Abstract
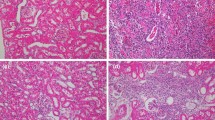
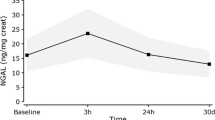
Urinary loss of the tubular marker enzyme N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (NAG) immediately following extracorporeal lithotripsy suggests corresponding morphological changes in the kidney. To date, the morphological correlate of the enzymuria remains unclear. In this animal study with Wistar rats acute morphological changes in the tubulus cells beneath isolated tubulus necrosis were demonstrated. The mechanically induced lesions of the cell organelles included fragmentation of the lysosomes and severe alterations of the cell membrane. The tubulus damage was quantified. With the help of histochemical NAG straining and electron microscopic observations, a significant correlation between number and intensity of shock waves and tubular damage was found. The intracellular lesions described here are at least part of the morphological basis of shock-wave-induced enzymuria. The results show that enzymatic changes in urine reflect visible renal damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barka T (1960) A simple azo-dye method for histochemical demonstration of acid phospatase. Nature 187:248
Delius M, Enders G, Xuan ZR, Liebich HG, Brendel W (1988) Biological effects of shock waves: kidney damage by shock waves in dogs — dose dependence. Ultrasound Med Biol 14:117
Delius M (1993) Veränderungen der Niere nach Stoßwellen-applikation in Tierexperimenten. In: Chaussy CH, Eisenberger F, Jocham D, Wilbert D (eds) Stoßwellenlithotripsie: Aspekte und Prognosen. Attempto, Tübingen, pp 171–178
Folberth W, Staniewski T, Schätzle U (1993) Quantifizierbarkeit und Vergleichbarkeit von Druckpulsqualitäten. In: Chaussy CH, Eisenberger F, Jocham D, Wilbert D (eds) Stoßwellenlithotripsie: Aspekte und Prognosen. Attempto, Tübingen, pp 16–23
Haupt G, Donovan JM, Weber CH, Seemann O, Chvapil M, Nagle RB, Drach GW (1990) Auswirkungen sequentieller ESWL auf Struktur und Funktion der Hasenniere. Z Urol(poster):180
Hayashi M (1965) Histochemical demonstration ofN-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase employing naphtol AS-BI-N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase as a substrate. J Histochem Cytochem 13:355
Jung K, Kirschner P, Wille A, Brien G (1993) Excretion of urinary enzyme after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: A critical reevaluation. J Urol 149:1409
Kallerhoff M, Müller-Siegel K, Horneffer C, Verwiebe R, Weber MH, Ringert RH (1993) Quantifizierung renaler Parenchymschäden nach extrakorporaler Stoßwellenlithotripsie mittels Harneiweißanalytik. In: Chaussy CH, Eisenberger F, Jocham D, Wilbert D (eds) Stoßwellenlithotripsie: Aspekte und Prognosen. Attempto, Tübingen, pp 194–201
Karalezli G, Gögüs O, Bedük Y, Köküüslu C, Sarica K, Kutsal O (1993) Histopathologic effects of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy on rabbit kidney. Urol Res 21:67
Karlsen SJ, Berg KJ (1991) Acute changes in kidney function following extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for renal stones. Br J Urol 67:241
Köhrmann KU, Rassweiler J, Alken P (1993) Standardisierte Bestimmung der Morphologie des stoßwelleninduzierten Nierentraumas. In: Chaussy CH, Eisenberger F, Jocham D, Wilbert D (eds) Stoßwellenlithotripsie: Aspekte und Prognosen. Attempto, Tubingen, pp 155–170
Lojda Z (1976) Vorbereitung des Gewebes. In: Lojda Z, Gossrau R, Schiebler TH (eds) Enzymhistochemische Methoden. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York pp 22–45
Malyusz M, Braun D (1981) Enzymuria (the output of gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase and ofN-acetyl-beta-d-glucosa-minidase) in the course of experimental renovascular hypertension. Enzyme 26:32
Maruhn D, Fuchs J, Mues G, Bock KD (1976) Rapid colorimetric assay of β-galactosidase andN-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in human urine. Clin Chim Acta 73:453
Maunsbach AB (1979) The tubule. In: Johannessen IV (ed) Electron microscopy in human medicine, vol 9: Urogenital system and breast. MacGraw-Hill, New York, pp 143–157
Meadows R (1978) The renal tubules: I. In: Meadows R (ed) Renal histopathology. A light, electron, and immunofluorescent microscopy study of renal disease, 2nd edition. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 164–184
Muschter R, Schmeller N, Reimers J, Kutscher KR, Knipper A, Hofstätter AG, Löhrs U (1987) ESWL-induced renal damage — experimental study. In: Jacobi GH, Rübben H, Harzmann R (eds) Investigative urology 2. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 193–196
Neisius D, Seitz G, Gebhardt T, Ziegler M (1989) Dose-dependent influence on canine 8 renal morphology after application of extracorporeal shock waves with Wolf Piezolith. J Endourol 3:337
Neisius D, Jung P, Gebhardt T (1993) Stoßwelleninduziertc morphologische Veränderungen an der Niere. In: Chaussy CH, Eisenberger F, Jocham D, Wilbert D (eds) Stoßwellenlithotripsie: Aspekte und Prognosen. Attempto, Tübingen, pp 179–186
Raab WP (1972) Diagnostic value of urinary enzyme determinations, Clin Chem 18:5
Recker F, Jaeger P, Knoenagel H, Bex A, Ausfeld R (1990) Intrarenal parenchymal lesion following ESWL — its pathomechanism and dependence on application form. Z Urol (poster 2):86
Recker F, Hofmann W, Bex A, Tscholl R (1992) Quantitative determination of urinary marker proteins: A model to detect intrarenal bioeffects after extracorporeal lithotripsy. J Urol 148:1000
Saß W, Zoephel O, Zimmermann J, Weichert-Jacobsen K, Seifert J (1990) Definierte Steinfrag-mentation zur Standardisierung an unterschiediche Lithotriptern — standardized efficacy measurements of different lithotripters. Langenbecks Arch Chir (Suppl 1):403
Skrezek C, Bertermann H, Schulz FP, König B (1990) NAG — cin sensitiver Marker für Nierenfunktionstörungen. Urologe [A] 29:27
Trinchieri A, Mandressi A, Zanetti A, Ruoppolo M, Tombolini P, Pisani E (1988) Renal tubular damage after renal stone treatment. Urol Res 16:101
Trinchieri A, Zanetti G, Tombolini P, Mandressi A, Ruoppolo M, Tura M, Montanari E, Pisani E (1990) Urinary NAG excretion after anaesthesia-free extracorporeal lithotripsy of renal stones. Urol Res 118:259
Urivetzky M, Motola J, King L, Smith AD (1989) Impact of percutaneous renal stone removal on renal function: assessment by urinary lysozyme activity. Urology 33:305
Weber C, Moran ME, Braun EJ, Drach GW (1992) Injury of rat vessels following extracorporeal shock wave treatment. J Urol 147:476
Weichert-Jacobsen K, Bertermann H, Skrezek C, Wand H (1990) Quantification of renal parenchymal damage following ESWL/EPL treatment by NAG-enzymuria. Eur Urol 18(Suppl 1):361
Weichert-Jacobsen K, Bertermann H, Skrezek C (1991) Extensive renal parenchymal damage induced by ESWL of pyelonephritic or obstructed kidneys, a clinical study. J Urol 145:245A
Weichert-Jacobsen K, Skrezek C, Papadopoulos I, Wirth B (1993) Quantification of renal parenchymal damage induced by EPL — an animal study. Urol Res 21:162
Wilbert DM, Bichler KH, Strohmaier WL, Flüchter SH (1988) Glomerular and tubular damage after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy assessed by measurement of urinary proteins, J Urol 139:326A
Zeller J (1973) Zur Cytochemie der Lysosomen der Rattenniere unter normalen und experimentellen Bedingungen. Histochemie 35:235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weichert-Jacobsen, K., Scheidt, M., Külkens, C. et al. Morphological correlates of urinary enzyme loss after extracorporeal lithotripsy. Urol. Res. 25, 257–262 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00942095
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00942095