Abstract
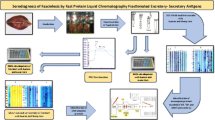
The soluble antigens ofEntamoeba histolytica trophozoites were analysed in detail by biochemical and immunochemical methods. The antigen was highly complex and heterogeneous as revcaled by Sephacryl S-300 column chromatography, which showed four distinct fractions. The molecular mass of fractions FI, FII, FIII and FIV was 660, 170, 65 and 13 kDa, respectively. Protein was the major constituent in crude soluble antigen (CSA) and fractions FI and FII (67%, 80% and 90%, respectively). Polysaccharide was predominant in the FIII fraction (59%). Antigenic activity observed after different physico-chemical treatments revealed that CSA and FI antigens were predominantly glycoprotein in nature. However, the antigenicity of FIII antigen was greatly reduced after sodium meta-periodate treatment, whereas no alteration in reactivity was discerned after trypsin treatment. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis demonstrated nearly 28 Coomassie blue bands for CSA and 20, 16, 15 and 3 polypeptide bands for the FI, FII, FIII and FIV fractions, respectively. The molecular mass of the polypeptides of these bands ranged from 210 to 20 kDa. Antigenic activity was observed in CSA and in the first three fractions, both in counter immunoelectrophoresis (CIEP) and in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). However, the highest antigenic activity was noted in fraction FI. Major immunoreactive polypeptides of CSA and FI antigens against whole trophozoite antibody were observed in the 10- to 170-kDa regions. However, major differences in the immunoreactivity of the two antigens were noted at 116 and 14 kDa for FI antigen and at 84, 30 and 20 kDa for CSA. The binding of the FI antibody to the surface of the live parasite and the loss of immunoreactive polypeptides from the FI antibody after its adsorption with live trophozoites ofE. histolytica suggest a correspondence between FI and surface antigens ofE. histolytica. The efficacy of active immunization with CSA and its different fractions showed that antigenicity and immunogenicity were closely associated with the high-molecular-weight proteins, as 91% protection was observed for the FI antigens, whereas the FII and FIII fractions and CSA provided only 41%, 33% and 41% protection, respectively. These data suggest that FI antigen can be used in the serodiagnosis of and immunoprophylaxis against amoebiasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Khan HM, Madhi AA, Kumar H, Khan N (1988)Entamoeba histolytica antigens as possible vaccinogen? A short review. J Chromatogr 440:467–472
Alam M, Ahmed S (1974) Immunogenicity ofEntamoeba histolytica antigen fractions. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 68:370–373
Aley SB, Scott WA, Cohn ZA (1980) Plasma membrane ofEntamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med 152:391–401
Ali Khan Z, Meerovitch E (1970) Studies on the purification ofEntamoeba histolytica antigen by gel filtration: II. The antigenic properties of the isolated fraction. Can J Microbiol 16:489–498
Bhattacharya A, Bhattacharya S, Sharma MP, Diamond LS (1990) Metabolic labelling ofEntamoeba histolytica antigen: characterization of a 28 kD major intracellular antigen. Exp Parasitol 3:255–263
Blakely P, Sarguent PG, Reed SL (1990) An immunogenic 30 kD surface antigen of a pathogenic isolate ofEntamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis 4:949–954
Bos HJ (1977) Fraction and serological characterization ofEntamoeba histolytica antigen. Acta Leiden 45:105–116
Butscher WG, Faubert GM (1988) The therapeutic action of monoclonal antibodies against a surface glycoprotein ofGiardia muris. Immunology 64:175–180
Chang KP, Fong D (1983) Cell biology of host-parasite membrane interaction in leishmaniasis. In: Everced D, Collins GM (eds) cytopathology of parasitic diseases. (Ciba Foundation Symposium 99) Pitman, London, pp 113–137
Chaudhuri PP, Pal S, Pal SC, Das P (1988) Studies onGiardia lamblia trophozoite antigen using Sephacryl S 300 column chromatography, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. In: Willis PM, Hammond BR (eds) Advances inGiardia research. University of Calgary Press, Calgary, pp 191–194
Chawla TC, Irshad M, Gandhi BM, Tandon BN (1987) Immunological characterization of axenicEntamoeba histolytica related antigens. Indian J Med Res 86:457–461
Das P, Pal S, Pal SC (1984) Evaluation of micro-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, indirect fluorescence antibody techniques for serodiagnosis of amoebiasis. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res 2:238–242
Das P, Narain L, Dutta GP, Pal S, Pal SC (1985) Improved method of producing liver abscess in hamster for screening of systematically active amoebicides. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 63:85–89
Das SR, Kidwai SA, Gupta AK (1979) Preparation of standard amoeba antigen from axenicEntamoeba histolytica and its use in serodiagnosis and seroepidemiology of amoebiasis. J Biosci 1:255
Diamond LS (1961) Axenic cultivation ofEntamoeba histolytica. Science 134:336–337
Diamond LS, Harlow DR, Cunnick CC (1978) A new medium for the axenic cultivation ofEntamoeba histolytica and otherEntamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 72:431–432
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Robers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:356–356
Edman U, Meraz MA, Rausser S, Agabain N, Meza J (1990) Characterization of an immunodominant soluble surface antigen from pathogenic and nonpathogenicE. histolytica. J Exp Med 172:879–888
Ghadirian E, Meerovitch E (1978) Vaccination against hepatic amoebiasis in hamsters. J Parasitol 64:742–743
Hames BD, Rickwood D (1986) Gel electrophoresis of proteins: a practical approach, 1st edn. IRL Press, Oxford
Haq A, Sharma A, Ahmed S (1984) Increased macrophage migration inhibition factor production in hamsters sensitized by amoebic antigen and glucan. Parasite Immunol 6:391–396
Jain P, Nain CK, Vinayak VK (1987) Vaccination against experimental hepatic amoebic infection — an evaluation of phosphatidyl choline liposomes as immunopotentiator. J Parasitol 73:859–860
Kettis AA, Thorstensson R, Utter G (1983) Antigenicity ofEntamoeba histolytica strain NIH 200: a survey of clinically relevant antigenic components. Am J Trop Med Hyg 32:512–522
Krupp IM (1977) Definition of the antigenic pattern ofEntamoeba histolytica and immunoelectrophoretic analysis of the variation of the patient response to amoebic disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg 26:387–392
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mann BJ, Petri WA Jr (1991) Cell surface proteins ofEntamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Today 7:173–176
Mathews HM, Moss DM, Visvesvara GS (1986) Analysis of antigens from membrane and soluble fractions ofEntamoeba histolytica. J Protozool 33:328–334
Meester FD, Shaw E, Scholze H, Stolarsky T, Mirelman D (1990) Specific labelling of cysteine proteinases in pathogenic and nonpathogenicEntamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun 58:1396–1401
Petri WA, Ravdin JI (1991) Protection of gerbils from amoebic liver abscess by immunization with the galactose specific adherence lectin ofEntamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun 59:97
Ravdin JI, Croft BY, Guerrant RL (1980) Cytopathogenic mechanisms ofEntamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med 152:377–390
Sawhney S, Chakraborti RN, Jain P, Vinayak VK (1980) Immunogenicity of axenicEntamoeba histolytica antigen and its fractions. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 74:26–29
Sepul'veda B, Che'vez A, Iturbe Alessio I, Ortiz-Ortiz L (1973) Efecto de la gamma-glubulina immune antiamibiana sobre el trofozoito deEntamoeba histolytica. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 4 [Suppl 1]:79–86
Sepu'lveda B, Arroyo-Begovich A, Tanimoto-Weki M, Martinez-Palomo A, Ortiz-Ortiz L (1978) Induction de inmunidad protectora antiamibiana con nuevos antigenos en el hamster lactante. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 9 [Suppl 1]:309–328
Stanley SL Jr, Becker A, Kung-Jenkins C, Foster L, Li E (1990) Cloning and expression of a membrane antigen ofEntamoeba histolytica possessing multiple tandem repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4976–4980
Swartzwelder JC, Avant WH (1952) Immunity to amoebic infection in dogs. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1:567
Tachibana H, Kobayashi S, Kato Y, Nagakura K, Keneda Y, Takeuchi T (1990) Identification of a pathogenic isolate specific 30 000 Mr. antigen ofEntamoeba histolytica by using a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun 58:955–960
Thompson PE, Graedel SK, Schneider CR, Stucki WP, Gordon RM (1968) Preparation and evaluation of standardized amoeba antigen from axenic culture ofEntamoeba histolytica. Bull WHO 39:349–365
Towbin HT, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polycrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedures and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Vinayak VK, Sawhney S, Jain P, Chakravarti RN (1980) Protective effects of crude and chromatographic fractions of axenicEntamoeba histolytica in guinea pigs. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 74:483–487
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, P., Sengupta, K., Pal, S. et al. Biochemical and immunological studies on soluble antigens ofEntamoeba histolytica . Parasitol Res 79, 365–371 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931824
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931824