancer Res 53: 1262–1268, 1993
Wielenga VJM, Heider KH, Offerhaus GJA, Adolf GR, van den Berg F, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST: Expression of CD44 variant proteins in human colorectal cancer is related to tumor progression. Cancer Res 53: 4754–4756, 1993
Manten-Horst E, Danen EHJ, Smit L, Snoek M, Le Poole C, Van Muijen GNP, Pals ST, Ruiter DJ: Expression of CD44 splice variants in human cutaneous melanoma and melanoma cell lines is related to tumor progression and metastatic potential. Submitted for publication, 1994
Kuppner MC, Van Meir EG, Gauthier TH, Hamou H-F, de Tribolet N: Differential expression of the CD44 molecule in human brain tumours. Int J Cancer 50: 572–566, 1992
Asher R, Bignami A: Hyaluronate binding and CD44 expression in human glioblastoma cells and astrocytes. Exp Cell Res 203: 80–90, 1992
Pilkington GJ, Akinwunmi J, Ognjenovic N, Rogers JP: Differential binding of anti-CD44 on human gliomasin vitro. Neuroreport 4: 259–262, 1993
Radotra B, McCormick D, Crockard A: CD44 plays a role in adhesive interactions between cells and extracellular matrix components. Neuropath Appl Neurobiol 20: 399–405, 1994
Merzak A, Koocheckpour S, Pilkington GJ: CD44 mediates human glioma cell adhesion and invasionin vitro. Cancer Res 54: 3988–3992, 1994
LiH, Hamou M-F, de Tribolet N, Jaufeerally R, Hofmann M, Diserens A-C, van Meir EG: Variant CD44 adhesion molecules are expressed in human brain metastases but not in glioblastomas. Cancer Res 53: 5345–5349, 1993
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW: Histological typing of tumours of the central nervous system. In: World Health Organization International Histological Classification of Tumours. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, 1993
Albelda SM: Role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab Invest 68: 4–17, 1993
Ruoslahti E: Control of cell motility and tumour invasion by extracellular matrix interactions. Br J Cancer 66: 239–242, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaaijk, P., Troost, D., Morsink, F. et al. Expression of CD44 splice variants in human primary brain tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 26, 185–190 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052621
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052621