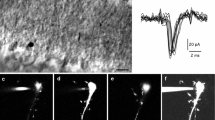
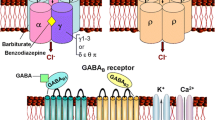
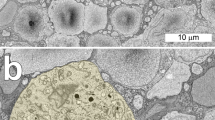
Abstract
GABAergic neurons in the vertebrate retina have received intensive study. Yet there are several notable examples of a “mismatch” among the cytochemical markers used to identify GABAergic neurons. The mismatch between [3H]GABA uptake autoradiography and all other indicators of GABAergic neurons as they pertain to amacrine cells in goldfish retina is examined in this overview. The discrepancies can be accounted for largely by barriers to diffusion presented by significant GABA uptake sinks at the inner and outer margins of the retina and by the differential subcellular distribution of the various markers for GABAergic neurons. Also, conditions producing a redistribution of [3H]-GABA and endogenous GABA stores within the retina are described and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts, E., and Frankel, S. 1950. γ-Aminobutyric acid in brain: its formation from glutamic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 187:55–63.
Mandel, P., and DeFeudis, F. V. 1979. GABA-Biochemistry and CNS Functions, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol. 123, Plenum Press, New York.
Erdo, S. L., and Wolff, J. R. 1990. γ-Aminobutyric acid outside the mammalian brain. J. Neurochem. 54:363–372.
Roberts, E. 1978. New directions in GABA research. I: Immunocytochemical studies of GABA neurons. pages 28–45,in Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Scheel-Kruger, J., and Kofod, H. (eds.), GABA-Neurotransmitters: Pharmacochemical, Biochemical and Pharmacological Aspects, Academic Press, New York.
Wuenschell, C. W., Fisher, R. S., Kaufmann, D. L., and Tobin, A. J. 1986.In situ hybridization to localize mRNA encoding the neurotransmitter synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase in mouse cerebellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 83:6139–6197.
Sarthy, P. V., and Fu, M. 1989. Localization of L-glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA in cat retinal horizontal cells byin situ hybridization. J. Comp. Neurol. 288:593–600.
Sarthy, P. V., and Fu, M. 1989. Localization of L-glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA in monkey and human retina byin situ hybridization. J. Comp. Neurol. 288:691–697.
Herkenham, M. 1987. Mismatches between neurotransmitter and receptor localizations in brain: observations and implications. Neuroscience 23:1–38.
Dowling, J. E. 1987. The Retina: An Approachable Part of the Brain, Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Yazulla, S. 1986. GABAergic mechanisms in the retina. Prog. in Retinal Res. 5:1–52.
Mosinger, J. L., and Yazulla, S. 1987. Double-label analysis of GABA-like and GAD-like immunoreactivity in rabbit retina. Vision Res., 27:23–30.
Chun, M. H. and Wassle, H. 1989. GABA-like immunoreactivity in the cat retina: electron microscopy. J. Comp. Neurol. 279:55–67.
Wassle, H., and Chun, M. H. 1989. GABA-like immunoreactivity in the cat retina: light microscopy. J. Comp. Neurol. 279:43–54.
Yazulla, S. 1985. Factors controlling the release of GABA from goldfish retinal horizontal cells. Neurosci. Res., Suppl. 2, S147-S165.
Yazulla, S., and Brecha, N. 1980. Binding and uptake of the GABA analogue,3H-muscimol, in the retinas of goldfish and chicken. Invest. Ophthalmol., 19:1415–1426.
Yazulla, S., and Kleinschmidt, J. 1983. Carrier-mediated release of3H-GABA from goldfish retinal horizontal cells. Brain Res., 263:63–75.
Yazulla, S. 1981. GABAergic synapses in the goldfish retina: an autoradiographic study of3H-muscimol and 3H-GABA binding. J. Comp. Neurol. 200:83–93.
Wenthold, R. J., Zempel, J. M., Parakkal, M. H., Reeks, K. A., and Altschuler, R. A. 1986. Immunocytochemical localization of GABA in the cochlear nucleus of the guinea pig. Brain Res. 380:7–18.
Su, Y. Y. T., Wu, J.-Y., and Lam, D. M. K. 1983. Species specifities ofl-glutamic acid decarboxylase: Immunochemical comparisons. Neurochem. Intl. 5:587–592.
Lin, C.-T., Li, H.-Z., and Wu, J.-Y. 1983. Immunocytochemical localization ofl-glutamate decarboxylase, gamma aminobutyric acid transaminase, cysteine-sulfinic acid decarboxylase, aspartate aminotransferase and somatostatin in rat retina. Brain Res. 270:273–283.
Vitorica, J., Park, D., Chin, G., and, de Blas, A. L. 1988. Monoclonal antibodies and conventional antisera to the GABAA receptor/benzodiazepine receptor/Cl− channel complex. J. Neurosci. 8:615–622.
Eldred, W. D., Zucker, C., Karten, H. J., and Yazulla, S. 1983. Comparison of fixation and penetration enhancement techniques for use in ultra-structural immunocytochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31:285–292.
Mosinger, J. L., and Yazulla, S. 1985. Co-localization of3H-GABA uptake and GAD-like immunoreactivity in amacrine cells of rabbit retina. J. Comp. Neurol., 240:396–406.
Yazulla, S. Studholme, K. M., and Wu, J.-Y. 1986. Comparative distribution of3H-GABA uptake and GAD-immunoreactivity in goldfish retinal amacrine cells: a double-label analysis. J. Comp. Neurol. 244:149–162.
Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., and Johnston, G. A. R. 1978. Structure activity studies on the inhibition of GABA binding to rat brain membranes by muscimol and related compounds. J. Neurochem. 30:1377–1382.
Johnston, G. A. R., Kennedy, S. M. E., and Lodge, D. 1978. Muscimol uptake, release and binding in rat brain slices. J. Neurochem. 31:1519–1523.
Ball, A. K., and Brandon, C. 1986, Localization of [3H]-GABA,-muscimol, and — glycine uptake in goldfish retinas stained for glutamate decarboxylase. J. Neurosci. 6:1621–1627.
Ball, A. K. 1987. Immunocytochemical and autoradiographic localization of GABAergic neurons in the goldfish retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 255:317–325.
Chun, M. H., Wassle, H., and Brecha, N. 1988. Colocalization of [3H]muscimol uptake and choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in amacrine cells of the cat retina. Neurosci. Lttr. 94:259–263.
Hendrickson, A., Tyan, M., Noble, B., and Wu. J.-Y. 1985. Localization of3H-muscimol and antisera to GABA and glutamic acid decarboxylase within the same neurons in monkey retina. Brain Res. 348:391–396.
Pourcho, R. G., and Goebel, D. J. 1983. Neuronal subpopulations in cat retina which accumulate the GABA agonist,3H-muscimol: a combined Golgi and autoradiographic study. J. Comp. Neurol. 219:25–35.
Agardh, E., and Ehinger, B. 1982.3H-muscimol,3H-nipecotic acid and3H-isoguavacine as autoradiographic markers for GABAergic neurotransmission. J. Neural Trans. 54:1–18.
Iversen, L. I., and Neal, M. J. 1968. The uptake of3H-GABA by slices of rat cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 15:1141–1149.
Iversen, L. L. 1971. Role of transmitter uptake mechanisms in synaptic neurotransmission. Br. J. Pharmacol. 41:571–591.
Martin, D. L. 1976. Carrier-mediated transport and removal of GABA from synaptic regions. pages 347–387,in Roberts, E., Chase, T. N. and Tower, D. B. (eds) GABA in Nervous System and Function, Raven Press, New York.
Storm-Mathisen, J., Fonnum, F., and Malthe-Sorenssen, D. 1976. GABA uptake in nerve terminals, pages 387–394.in Roberts, E., Chase, T. N. and Tower, D. B. (eds), GABA in Nervous System and Function, Raven Press, New York.
Lam, D. M. K., and Steinman, L. 1971. The uptake of [γ-3H] aminobutyric acid in the goldfish retina. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2777–2781.
Marc, R. E., Stell, W. K., Bok, D., and Lam, D. M. K. 1978. GABAergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 182:221–246.
Yazulla, S., and Brecha, N. 1981. Localized binding of3H-muscimol to synapses in the chick retina. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 78:643–647.
Zucker, C., Yazulla, S., and Wu, Y.-Y. 1984. Noncorrespondence of3H-GABA uptake and GAD-localization in goldfish amacrine cells. Brain Res., 298:154–158.
Marc, R. E. 1986. Neurochemical stratification of the inner plexiform layer of the vertebrate retina. Vision Res. 26:223–238.
Muller, J. F., and Marc, R. E. 1990. GABA-ergic and glycinergic pathways in the inner plexiform layer of the goldfish retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 291:281–304.
Marshall, J., and Voaden, M. J. 1974. An autoradiographic study of the cells accumulating3H-gamma-aminobutyric acid in the isolated retinas of pigeons and chickens. Invest. Ophthalmol. 13:602–607.
Schon, F., and Kelly, J. S. 1975. Selective uptake of β-alanine by glia: association with the glial uptake system for GABA. Brain Res. 86:243–257.
Yazulla, S., and Kleinschmidt, J. 1982. Dopamine blocks carrier-mediated release of GABA from retinal horizontal cells. Brain Res., 233:211–215.
Yazulla, S. 1983. Stimulation of GABA release from retinal horizontal cells by potassium and acidic amino acid agonists. Brain Res., 275:61–74.
Schwartz, E. A. 1982. Calcium-independent release of GABA from isolated horizontal cells for the toad retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 323:211–227.
Ayoub, G. S., and Lam, D. M. K. 1984. The release of γ-aminobutyric acid from horizontal cells of the goldfish (Carassius auratus) retina. J. Physiol. 355:191–214.
Massey, S. C. 1990. Cell types using glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the vertebrate retina. Prog. Retinal Res. 9:399–426.
Vaughn, J. E., Famiglietti, Jr., E. V., Barber, R. P., Saito, K., Roberts, E., and Ribak, C. E. 1981. GABAergic amacrine cells in rat retina: immunocytochemical identification and synaptic connectivity. J. Comp. Neurol. 197:113–127.
Yazulla, S., Studholme, K., and Wu, J.-Y. 1987. GABAergic input to the synaptic terminals of mb1 bipolar cells in the goldfish retina. Brain Res. 411:400–405.
Hyde, J. C., and Robinson, N. 1974. Localization of sites of GABA catabolism in the rat retina. Nature (Lond.) 248:432–433.
Neal, M. J., Cunningham, J. R., Shah, M. A., and Yazulla, S. 1989. Immunocytochemical evidence that vigabatrin in rats causes GABA accumulation in glial cells of the retina. Neurosci. Lett. 98:29–32.
Bruun, A., Ehinger, B. and Systma, V. M. 1984. Neurotransmitter localization in the Skate retina. Brain Res. 295:233–249.
Blanks, J. C., and Roffler-Tarlov, S. 1982. Differential localization of radioactive gamma-aminobutyric acid and muscimol in isolated andin vivo mouse retina. Expt. Eye Res. 35:573–584.
Bruun, A., and Ehinger, B. 1974. Uptake of certain possible neurotransmitters into retinal neurons of some mammals. Expt. Eye Res. 19:435–437.
Ehinger, B. 1977. Glial and neuronal uptake of GABA, glutamic acid, glutamine and glutathione in the rabbit retina. Expl. Eye Res. 25:221–234.
Neal, M. J., and Iversen, L. L. 1972. Autoradiographic localization of3H-GABA in rat retina. Nature, New Biol. 235:217–218.
Sarthy, P. V. 1983. Release of [3H] γ-aminobutyric acid from glial (Muller) cells of the rat retina: effects of K+, veratridine, and ethylenediamine. J. Neurosci. 3:2494–2503.
Mosinger, J. L., Studholme, K. M. and Yazulla, S. 1986. Immunocytochemical localization of GABA in the retina: A species comparison. Exp. Eye Res., 42:631–644.
Agardh, E., Bruun, A., Ehinger, B., Ekstrom, P., van Veen, T., and Wu, J.-Y. 1987. Gamma-aminobutyric acid- and glutamic acid decarboxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the retinas of different vertebrates. J. Comp. Neurol. 258:622–630.
Cubells, J. F., Walkley, S. U., and Makman, M. H. 1988. The effects of gabaculinein vivo on the distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the rat retina. Brain Res. 458:82–90.
Neal, M. J., and Bowery, N. G. 1979. Differential effects of veratridine and potassium depolarization on neuronal and glial GABA release. Brain Res. 167:337–343.
Hurd, II, L. B., and Eldred, W. D. 1989. Localization of GABA-and GAD-like immunoreactivity in the turtle retina. Vis. Neurosci. 3:9–20.
Brandon, C. 1985. Retinal GABA neurons: localization in vertebrate species using a new antiserum against rabbit brain glutamate decarboxylase. Brain Res. 344:286–295.
Su, Y. Y. T., Wu, J.-Y., and Lam, D. M. K. 1979. Purification of L-glutamic acid decarboxylase from catfish brain. J. Neurochem. 33:169–179.
Kaufmann, D. L., McGinnis, J. F., Kreiger, N. R. and Tobin, A. J. 1986. Brain glutamate decarboxylase cloned in lambda-gtll: Fusion protein produces gamma-aminobutyric acid. Science 232:1138–1140.
Yazulla, S., Studholme, K. M., Vitorica, J., and de Blas, A. L. 1989. Immunocytochemical localization of GABAA receptors in goldfish and chicken retinas. J. Comp. Neurol., 280:15–26.
Ishida, A. T., Stell, W. K. and Lightfoot, D. O. 1980. Rod and cone inputs to bipolar cells in goldfish retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 191:315–335.
Tachibana, M., and Kaneko, A. 1987. γ-aminobutyric acid exerts a local inhibitory action on the axon terminal of bipolar cells: evidence for negative feedback from amacrine cells. Proc. Nat. Acad, Sci. USA 84:3501–3505.
Ymer, S., Schofield, P. R., Draguhn, A., Werner, P., Kohler, M. and Seeburg, P. H. 1989. GABAA receptor subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNAs. The EMBO Journal 8:1665–1670.
Engbretson, G. A., Anderson, K. J., and Wu, J.-Y. 1988. GABA as a potential transmitter in lizard photoreceptors: Immunocytochemical and biochemical evidence. J. Comp. Neurol. 278:461–471.
Nishimura, Y., Schwartz, M. L., and Rakic, P. 1986. GABA and GAD immunoreactivity of photoreceptor terminals in primate retina. Nature (Lond.) 320:753–756.
Yazulla, S. 1986. Is GABA the neurotransmitter for some photoreceptors? Nature, 320:685–685.
Yazulla, S. 1985. Evoked efflux of3H-GABA from goldfish retina in the dark. Brain Res., 325:171–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Eugene Roberts
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazulla, S. The mismatch problem for GABAergic amacrine cells in goldfish retina: Resolution and other issues. Neurochem Res 16, 327–339 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00966096
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00966096