Synopsis
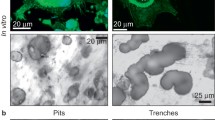
Methods for the histochemical demonstration of enzymes in whole cell preparations of odontoclasts and osteoclasts are described. Enzyme histochemical characteristics of human and kitten odontoclasts from resorbing primary teeth and of osteoclasts from kitten femur metaphyses were determined and compared. The enzyme profiles, times for the appearance of detectable reaction product, intensity of the reactions and localization of the reaction products were similar in all three types of giant cell. These findings suggest that odontoclasts have enzyme properties and metabolic functions similar to those of osteoclasts. Species differences appear to be minor, although the NADP-dependent enzymes are less active in human than in kitten odontoclasts. Both odontoclasts and osteoclasts are rich in enzymes concerned with energy production and possess considerable activity of enzymes usually associated with catabolic functions. Metabolic pathways are well developed in respect of the utilization of succinic, malic, glutamic, lactic and isocitric acids, β-hydroxybutyric acid and glucose-6-phosphate, and they also possess phosphatases, non-specific esterases and leucine naphthylamidase. The distribution of enzyme reaction products for the individual enzymes demonstrated is consistent with the presence in these cells of large numbers of mitochondria and lysosome-like organelles. Considerable phosphatase activity is demonstrable in both odontoclasts and osteoclasts at both neutral and acid pH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison, W. C. (1976).Properties and functions of odontoclasts. A comparative study. PhD. thesis. University of Birmingham.
Addison, W. C. (1978a). Enzyme histochemical properties of kitten osteoclasts in bone imprint preparations.Histochem. J. 10, 645–56.
Addison, W. C. (1978b). β-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase activity in human and kitten odontoclasts and kitten osteoclasts.Histochem. J. 10, 731–7.
Altmann, F. P. (1969). The quantitative elution of nitro-blue formazon from tissue sections.Histochemie 17, 319–26.
Altmann, F. P. (1972). Quantitative dehydrogenase histochemistry with special reference to the pentose shunt dehydrogenases.Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 4, 225–68.
Balogh, B. L. &Klapper, Z. F. (1961). Oxidative enzymes in the foreign body giant cell.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 9, 713–4.
Barka, T. (1962). Cellular localisation of acid phosphatase activity.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 231–2.
Belanger, L. G. (1965). Demineralisation with EDTA by constant replacement.Anat. Rec. 153, 41–8.
Bendall, D. S. &De Duve, C. (1960). Tissue fractionation studies. 14. The activation of latent dehydrogenases in mitochondria from rat liver.Biochem. J. 74, 444–50.
Bitensky, L. (1962). The demonstration of lysosomes by the controlled temperature freezing-sectioning method.Q. Jl. microsc. Soc. 103, 205–9.
Borle, A. B., Nichols, N. &Nichols, G. (1960). Metabolic studies of bone in vitro.J. biol. Chem. 235, 1206–14.
Burstone, M. S. (1962). In:Enzyme Histochemistry. New York: Academic Press.
Chayen, J., Bitensky, J. &Butcher, R. G. (1973).Practical Histochemistry. London: John Wright.
Doty, S. B. &Schofield, B. H. (1972). Electron microscopic localization of hydrolytic enzymes in osteoclasts.Histochem. J. 4, 245–58.
Freilich, L. S. (1971). Ultrastructure and acid phosphates cytochemistry of odontoclasts. Effect of parathyroid extract.J. dent. Res. 50, 1047–55.
Freyvogel, T. A., Hunter, R. L. &Smith, E. M. (1968). Non-specific esterases in mosquitos.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 765–90.
Fuks, B. B., Vinogradov, V. V., Shishkin, G. S. &Maksimouski, B. (1965). Proteins, mucopolysaccharides, enzymes and DNA in skin wounds in alimentary and combined alimentary and chemical avitaminosis C.Fed. Proc. Trans. Suppl.24, 213–7.
Fullmer, H. M. (1964). Dehydrogenases in developing bone in the rat.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 12, 210–4.
Gibson, W. A. &Fullmer, H. M. (1967). Histochemistry of the periodontal ligament. II. The phosphates.Periodontics 5, 226–32.
Goggins, J. F., Lazarus, G. S. &Fullmer, H. M. (1968). Hyalurinadase activity of alveolar macrophages.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 688–92.
Gomori, G. (1952).Microscopic Histochemistry. p. 193. Chicago: Chicago University Press.
Hammarstrom, L. E. &Hasselgren, G. (1974). Acid phosphatase in developing teeth and bone of man and Macaque monkey.Scand. J. dent. Res. 82, 381–95.
Hayashi, M., Makajima, Y. &Fishman, W. H. (1964). The cytologic demonstration of beta-glucuronidase employing naphthol AS-B1 glucuronide and hexazonium pararosoniline. A preliminary report.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 12, 293–7.
Hermann-Erlee, M. P. (1961). A histochemical investigation of embryonic long bones. The effect of parathyroid hormone on the activity of a number of enzymes.Proc. Kon. Med. Akad. Wet. 65C, 22–40.
Holt, S. J. &Withers, R. F. J. (1958). Studies in enzyme cytochemistry. V. An appraisal of indigogenic reactions for esterase localisation.Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B148, 520–32.
Hopsu-Havu, V. K., Arstila, A. U., Helminen, J. J. &Kalino, H. O. (1967). Improvements in the method for the electron microscopic localisation of aryl suphatase.Histochemie 8, 54–64.
Hosoda, S. &Takaso, S. (1967). Non-specific esterase activity in histiocytes.Nature (Lond.) 190, 927.
Jeffree, G. M. (1970). The histochemical differentiation of various phosphatases in a population of osteoclasts by a simultaneous coupling method using different diazonium salts, with observations on the presence of inhibitors in stable diazonium salts.Histochem. J. 2, 231–42.
Kallio, D. M., Grant, P. R. &Minkin, C. (1972). Ultrastructural effects of calcitonin on osteoclasts in tissue culture.J. ultrastruct. Res. 39, 205–16.
Kornberg, H. L. (1961). The breakdown and synthesis of fatty acids. In:Biochemists' Handbook (ed. G. Lond), pp. 558–63. London: Spon.
Lake, B. D. (1966). The histochemistry of phosphatases; the use of lead acetate instead of lead nitrate.J. Roy. Microsc. Soc. 85, 73–5.
Lehninger, A. L. (1965).The Mitochondrion. Molecular Basis of Structure and Function. New York: Benjamin.
Lipp, W. (1959). Aminopeptidases in bone.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 7, 205.
Lojda, Z. (1962). Quoted by Pearse, A.G.E. In:Histochemistry, Vol. I. 3rd Edn. p. 732. Boston: Little, Brown.
Lundin, L. C. &Allison, A. C. (1966). Acid hydrolase iso-enzymes.Acta. chem. scand 20, 2579–81.
Niemsi, M. &Sylvan, B. (1967). Intracellular and interstitial enzyme activity in early experimental granulomas.Acta path. microbiol. scand. 70, Suppl. 76–7.
Pearse, A. G. E. (1968).Histochemistry, Theoretical and Applied, Vol. I. 3rd Edn. London: Churchill Livingstone.
Pearse, A. G. E. (1972).Histochemistry, Theoretical and Applied, Vol. II. 3rd Edn. London: Churchill Livingstone.
Reynolds, J. J. &Dingle, J. T. (1970). A sensitive in vitro method for studying the induction and inhibition of bone resorption.Calc. Tiss. Res. 4, 339–49.
Rosenberg, R. M. &Rolon, C. I. (1962). Species variability and the substrate specificity of intracellular phosphatases; a comparison of the lead salt and azo dye method.Histochemie 3, 1–16.
Seligman, A. M., Karnovsky, M. J., Wassterkrug, H. L. &Haaker, J. S. (1968). Non-droplet ultrastructural demonstration of cytochrome oxidase activity with a polymerising osmiophilic reagent, diamino benzidine (DAB).J. Cell Biol. 38, 1–14.
Severson, A. R., Tonna, E. A. &Pavelec, M. (1967). Application and evaluation of the lead-adenosine triphosphatase method in skeletal tissue.Stain Technol. 43, 221–5.
Severson, A. T., Tonna, E. A. &Pavelec, M. (1968). Application and evaluation of the lead-adenosine triphosphate method in skeletal tissue.Stain Technol. 43, 221–5.
Stuart, J. &Simpson, J. S. (1970). Dehydrogenase enzyme cytochemistry of unfixed leucocytes.J. clin. Path. 23, 517–21.
Vaughan, J. M. (1970).The Physiology of Bone. Oxford: Claverdon Press.
Wachstein, M. &Meisel, E. (1957). Histochemistry of hepatic phosphatases at a physiological pH.Am. J. clin. Path. 27, 13–21.
Walker, D. G. (1961). Citric acid cycle in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. A histochemical study of normal and PTH treated rats.Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 108, 80–99.
Walker, D. G. (1972). Enzymatic and electron microscopic analysis of isolated osteoclasts.Calc. Tiss. Res. 9, 296–309.
Yaeger, J. A. &Kraucunas, E. (1969). Fine structure of the resorptive cells in the teeth of frogs.Anat. Rec. 164, 1–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Addison, W.C. Enzyme histochemical characteristics of human and kitten odontoclasts and kitten osteoclasts: a comparative study using whole cells. Histochem J 11, 719–735 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01004735
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01004735