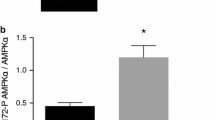
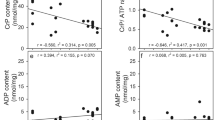
Abstract
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is the key enzyme in cerebral glutamine production. Understanding the regulation of the expression of GS is important for definition of the control of glutamine metabolism in brain. Therefore, we studied the control of GS expression by 8-bromo cyclic AMP in primary cultures of astrocytes prepared from brains of neonatal rats. GS activity was increased by 8-bromo cyclic AMP in a dose- and time-dependent manner. This increase was associated with a corresponding increase in the steady-state level of GS mRNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez-Hernandez, A., Bell, K. P., and Norenberg, M. D. 1977. Glutamine synthetase: glial localization in brain. Science 195:1356–1358.
Waniewski, I. A., and Martin, D. L. 1986. Exogenous glutamate is metabolized to glutamine and exported by rat primary astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 47:304–313.
Browning, E. T., and Nicklas, W. J. 1982. Induction of glutamine synthetase by dibutyryl cyclic AMP in C6 glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 39:336–341.
Nagamine, Y., and Reich, E. 1985. Gene expression and cAMP Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:4606–4610.
Hertz, L., Juurlink, B. H. J., Fosmark, H., and Schousboe, A. 1982. Astrocytes in primary culture, Pages 175–186,in Pfeiffer, S. E. (ed.), Neuroscience Approached Through Cell Culture, Vol. 1, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
McCarthy, K., and deVellis, J. 1980. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglia cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J. Cell. Biol. 85:890–902.
Max, S. R., Thomas, J. W., Banner, C., Vitković, L., Konagaya, M., and Konagaya, Y. 1987. Glucocorticoid receptor mediated induction of glutamine synthetase in skeletal muscle cellsin vitro. Endocrinology 120:1179–1183.
Max, S. R., Mill, J., Mearow, K., Konagaya, M., Konagaya, Y., Thomas, J. W., Banner, C., and Vitkovć, L. 1988. Dexamethasone regulates glutamine synthetase expression in rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 255:E397-E403.
Chirgwin, J. M., Przybula, A. E., MacDonald, R. J., and Rutter, W. J. 1979. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18:5294–5299.
Rave, N., Crvenjakov, R., and Boedtker, H. 1979. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzylmethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 6:3559–3567.
Mearow, K. M., Mill, J. F., and Vitković L. 1989. The ontogeny and localization of glutamine synthetase gene expression in rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 6:223–232.
Thomas, P. S. 1980. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:5201–5205.
Sanders, P. G., and Wilson, R. H. 1984. Amplification and cloning of the Chinese hamster glutamine synthetase gene. Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ. J. 3:65–71.
Feinberg, P. G., and Vogelstein, B. 1983. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 132:6–13.
Feinberg, P. G., and Vogelstein, B. 1984. A technique for radiolbeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 137:266–267.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Winer, B. J. 1962. Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. p. 302. McGraw Hill, New York.
Zielke, H. R., Tildon, J. T., and Max, S. R. 1989. cAMP increases glutamine synthetase activity in astrocytes. Trans. Am. Soc. Neurochem. 20:125.
Bhandari, B., Burns, D. M., Hoffman, R. C., and Miller, R. E. 1986. Glutamine synthetase mRNA in cultured 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Complexity, content and hormonal regulation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 47:49–57.
Kumar, S., Holmes, E., Scully, S., Birren, B. W., Wilson, R. H., and de Vellis, J. 1986. The hormonal regulation of gene expression of glial markers: glutamine synthetase and glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase in primary cultures of rat brain and in C6 cell line. J. Neurosci. Res. 16:251–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Max, S.R., Landry, M.E. & Zielke, H.R. Induction of glutamine synthetase by 8-bromo cyclic AMP in primary cultures of rat brain astrocytes. Neurochem Res 15, 583–586 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00973746
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00973746