Abstract
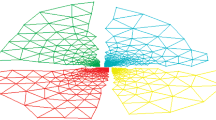
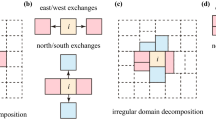
A new parallel cluster-finding algorithm is formulated by using multigrid relaxation methods very similar to those used for differential equation solvers. For percolation clusters, this approach drastically reduces critical slowing down relative to local or scan relaxation methods. Numerical studies of scaling properties with system size are presented in the case of the 2D percolation clusters of the Swendsen-Wang Ising dynamics running on the Connection Machine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Stauffer,Introduction to Percolation Theory (Taylor and Francis, London, 1984).
R. Swendsen and J. S. Wang,Phys. Rev. Lett. 58:86 (1987).
W. Klein, T. Ray, and P. Tamayo,Phys. Rev. Lett. 62:163 (1989).
P. Tamayo, R. C. Brower, and W. Klein,J. Stat. Phys. 58:1083 (1990).
R. G. Edwards and A. D. Sokal,Phys. Rev. D 38:2009 (1988); A. Sokal, Monte Carlo methods in statistical mechanics: Foundations and new algorithms, lecture notes.
C. M. Fortuin and P. W. Kasteleyn,Physica 57:536 (1972); P. W. Kasteleyn and C. M. Fortuin,J. Phys. Soc. Japan Suppl. 26s:11 (1969).
A. Coniglio and W. Klein,J. Phys. A 13:2775 (1980).
J. Hoshen and R. Kopelman,Phys. Rev. B 14:3438 (1976).
R. M. Karp, The transitive closure of a random digraph,TR-89-047, August 1989, International Computer Science Institute, Berkeley, California.
J. Woo and S. Sahni, Hypercube computing: Connected components,J. Supercomputing 3:209–234 (1989).
A. N. Burkitt and D. W. Heermann,Comp. Phys. Comm. 54:201 (1989).
A. Hansen and S. Roux,J. Phys. A 20:L873 (1987).
A. Stoll,J. Phys. Cond. Matter 1:6959 (1989).
D. Kandel, E. Domany, D. Ron, A. Brandt, and E. Loh, Jr.,Phys. Rev. Lett. 60:1591 (1988).
H. J. Herrmann and H. E. Stanley,J. Phys. A 21:L829 (1988).
N. Ito, M. Taiji, and M. Suzuki,J. Phys. (Paris)49:C8–1397 (1988).
W. Press, B. Flannery, S. Teukolsky, and W. Vetterling,Numerical Recipes (Cambridge University Press, 1988).
H. D. Simon, ed.,Scientific Applications of the Connection Machine, (World Scientific, Singapore, 1989).
P. C. Hohenberg and B. Halperin,Rev. Mod. Phys. 49:435 (1977).
J. S. Wang, Private communication.
T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson, and R. L. Rivest,Introduction to Algorithms (MIT Press, 1990); D. Knuth,The Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 3 (Addison-Wesley, 1973).
R. Brower and P. Tamayo,Phys. Rev. Lett. 62:1087 (1989).
U. Wolff,Phys. Rev. Lett. 60:1461 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brower, R.C., Tamayo, P. & York, B. A parallel multigrid algorithm for percolation clusters. J Stat Phys 63, 73–88 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01026593
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01026593