Abstract
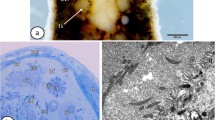
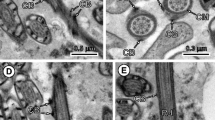
The development of spermatozoa in the polyopisthocotylean fish-gill flukesProtomicrocotyle ivoriensis andGastrocotyle sp. was investigated by light and transmission electron microscopy. In both species the spermatogonia were undifferentiated cells, the cytoplasm of which contained numerous free ribosomes, and successive mitoses gave rise to primary spermatocytes, which are clearly identified by the presence of synaptonemal complexes in their nuclei. As compared with that of the spermatogonia, the cytoplasm of the primary spermatocytes contained an increased number of ribosomes. Golgi complexes were frequently seen in the spermatocytes ofP. ivoriensis but not inGastrocotyle sp. InP. ivoriensis the secondary spermatocytes were separated by interspaces between the irregularly shaped cell surfaces. In both species a syncytial mass of spermatids developed, which gave rise to 64 spermatozoa. Cross sections of the mature spermatozoa of both species revealed the presence of numerous submembranous microtubules and two axonemes showing a pattern of 9 doublet peripheral microtubules plus a central one. In contrast toP. ivoriensis, inGastrocotyle sp. the axonemes originated from different places at the axis of the spermatozoon. With respect to the other results obtained, the spermiogenesis and the fine structure of spermatozoa of both species studied were similar to previous findings in other polyopisthocotyleans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
arms
- AX :
-
axoneme
- BB :
-
basal body
- C :
-
condensed chromatin
- CB :
-
centre body
- CE :
-
centriole
- CG :
-
circular groove
- CM :
-
cortical microtubule
- CP :
-
cytoplasmic process
- DM :
-
doublet microtubules
- ER :
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- G :
-
Golgi body
- HC :
-
heterochromatin
- K :
-
knob-like protrusion
- M :
-
mitochondrion
- MI :
-
microtubuli
- N :
-
nucleus
- NN :
-
nucleolus
- P :
-
perinuclear space
- PSC :
-
primary spermatocyte
- R :
-
ribosome
- RS :
-
radial spoke
- S :
-
synaptonemal complex
- SC :
-
spermatocyte
- SG :
-
spermatogonium
- SP :
-
spermatid
- SR :
-
striated rootlet
- SZ :
-
spermatozoon
- V :
-
vesicle
References
Burton PR (1967) Fine structure of the reproductive system of a frog lung fluke: II. Penetration of the ovum by a spermatozoon. J Parasitol 53:994–999
Halton DW, Hardcastle A (1976) Spermatogenesis in a monogenean,Diclidophora merlangi. Int J Parasitol 6:43–53
Hershenov BR, Tulloch GS, Johnson AD (1966) The fine structure of trematode sperm-tails. Trans Am Microsc Soc 85:480–483
Justine JL, Mattei X (1982) Presence de spermatozoides à un seul axonème dans trois familles de Monogènes Monopisthocotylea: Ancyrocephalidae, Diplectanidae et Monocotylidae. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 57:419–420
Justine JL, Mattei X (1983a) Etude ultrastructurale comparée de la spermiogenese des Monogènes: 1.Megalocotyle (Monopisthocotylea: Capsalidae). J Ultrastruct Res 82:296–308
Justine JL, Mattei X (1983b) Comparative ultrastructural study of spermiogenesis in monogeneans (flatworms): 2.Heterocotyle (Monopisthocotylea: Monocotylidae). J Ultrastruct Res 84:213–223
Justine JL, Mattei X (1983c) Comparative ultrastructural study of spermiogenesis in monogeneans (flatworms): 3. Two species ofAmphibdelloides (Monopisthocotylea: Amphibdellatidae). J Ultrastruct Res 84:224–237
Justine JL, Mattei X (1984a) Ultrastructure du spermatozooide du MonogèneHexostoma (Polyopisthocotylea, Hexostomatidae). Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 59:227–229
Justine JL, Mattei X (1984b) Comparative ultrastructural study of spermiogenesis in monogeneans (flatworms): 4.Diplectanum (Monopisthocotylea: Diplectanidae). J Ultrastruct Res 88:77–91
Justine JL, Lambert A, Mattei X (1985a) Spermatozoon ultrastructure and phylogenetic relationships in the monogeneans (Platyhelminthes). Int J Parasitol 15:601–608
Justine JL, Le Brun N, Mattei X (1985b) First report of aflagellate spermatozoon in a parasitic platyhelminth, found in the monogeneanDiplozoon gracile (Polyopisthocotylea, Diplozoidea). Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 60:761–762
Morseth DJ (1969) Spermatail fine structure ofEchinococcus granulosus andDicrocoelium dendriticum. Exp Parasitol 24:47–53
Rohde K (1971) Phylogenetic origin of trematodes. Parasitol Schriftenr 21:17–27
Rohde K (1980) Some aspects of the ultrastructure ofGotocotyla secunda andHexostoma thynni. Angew Parasitol 21:32–48
Rosario B (1964) An electron microscope study of spermatogenesis in cestodes. J Ultrastruct Res 11:412–427
Shapiro JE, Hershenov BR, Tulloch GS (1961) The fine structure ofHaematoloechus spermatozoan tail. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:211–217
Silveira M, Porter KR (1964) The spermatozoids of flatworms and their microtubular systems. Protoplasma 59:240–265
Tuzet O, Ktari MH (1971a) La spermiogénèse et la structure du spermatozooide deMicrocotyle mormyri Lorenz, 1878 (Monogenea). CR Acad Sci 272:2702–2705
Tuzet O, Ktari MH (1971b) Recherches sur l'ultrastructure du spermatozooide de quelques Monogènes. Bull Soc Zool Fr 96:535–540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmahl, G., Obiekezie, A. Fine structure of spermatogenesis in polyopisthocotylid monogeneans (Protomicrocotyle ivoriensis, Gastrocotyle sp.). Parasitol Res 77, 115–122 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935424
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935424