Abstract
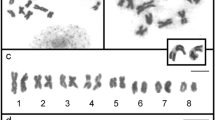
Orcein staining, differential staining with CMA and DAPI, and FISH with an rDNA probe were used to compare somatic chromosomes ofCeratozamia mexicana andMicrocycas calocoma. CMA-positive dots and hybridization signals appeared on chromosomes at early interphase and mitotic prophase, but in significantly different number in the two species. InCeratozamia mexicana, the CMA-positive and DAPI-negative bands and the hybridization signal were located at the terminal region of the long arm of three median-centromeric chromosomes, the terminal region of the short arm of two median-centromeric chromosomes and the terminal region of the long arm of two subterminal-centromeric chromosomes. InMicrocycas calocoma, they were located at the pericentric region of two median-centromeric chromosomes. These chromosome data suggested thatMicrocycas has no simple Robertsonian relationship toCeratozamia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anamthawat-Jonsson, K., Schwarzacher, T., Heslop-Harrison, J. S., 1993: Behaviour of parental genomes in the hybridHordeum vulgare ×H. bulbosum. — J. Heredity84: 78–82.
Gerlach, W. L., Bedbrook, J. R., 1979: Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genus from wheat and barley. — Nucl. Acids Res.7: 1869–1885.
Hubbell, H. R., 1985: Silver staining as an indicator of active ribosomal genes. — Stain Technol.60: 285–294.
Jones, D. L., 1993: Cycads of the world. — Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press.
Kokubugata, G., Kondo, K., 1996: Differential fluorescent-banding patterns in chromosomes of four species ofCycas (Cycadaceae). — Bot. J. Linn. Soc.120: 51–55.
Kondo, K., Kokubugata, G., Hizume, M., Tanaka, R., Satake, T., 1995: A karyomorphological study of five species and one variety ofCycas. — Cytologia60: 141–147.
Levan, A., Fredga, K., Sandberg, A. A., 1964: Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. — Hereditas52: 201–220.
Marchant, C. J., 1968: Chromosome patterns and nuclear phenomena in the cycad familiesStangeriaceae andZamiaceae. — Chromosoma24: 100–134.
Mogford, D. J., 1979: Heterochromatin inEncephalartos. — Cytologia44: 951–954.
Moretti, A., 1982: Quinacrine fluorescence analysis of the chromosomes ofMacrozamia Miq. (Cycadales, Zamiaceae). — Delpinoa24: 129–136.
—, 1990a: Karyotypic data on north and central AmericanZamiaceae (Cycadales) and their phylogenetic implications. — Amer. J. Bot.77: 1016–1029.
—, 1990b: Cytotaxonomy of cycads. — Mem. New York Bot. Gard.57: 114–122.
—, 1984: Karyotype evolution by centromeric fission inZamia (Cycadales). — Pl. Syst. Evol.146: 215–223.
Sax, K., Beal, J. M., 1934: Chromosomes of theCycadales. — J. Arnold Arb.15: 255–228.
Schuster, J., 1932:Cycadaceae. — InEngler, A., (Ed.): Das Pflanzenreich,99. — Leipzig: Engelmann.
Schweizer, D., Nagl, W., 1976: Heterochromatin diversity inCymbidium, and its relationship to differential DNA replication. — Exp. Cell Res.98: 411–423.
Stevenson, D. W., 1990a: Morphology and systematics of theCycadales. — Mem. New York Bot. Gard.57: 8–55.
—, 1990b:Chigua, a new genus in theZamiaceae with comments on its biogeographical significance. — Mem. New York Bot. Gard.57: 169–172.
—, 1992: A formal classification of the extant cycads. — Brittonia44: 220–223.
Timmis, J. N., Deumling, B., Ingle, J., 1975: Localization of satellite DNA sequences in nuclei and chromosomes of two plants. — Nature257: 152–155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokubugata, G., Kondo, K. Comparative karyotype analysis ofCeratozamia mexicana andMicrocycas calocoma (Zamiaceae) using fluorochrome banding (CMA/DAPI) and fluorescence in situ hybridization of ribosomal DNA. Pl Syst Evol 210, 41–50 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984726
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984726