Abstract
The localization of three key signal transduction components was indicated in rat heart tissue by immunocytochemical and histochemical experiment. It was shown that:
-
1.
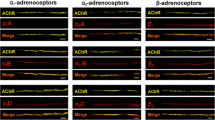
The M2 muscarinic receptors are localized along outer cell membranes and T-tubule membranes of cardiomyocytes but additionally at membranes of endothelial cells and fibroblasts.
-
2.
Giα was found along outer cell membranes of cardiomyocytes and other cells of the heart and also inside the cells of the perinuclear space in close contact to the nuclei envelope and the endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Goα were found to be associated mainly in atrial tissue, especially at the nerval (neuronal) endings located among the cardiac muscle cells. This was shown in parallel incubation with specific neuronal antibody as a marker for these structures.
-
3.
Adenylyl cyclase was localized along the sarcolemma and the T-tubule membranes in normal cardiomyocytes of rat and guinea pig hearts. Under ischemic conditions, the adenylyl cyclase was also seen in junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. The reasons for this changed localization need further elucidation. Binding of the adenylyl cyclase within the molecular structure of the membrane or variation of the marker penetration remain to be clarified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobs KH, Aktories K, Schultz G: Mechanisms and components involved in adenylate cyclase inhibition by hormones. Adv Cyclic Nucl Res and Prot Phosphoryl 17: 135–143, P. Greengardet al. (eds). Raven Press, New York, 1985
Martin MW, Boyer JL, May JM, Birnbaumer L, Harden TK: Muscarinic receptors and their interactions with G proteins. In: R. Iyengar and L. Birnbaumer (eds). G proteins. Academic Press Inc, 1990, pp 317–354
Neer EJ, Clapham DE: Signal transduction through G proteins in the cardiac myocyte. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2: 6–11, 1992
Brown AM: Regulation of heartbeat by G protein-coupled ion channels. Am J Physiol 259: 1621–1628, 1993
Peralta EG, Ashkenazi A, Winslow JW, Smith D, Ramachandran J, Capon DJ: Distinct primary structures, ligand-binding properties and tissue specific expression of four human muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J 13: 3923, 1987
Peralta EG, Winslow JW, Peterson GL, Smith DH, Ashkenazi A, Ramachandran J, Schimerlik MI, Capon DJ: Primary structure and biochemical properties of a muscarinic receptor. Science 230: 600, 1987
Fu M, Schulze W, Wolf WP, Hjalmarson A, Hoebeke J: Immunocytochemical localization of M2 muscarinic receptors in rat ventricles with anti-peptide antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem 42: 337–343, 1994
Fu M, Wallukat G, Hjalmarson A, Hoebeke J: Agonist-like activity of anti-peptide antibodies to autoimmune epitope on the second extracellular loop of human muscarinic receptors. Receptors and Channels 2: 121–130, 1994
Doods HN, Dämmgen J, Mayer N, Rinner I: Muscarinic receptors in the heart and vascular system. Progress in Pharmacol and Clinic Pharmacol 7/1: 47–72, 1989
Robishaw JD, Foster KA: Role of G proteins in the regulation of the cardiovascular system. Annu Rev Physiol 51: 229–244, 1989
Holmer SR, Homcy CJ: G proteins in the heart. A redundant and diverse transmembrane signaling network. Circulation 84: 1891–1902, 1989
Barr FA, Leyte A, Mollner S, Pfeuffer T, Tooze SA, Huttner WB: Trimeric G-proteins of the trans-Golgi network are involved in the formation of constitutive secretory vesicles and immature secretory granules. FEBS Lett 294: 239–243, 1991
Leyte A, Barr FA, Kehlenbach RH, Huttner WB: Multiple trimeric G-proteins on the trans-Golgi network exert stimulatory and inhibitory effects on secretory vesicle formation. EMBO J 11: 4795–4804, 1992
Hermounet S, de Mazancourt P, Spiegel AM, Farquhar MG, Wilson BS: High level expression of transfected G protein αi3 subunit is required for plasma membrane targeting and adenylyl cyclase inhibition in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 312: 223–228, 1992
Schulze W, Buchwalow IB, Wolf WP, Will-Shahab L: Comparative immunocytochemical demonstration of G proteins in rat heart tissue. Acta Histochem 96: 87–95, 1994
Will-Shahab L, Rosenthal W, Schulze W, Küttner I: G protein function in the ischaemic myocardium. Eur Heart J 12: 135–138, 1991
Eschenhagen T: G proteins and the heart. Cell Biol Internat 7: 723–749, 1993
Asano T, Kamiya N, Semba R, Kato K: Ontogeny of the GTP-binding protein Go in rat brain and heart. J Neurochem 51: 1711–1716, 1988
Asano T, Semba R, Kimiya N, Ogasawara N, Kato K: Go, a GTP-binding protein: immunochemical and immunohistochemical localization in the rat. J Neurochem 50: 1164–1169, 1988
Scherer NM, Toro MJ, Entman ML, Birnbaumer L: G-protein distribution in canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemma. Comparison to rabbit skeletal muscle membranes and to brain and erythrocyte G-proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 259: 431–440, 1987
Fleming JW, Wisler PL, Watanabe AM: Signal transduction by G proteins in cardiac tissue. Circulation 85: 420–433, 1992
Eschenhagen T, Mende U, Nose M, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Haverich A, Hirt S, Döring V, Kalmar P, Höppner W, Seitz HJ: Increase messenger RNA level of the inhibitory G-protein α-subunit Giα-2 in human end-stage heart failure. Circ Res 70: 688–696, 1992
Eschenhagen T, Mende U, Nose M, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Schulte am Esch J, Warnholtz A: Long term β-adrenoceptor-mediated upregulation of Giα- and Goα-mRNA levels and pertussis toxin sensitive G-proteins in rat heart. Mol Pharmacol 42: 773–783, 1992
Böhm M, Eschenhagen T, Gierschik P, Larisch K, Lensche H, Mende U, Schmitz W, Schnabel P, Scholz H, Steinfath M, Erdmann E: Radioimmunochemical quantification of Giα in right and left ventricles from patients with ischaemic and dilated cardiomyopathy and predominant left ventricular failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 26: 133–149, 1994
Gilman AG: G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell 36: 577–579, 1984
Neer EJ: G proteins: Critical control points of transmembrane signals. Prot Science 3: 3–14, 1994
Krupinski J, Coussen F, Bakalyar HA, Tang WJ, Feinstein PG, Orth K, Slaughter C, Reed RR, Gilman AG: Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science 244: 1558–1564, 1989
Katsushika S, Chen L, Kawabe J-I, Nilakantan R, Halnon NJ, Homcy CJ, Ishikawa Y: Cloning and characterization of a sixth adenylyl cyclase isoform: Types V and VI constitute a subgroup within the mammalian adenylyl cyclase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8774–8778, 1992
Slezak J, Geller SA: Cytochemical demonstration of adenylyl cyclase in cardiac muscle: effect of dimethyl sulfoxide. J Histochem Cytochem 27: 774, 1979
Slezak J, Geller SA: Cytochemical studies of myocardial adenylate cyclase after its activation and inhibition. J Histochem Cytochem 32: 105–113, 1984
Schulze W: Cytochemistry of adenylate cyclase. Quantitative analysis of the effect of cytochemical procedures on adenylate cyclase in heart tissue homogenates. Histochemistry 75: 133–145, 1982
Schulze W: Methods for histochemical localization of adenylate cyclase and guanylate cyclase in heart membranes. In: N.S. Dhalla (ed.). Methods in Studying Cardiac Membranes. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, Florida Vol II: 83–109, 1984
Schulze W, Will-Shahab L: Zum Verhalten der Adenylatzyklase im isch ämischen und nekrotischen Herzgewebe. Acta histochem (Suppl) XXX: 157–165, 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulze, W., Wolf, WP., Fu, M.L.X. et al. Immunocytochemical studies of the Gi Protein mediated muscarinic receptor-adenylyl cyclase system. Mol Cell Biochem 147, 161–168 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00944796
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00944796