Abstract
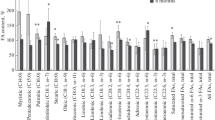
The fatty acid composition of individual glycerolipids in brain and sciatic nerve of rats made diabetic with streptozotocin and sacrificed 8 weeks later was determined and compared to the alterations that occurred in liver and kidney glycerlipids. A substantial decrease in the proportion of arachidonic acid and increases in the relative content of linoleic and docosahexenoic (22∶6n3) acids occurred in the phosphoglycerides of visceral tissues from diabetic animals as reported by others. In contrast, except for a small rise in the percentage of linoleic acid, no consistent changes in fatty acid composition of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, ethanolamine plasmalogen, phosphatidylinositol or phosphatidylerrine from brain or nerve were detected. The fatty acids of triacylglycerol associated with nerve exhibited alterations similar to those characteristic of liver. The differences which developed as a result of diabetes were completely prevented if animals were maintained continuously on insulin commencing shortly after administration of streptozotocin. It is concluded that the fatty acid composition of brain and nerve phosphoglycerides are unusually resistant to alteration in the diabetic animal and that consequently, changes in bulk membrane fluidity are unlikely to contribute to functional abnormalities displayed by diabetic peripheral nerve.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PC:
-
phosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
phosphatidylethanolamine
- EP:
-
ethanolamine plasmalogen
- PS:
-
phosphatidylserine
- PI:
-
phosphatidylinositol
References
Thomas, P. K., andEliasson, S. G. 1984. Diabetic neuropathy. Pages 1773–1810,in Dyck, P. J., Thomas, P. K. Lambert, E. H., andBunge, R. (eds). Peripheral Neuropathy (2nd ed) W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia.
Eliasson, S. J. 1964. Nerve conduction changes in experimental diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 43:2353–2358.
Sharma, A. K., andThomas, P. K. 1974. Peripheral nerve structure and function in experimental diabetes. J. Neurol. Sci. 23:1–15.
Fraser, D. M., Campbell, I. W., Ewing, D. J., Murray, A., Neilson, G. M. M., andClarke, B. F. 1977. Peripheral and autonomic nerve function in newly diagnosed diabetes melitus. Diabetes 26:546–550.
Clements, R. S. 1979. Diabetic neuropathy: New concepts of its etiology. Diabetes 28:604–611.
Greene, D. A. 1983. Metabolic abnormalities in diabetic peripheral nerve: Relation to impaired function. Metabolism 32:Suppl. 1:118–123.
Brown, M. J., Iwamori, M., Kishimoto, Y., Rapoport, R., Moser, H. W., andAsbury, A. K. 1979. Nerve lipid abnormalities in human diabetic neuropathy: A correlative study. Ann. Neurol. 5:245–252.
Eliasson, S. G. 1966. Lipid synthesis in peripheral nerve from alloxan diabetic rats. Lipids 1:237–240.
Spritz, N., Singh, H., andMarinan, B. 1975. Metabolism of peripheral nerve myelin in experimental diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 55:1049–1056.
Whiting, P. H., Palmano, K. P., andHawthorne, J. N. 1979. Enzymes of myoinositol and inositol lipid metabolism in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Biochem. J. 179:549–553.
Hothersall, J. S., andMcLean, P. 1979. Effect of experimental diabetes and insulin on phosphatidylinositol synthesis in rat sciatic nerve. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 88:477–484.
Natarajan, V., Dyck, P. J., andSchmid, H. H. O. 1981. Alterations of inositol lipid metabolism of rat sciatic nerve in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J. Neurochem. 36:413–419.
Bell, M. E., Peterson, R. G., andEichberg, J. 1982. Metabolism of phospholipids in peripheral nerve from rats with chronic streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Increased turnover of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. J. Neurochem. 39:192–200.
Faas, F. H., andCarter, W. J. 1983. Altered microsomal phospholipid composition in the streptozotocin diabetic rat. Lipids 18:339–342.
Holman, R. T., Johnson, S. B., Gerrard, J. M., Mauer, S. M., Kupcho-Sandberg, S., andBrown, D. M. 1983. Arachidonic acid deficiency in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 80:2375–2379.
Clarke, D. L., Hamel, F. G., andQueener, S. F. 1983. Changes in renal phospholipid fatty acids in diabetes melitus: Correlation with changes in adenylate cyclase activity. Lipids 18:696–705.
Huang, X. S., Horrosin, D. F., Manku, M. S., Mitchell, J., andRyan, M. A. 1984. Tissue phospholipid fatty acid composition in the diabetic rat. Lipids 19:367–370.
Folch, J., Lees, M., andSloane-Stanely, G. H. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226:497–509.
Vitello, P., andZanetta, J. P. 1978. Thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids. J. Chromat. 166:637–640.
Horrocks, L. A. andSun, G. Y. 1972. Ethanolamine Plasmalogens Pages 223–231,in Marks, N., andRodnight, R. (eds.), Research Methods in Neurochemistry, Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York.
Morrison, W. R. andSmith, L. M. 1964. Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters and dimethylacetals from lipids with boron trifluoride-methanol. J. Lipid Res. 5:600–608.
Klein, F., andMandel, P. 1976. Distribution of the fatty acids of the lipids of normal sciatic nerve of the rat. Biochimie 60:81–84.
Yao, J. K., Dyck, P. J., VanLoon, J. A., andMoyer, T. P. 1981. Free fatty acid composition of human and rat peripheral nerve. J. Neurochem. 36:1211–1218.
Holub, B. J., Kuksis, A. andThompson, W. 1970. Molecular species of mono-di- and triphosphoinositides of bovine brain. J. Lipid Res. 11, 558–564.
Yao, J. K., Natarajan, V., andDyck, P. J. 1980. The sequential alterations of endoneurial cholesterol and fatty acid in Wallerian degeneration. J. Neurochem. 35:933–940.
Peluffo, R., Hyola, S., andBrenner, R. R. 1970. Metabolism of fatty acids of the linoleic acid series in testicles of diabetic rats. Amer. J. Physiol. 218:669–673.
Eck, M. G., Wynn, J. O., Carter W. J., andFaas, F. H. 1979. Fatty acid desaturation in experimental diabetes melitus. Diabetes 28:479–485.
Pratt, J. H., Berry, J. F., Kaye, B., andGoetz, F. C. 1969. Lipid class and fatty acid composition of rat brain and sciatic nerve in alloxan diabetes. Diabetes: 18:556–561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special Issue dedicated to Dr. Eugene Kreps.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CJ., Peterson, R. & Eichberg, J. The fatty acid composition of glycerolipids in nerve, brain, and other tissues of the streptozotocin diabetic rat. Neurochem Res 10, 1453–1465 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988859
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988859