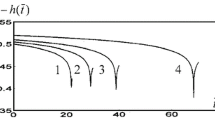
Abstract
An approximate equation of motion is derived and is used in the analysis of a dynamically propagating crack in a highly orthotropic fiber composite infinite strip subjected to constant displacement Mode I loading. With the use of Fourier transforms, the problem is reduced to an equation which is solved by the Wiener-Hopf technique. The dynamic stress intensity factor is derived and is expressed as the product of a velocity correction factor and a static stress intensity factor. The corresponding dynamic energy release rate is derived also and it is found not to be explicitly dependent upon the crack-tip velocity. It is found experimentally that the long strip configuration subjected to constant extensional displacement can simulate constant crack propagation velocities. Accordingly, the model's dynamic energy release rate is used to determine the dynamic fracture energy (toughness) of 90° Hercules AS/3501-6 graphite epoxy composites.
Résumé
On déduit une équation approximative de mouvement et on l'utilise dans l'analyse d'une fissure se propageant de manière dynamique dans une bande infinie en fibres composites à haute orthotropicité sujette à une mise en charge de mode I à déplacement constant. En utilisant les transformées de Fourier, on ramène le problème à une équation qui est solutionable par la technique de Wiener-Hopf. Le facteur d'intensité de contrainte dynamique en est déduit et est exprimé comme le produit d'un facteur de correction de vitesse et d'un facteur d'intensité de contrainte statique. Le taux de relaxation d'énergie dynamique correspondante est également déduit et l'on trouve qu'il n'est pas explicitement dépendant de la vélocité à la pointe de la fissure. On trouve par voie expérimentale que la configuration d'une bande longue soumis à des déplacements constants en traction permet de simuler des vitesses de propagation constante. Dès lors, on utilise le taux de relaxation d'énergie dynamique du modèle à la détermination de l'énergie de rupture dynamique ou ténacité des composites époxygraphites 90° Hercules AS/3501-6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Nilsson,International Journal of Fracture Mechanics 8, No. 4 (1972) 403–411.
T.L. Paxson and R.A. Lucas, inDynamic Crack Porpagation, G.C. Sih (ed.), Noordhoff, Leyden (1973) 415–426.
J.H. Williams, Jr. and P.N. Kousiounelos,Fibre Science and Technology 11, No. 2 (1978) 83–88.
P.N. Kousiounelos, “Dynamic Crack Propagation in Unidirectional Fiber Composites”, Sc.D. Thesis, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, M.I.T. (May 1979).
P.N. Kousiounelos and J.H. Williams, Jr., Fibre Science and Technology, 13 (1980) 97–118.
P.N. Kousiounelos and J.H. Williams, Jr., Fibre Science and Technology, 14 (1981) 91–97.
H. Kolsky,Stress Waves in Solids, Dover Publications, Inc. (1963).
S.G. Lekhnitskii,Anisotropic Plates, Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York.
P.C. Paris and G.C. Sih, in ASTM STP 381, American Society for Testing and Materials (1965) 30–83.
P.N. Kousiounelos, “Fracture of Graphite Fiber Composites”, S.B.-S.M. Thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, M.I.T. (May 1976).
W.G. Knauss,Journal of Applied Mechanics 33 (1966) 356–362.
B. Noble,Methods Based on the Wiener-Hopf Technique, Pergamon Press (1958).
G.C. Sih and E.P. Chen, inMechanics of Fracture, Vol. 4,Elastodynamic Crack Problems, G.C. Sih (ed.) 75–2.
B.V. Kostrov and L.V. Nikitin,Archiwum Mechaniki Stosowanej 6, 22 (1970) 749–760.
K.B. Broberg, inRecent Progress in Applied Mechanics, K.B. Broberg et al. (eds.), Almquist and Wicksell, Stockholm (1967) 125–151.
Erdelyiet al., Tables of Integral Transforms, McGraw Hill Book Co., Inc. (1954).
L.B. Freund, inThe Mechanics of Fracture, F. Erdogan (ed.), AMD Vol. 19, The American Scoiety of Mechanical Engineers (1976) 105–134.
Hercules Incorporated Systems Group, “Preparation of Laminate Test Specimens from Graphite Prepreg”, HD-SG-2-6005C, September 15, 1976.
J.H. Williams, Jr., P.N. Kousiounelos and S.S. Lee, “Dynamic Fracture in Orthotropic Fiber Composites”, Naval Air Systems Command, Contract No. N00019-77-C-0294 (May 1978).
J.H. Williams, Jr., H. Nayeb-Hashemi and S.S. Lee, “Ultrasonic Attenuation and Velocity in AS/3501-6 Graphite Fiber Composite”, Composite Materials and Nondestructive Evaluation Laboratory, M.I.T. (August 1979).
J.H. Williams, Jr. and P.N. Kousiounelos,Engineering Fracture Mechanics 14 (1981) 165–170.
J.H. Williams, Jr., S.S. Lee and P.N. Kousiounelos,Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 14 (1981) 427–438.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kousiounelos, P.N., Williams, J.H. Dynamic fracture of unidirectional graphite fiber composite strips. Int J Fract 20, 47–63 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00942164
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00942164