Abstract
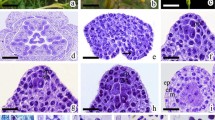
Aspects of the life history ofKyllinga monocephala are described. Anther wall development corresponds to the Monocot type. The endothecium shows spiral thickenings. The tapetum is glandular and has uninucleate cells. Ubisch granules are present. Mature pollen grains (pseudomonads) are 3-celled at maturity. Ovules are bitegmic, crassinucellate and develop a funicular obturator. The embryo development conforms to theJuncus-variation of the Onagrad type. Endosperm, seed coat and pericarp are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blatter, E., McCann, C., 1935:Cyperaceae in revision of the flora of the Bombay presidency. — J. Bombay Natur. Hist. Soc.37, 15–35.
Clarke, C. B., 1894:Cyperaceae. — InHooker, J. D., (Ed.): The Flora of British India. Vol.6. — London: L. Reeves.
Cooke, T., 1908: The Flora of the Presidency of Bombay. Vol.2. — London: Taylor & Francis.
Davis, G. L., 1966: Systematic Embryology of the Angiosperms. — New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Gamble, J. S., 1931: Flora of the Presidency of Madras. — London: Adlard & Son & West Newman.
Haines, H. H., 1924: Botany of Bihar and Orissa. — London: Adlard & Son & West Newman.
Hooker, J. D., 1897: Flora of British India6. — London: L. Reeves & Co. Ltd.
Holttum, R. E., 1948: The spikelets inCyperaceae. — Bot. Rev.14, 525–541.
Hutchinson, J., 1959: The Families of Flowering Plants 2. Monocotyledons. 2nd ed. — London: Macmillan.
Johansen, D. A., 1950: Plant Embryology. — Waltham, Mass.: Chronica Botanica Comp.
Koyama, T., 1961: Classification of familyCyperaceae, I. — J. Fac. Sci. Univ.8 (3), 37–148.
Mirashi, M. V., Donde, Vinodini, P., 1962: Studies in theCyperaceae of Nagpur. — Bot. Soc. Coll. Sci., Nagpur. Bull.3, 42–58.
Padhye, M. D., 1966–67: The pollen grainsKyllinga Rottb. — Palynol. Bull.,2 (3), 101–103.
—, 1971a: Studies inCyperaceae II. Embryology ofCyperus iria L. — Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad.37, 1–10.
—, 1971b: Studies inCyperaceae III. Life history ofKyllinga brevifolia Rottb. with a brief discussion on systematic position ofKyllinga. — Bot. Gaz. (Crawfordsville)132, 172–179.
Pax, F., 1887:Cyperaceae. — InEngler, A., Prantl, K., (Eds.): Die natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien. — Leipzig: Engelmann.
Santapau, H., 1960: The flora of Khandala. 2nd ed. — Calcutta: Botanical Survey of India.
Sanyal, B. N., 1972: Cytological Studies on IndianCyperaceae II. TribeCyperae. — Cytologia37, 33–42.
Sedgwick, L. J., 1918: TheCyperaceae in Bombay Presidency. — J. Bombay Natur. Hist. Soc.25, 192–209.
Sharma, M., 1967: Pollen Morphology of Indian Monocotyledons. — J. Palynology. (Special volume)
van der Veken, P., 1965: Contribution à l'embryographie systématique desCyperaceae—Cyperoideae. — Bull. Jard. Bot. Etat. Brux.35, 285–354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makde, K.H., Bhuskute, S.M. Embryology ofKyllinga monocephala (Cyperaceae) and its systematic position. Pl Syst Evol 156, 143–150 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936069
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936069