Abstract
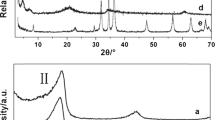
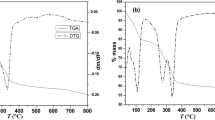
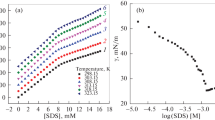
The intercalation of sodium dodecyl sulfate and exchange of dodecyl sulfate anion into layered double hydroxides has been examined by means of X-ray diffraction, infrared and thermogravimetric procedures. Three types of derivatives were obtained having mean interlayer spacings of ≈26 Å, 36 Å and 47 Å, respectively. These interlayer distances did not correlate with the amount of organic incorporated between the layers but, as shown by computer simulations, depended upon the orientation of the chains within the interlamellar space. In several reactions both intercalation of neutral sodium dodecyl sulfate as well as exchange of the dodecyl anion took place. Attempts to remove the alkyl sulfate chains with dilute acid resulted in dissolution of the more basic metals producing non-stoichiometric layered products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. T. Reichle:Chemtech 58 (1986).
R. Allmann:Chimia 24, 99 (1970).
G. Brown and M. C. Gastuche:Clay Miner. 7, 193 (1967).
L. Ingram and H. F. Taylor:Miner. Mag. 36, 465 (1967).
W. T. Reichle:Solid State Ionics 22, 15 (1986).
K. A. Carrado, A. Kostapapas and S. Suib:Solid State Ionics 26, 77 (1988).
S. Miyata:Clays Clay Miner. 31, 365 (1983).
A. Mediboure and R. Schollhorn:Rev. Chim. Miner. 23, 819 (1986).
M. A. Drezdon:Inorg. Chem. 27, 4628 (1988).
T. Kwan, G. A. Tsigdinos and T. J. Pinnavaia:J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110, 3653 (1988).
T. Kwan and T. J. Pinnavaia:Chem. Mater. 1, 381 (1989).
E. D. Dimotakis and T. J. Pinnavaia:Inorg. Chem. 29, 2993 (1990).
W. T. Reichle:J. Catal. 94, 547 (1985).
T. J. Pinnavaia, M. Rameswaran, E. G. Demotakis, E. P. Grannelis and E. G. Rightor:Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 87, 227 (1989).
S. Miyata and T. Kimura:Chem. Lett. Jpn. 843 (1973).
E. T. Iyagba: Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Pittsburg, PA, 1986.
K. Chibwe and W. Jones:J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 926 (1989).
H.-P. Boehm, J. Steinle and C. Vieweger:Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 16, 265 (1977).
H. Kopka, K. Beneke and G. Lagaly:J. Colloid Interface Sci. 123, 427 (1988).
M. Lal and A. T. Howe:J. Solid State Chem. 39, 368 (1981).
G. Lagaly:Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 15, 575 (1976).
CRYSTALS, D. Watkin,Chem. Crystallogr. Lab. Oxford, England; (b)MOGLI, Evans & Sutherland Corp., Salt Lake City, Utah; (c)COSMIC, J. G. Vinter, A. Davis and M. R. Saunders,J. Mol. Design,1 31 (1987).
R. Allmann and H. H. Lohse:N. Jahr. f. Mineral Monat. 161 (1966); R. Allmann,Acta Crystallogr. B24, 972 (1968);Chimia 24, 99 (1970).
S. Sundell:Acta. Chem. Scand. A31, 799 (1971).
S. K. Ghabru, A. R. Mermut and R. J. Arnaud:Clays Clay Miner. 37, 164 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clearfield, A., Kieke, M., Kwan, J. et al. Intercalation of dodecyl sulfate into layered double hydroxides. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 11, 361–378 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01041414
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01041414