Abstract
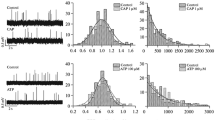
The role of postysynaptic potentiation (PSP) and asynchronous secretion of acetylcholine (ACh) in the generation of multiquantal currents and end plate currents (EPC) was investigated under voltage clamp conditions in transected sartorius muscle of the frog before and after 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) treatment. Compared with miniature EPC (MEPC), showing an average quantum content of 249, multiquantal EPC has a larger amplitude, longer rise-time, and longer decay-time (τepc). Magnesium ions (6–10 mM) reduce the amplitude and τspec of EPC without affecting its rise-time. Rhythmical stimulation (10 Hz for 60 sec) results in reduced amplitude and τ but increased rise-time of EPC. D-turbocurarine (5×10−7 M) and α-bungarotoxin (1×10−5 gm/ml) diminishes the difference between τepc and τmepc. In the presence of 4-AP, all these effects are much more pronounced. It is proposed that asynchronous secretion of ACh from motor nerve teminals causes prolongation of the rise-time and reduction of the amplitude of EPC but has little or no effect upon the decay rate of EPC. The slow decay of multiquantal EPC, both in the absence and in the presence of 4-AP, is almost entirely due to postynaptic interaction of ACh quanta, i.e., PSP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
I. N. Volkova and I. A. Kalilov, "Blockage of action potentials at portions of the frog nerve terminal," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,61, No. 9, 1433–1436 (1975).
A. L. Zefirov and I. A. Kalilov, "Features of electrical activity at different portions of the frog nerve terminal," Byull. Éksp. Biol. Med.,159, No. 1, 7–10 (1985).
L. G. Magazanik and M. L. Minenko, "Polymodality of distribution of synaptic delays at a frog nerve-muscle synapse," Neirofiziologiya,18, No. 6, 748–756 (1986).
L. G. Magazanik, E. E. Nikol'skii, and R. A. Giniatullin, "Dependence of the decay rate of end plate currents upon quantum content and preceding synaptic activity," Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,271, No. 2, 489–492 (1983).
L. G. Magazanik, V. V. Fedorov, and V. A. Snetkov, "Factors controlling the duration of a single postsynaptic response at nerve-muscle junctions," Neirofiziologiya,16, No. 5, 590–602 (1984).
M. L. Minenko and L. G. Magazanik, "The phenomenon of asynchronism of evoked release at frog nerve-muscle junction," Neirofiziologiya,18, No. 3, 346–354 (1986).
N. B. Datyner and P. W. Gage, "Phasic secretion of acetylcholine at a mammalian neuromuscular junction," J. Physiol.,303, 299–314 (1980).
Del Castillo, B. Katz, "Quanatal component of the end-plate potential," J. Physiol.,124, No. 2, 560–573 (1954).
L. Erdelyi, "The action of 4-aminopyridine on the electromotor synapse ofTorpedo marmorata," Neurosci., Lett.,39, No. 3, 291–294 (1983).
H. C. Hartzell, S. W. Kuffler, and D. Yashikami, "Postsynaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse," J. Physiol.,251, No. 2, 427–463 (1975).
B. Katz and R. Miledi, "The binding of acetylcholine to receptor and its removal from the synaptic cleft," J. Physiol.,231, No. 3, 549–574 (1973).
B. Katz and R. Miledi, "The measurement of synaptic delay and the time course of acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction," Proc. R. Soc., Ser. B.,161, 985, 483–495 (1965).
B. Katz and R. Miledi, "The measurement of quantal content during "chemical potentiation" of transmitter release," Proc. R. Soc., Ser. B.,205, 1046, 369-378 (1979).
J. J. Lambert, N. N. Durant, L. S. Reynolds, et al., "Characterization of end-plate conductance in transsected frog muscle: modification by drugs," J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap.,216, No. 1, 62–69 (1981).
H. Lundth and S. Thesleff, "The mode of action of 4-aminopyridine and guanidine on transmitter release from motor nerve terminals," Eur. J. Pharmacol.,42, No. 2, 411–412 (1977).
L. G. Magazanik, V. V. Fedorov, R. A. Giniatullin, "Functional role of cholinesterase in different types of neuromuscular junction," Cholinesterases, Berlin, New York (1984), pp. 229–242.
L. G. Magazanik, E. E. Nikolsky, and R. A. Giniatullin, "End-plate currents evoked by paired stimuli in frog muscle," Pfügers Arch.,401, No. 1, 185–192 (1984).
J. M. Molgo, M. Lemeignan, and P. Lechat, "Effects of 4-aminopyridine at the frog neuromuscular junction," J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap.,203, No. 1, 3, 653–663 (1977).
H. P. Rang, "The action of ganglionic blocking drugs on the synaptic responses of rat submandibular ganglion cells (with an Appendix by D. Colquhoun and H. P. Rang), Br. J. Pharmacol.,75, No. 1, 151–168 (1982).
M. A. Rogawski and J. L. Barker, "Effects of 4-aminopyridine on calcium action potentials and calcium current under voltage clamp in spinal neurons," Brain Res.,280, No. 1, 180–185 (1983).
F. Ruzzier, F. DiGergorio, and M. Scuka, "On the changes of the time course of end-plate currents during repetitive stimulation," Pfügers Arch.,393, 1, 121–122 (1982).
F. Ruzzier and M. Scuka, "Effects of repetitive stimulation on frog neuromuscular transmission," Pfügers Arch.,382, 2, 127–130 (1982).
R. H. Tomsen and D. F. Wilson, "Effects of 4-aminopyridine and 3,4-diaminopyridine on transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction," J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap.,227, No. 1, 260–265 (1983).
Additional information
Kurashov Meidcal Institute, Kazhan. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 23, No. 1, pp. 48–56, January–February, 1991.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giniatullin, R.A., Khazipov, R.N. End plate currents at the physiological level of quantal secretion and after potentiation of transmitter release by 4-aminopyridine. Neurophysiology 23, 40–47 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052288
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052288