Abstract
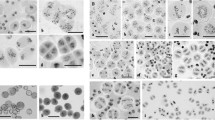
Meiotic chromosome associations in a spontaneously originated haploid plant of pearl millet have been studied and their phyletic significance discussed. Chromosome pairing could be observed at pachytene and diplotene. Out of a total of 285 PMC's studied at diakinesis-metaphase 1, 43 showed one bivalent and 7 had two bivalents per cell. Both rod- and ring-bivalents were observed. Apart from synapsis accompanied by chiasma formation, close associations of univalent chromosomes were observed. Out of 150 cells without true bivalents, 41 showed 1 s-s association and five, 2 s-s pairs per cell. On the basis of the realization of a maximum of two bivalents per cell, as also of a maximum of 2 s-s pairs, it has been inferred that the chromosome complement ofP. typhoides (n=7) has evolved from a basic set ofn=5 chromosomes. Other available evidence supporting this inference is also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jauhar P. P. (1968a). Inter-and intra-genomal chromosome pairing in an interspecific hybrid and its bearing on the basic chromosome number inPennisetum.Genetica 30: 360–370.
Jauhar, P. P. (1968b). Studies on the basic chromosome number inPennisetum. Proc. Intern. Symp. on “The Role of Genetics Today”, Hyderabad, India. (Abstr.).
Jauhar P. P. (1970). Chromosome behaviour and fertility of the raw and evolved synthetic tetraploids of Pearl millet,Pennisetum typhoides Stape etHubb.Genetica 41: 407–424.
Jauhar P. P. & A. B. Joshi (1966). Cytological studies in some species ofPanicum.Cytologia 31: 153–159.
Kempanna C. & R. Riley (1964). Secondary association between genetically equivalent bivalents.Heredity 19: 289–299.
Kimber G. & R. Riley (1963). Haploid angiosperms.Bot. Rev. 29: 480–531.
Magoon M. L. & K. R. Khanna (1963). Haploids.Caryologia 18: 191–235.
Narain A. & P. Singh (1968). Haploid meiosis and its bearing on the constitution of the castor oil plant.J. Hered. 59: 287–288.
Östergren G. & E. Vigfusson (1953). On position correlations of univalents and quasibivalents formed by sticky univalents.Hereditas 39: 33–50.
Person C. (1955). An analytical study of chromosome behaviour in a wheat haploid.Canad. J. Bot. 33: 11–30.
Ribbands C. R. (1937). The consequences of structural hybridity at meiosis inLilium x testaceum.J. Genet. 35: 1–24.
Riley R. (1966). Genetics in the regulation of meiotic chromosome behaviour.Sci. Progr. 54: 193–207.
Riley R. & V. Chapman (1957). Haploids and polyhaploids inAegilops andTriticum.Heredity 11: 195–207.
Riley R. & C. N. Law (1965). Genetic variation in chromosome pairing.Adv. Genet. 13: 57–114.
Sybenga J. (1966). The zygomere as hypothetical unit of chromosome pairing initiation.Genetica 37: 186–198.
Ting Y. C. (1966). Duplications and meiotic behaviour of the chromosomes in haploid maize (Zea mays L.).Cytologia 31: 324–329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jauhar, P.P. Haploid meiosis and its bearing on the phylogeny of pearl millet,Pennisetum typhoides stapf et hubb.. Genetica 41, 532–540 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00958932
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00958932