Abstract
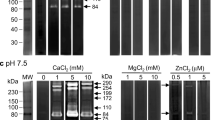
Purified human brain myelin was isolated, heat-treated to inactivate the endogenous proteolytic activity and incubated with cathepsin B purified from rat liver, at pH 6.0. Incubation resulted in a marked reduction of myelin basic protein (BP) and partial breakdown of proteolipid protein or Wolfgram protein. Degradation of myelin proteins was inhibited by E-64 analogue (E-64-a). E-64 is a specific thiol protease inhibitor isolated from a solid culture of Aspergillus japonicus. The present study suggests that cathepsin B may play some role in demyelination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Govindarajan, K. R., Rauch, H. C., Clausen, J., andEinstein, E. R. 1974. Changes in cathepsins B-1 and D, neutral proteinase and 2′, 3′-cyclic nucleotide-3′-phosphohydrolase activities in monkey brain with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 23:295–306.
Marks, N., Grynbaum, A., andLajtha, A. 1976. The breakdown of myelin-bound proteins by intra- and extracellular proteases. Neurochem. Res. 1:93–111.
Smith, M. E., Chow, S. H., andRolph, R. H. 1981. Partial purification and characterization of neutral proteases in lymph modes of rats with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neurochem. Res. 6:901–912.
Towatari, T., Kawabata, Y., andKatunuma, N. 1979. Crystallization and properties of cathepsin B from rat liver. Eur. J. Biochem. 102:279–289.
Barrett, A. J. 1972. A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteases. Anal. Biochem. 47:280–293.
Hanada, K., Tamai, M., Yamagishi, M., Ohmura, S., Sawada, J., andTanaka, I. 1978. Isolation and characterization of E-64, a new thiol protease inhibitor. Agric. Biol. Chem. 42:529–536.
Hanada, K., Tamai, M., Ohmura, S., Sawada, J., Seki, T., andTanaka, I. 1978. Structure and synthesis of E-64, a new thiol protease inhibitor. Agric. Biol. Chem. 42:529–536.
Norton, W. T., andPoduslo, S. E. 1973. Myelination in rat brain: Method of myelin isolation. J. Neurochem. 21:749–757.
Sato, S., Quarles, R. H., andBrady, R. O. 1982. Susceptibility of the myelin-associated glycoprotein and basic protein to a neutral protease in highly purified myelin from human and rat brain. J. Neurochem. 39:97–105.
Greenfield, S., Norton, W. T., andMorell, P. 1971. Quaking mouse: Isolation and characterization of myelin protein. J. Neurochem. 18:2119–2128.
Agrawal, H. C., Burton, R. M., Fishman, M. A., Mitchell, R. F., andPrensky, A. L. 1972. Partial characterization of a new myelin protein component. J. Neurochem. 19:2083–2089.
Laemmli, U. K., andFavre, M. 1973. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J. Mol. Biol. 80:575–599.
Yanagisawa, K., Sato, S., Amaya, N., andMiyatake, T. 1983. Degradation of myelin basic protein by calcium-activated neutral protease (CANP) in human brain and inhibition by E-64 analogue. Neurochem. Res. 8:1285–1293.
Mørland, B., andPedersen, A. 1979. Cathepsin B activity in stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Lab. Invest. 41:379–384.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanagisawa, K., Sato, S., Miyatake, T. et al. Degradation of myelin proteins by cathepsin B and inhibition by E-64 analogue. Neurochem Res 9, 691–694 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964515
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964515