Abstract
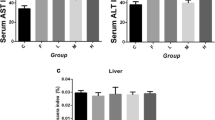
The change in calcium-binding protein regucalcin, mainly localized in liver, in the liver and serum of rats received a single oral administration of carbon tetrachloride (50%; 1.0 ml/100 g body weight) was investigated. The change of regucalcin mRNA levels in the liver was analyzed by Northern blotting using liver regucalcin cDNA (0.6 kb). At 10 and 24 h after the administration, liver regucalcin mRNA levels were reduced markedly. Moreover, regucalcin concentration in the liver and serum was estimated by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay (ELISA) with rabbit-anti-regucalcin IgG. Administration of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced a significant decrease in liver regucalcin concentration and a corresponding elevation of serum regucalcin concentration at 24 h after the administration. An appreciable increase in serum regucalcin concentration was seen at 2 h after the administration. Meanwhile, serum transaminases (GOT and GPT) activities were significantly increased by CCl4 administration, indicating that liver injury is induced. The present study demonstrates that hepatic regucalcin is released into the serum of rats administered orally CCl4, suggesting that the estimation of serum regucalcin is a useful tool for diagnosis of liver injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rasmussen J: Cell communications, calcium ion, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science 170: 404–412, 1970
Williamson JR, Cooper RK, Hoek JB: Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 243–295, 1981
Reihart PH, Taylor WM, Bygrave FL: The role of calcium ions in the mechanisms of action of α-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Biochem J 223: 1013, 1984
Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto T: Purification of calcium binding substance from soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 26: 1915–1918, 1978
Yamaguchi M, Sugii K: Properties of calcium-binding protein isolated from the soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 29: 567–570, 1981
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on protein kinase C activity in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Med Metab Biol 43: 140–146, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Tai H: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 106: 25–30, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett 279: 281–284, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Reversible effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on the Ca2+-induced inhibition of deoxyuridine 5′-triphosphatase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 110: 25–29, 1992
Simokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration stimulates the expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver. FEBS Lett 305: 151–154
Yamaguchi M, Isogai M: Tissue concentration of calcium-binding protein regucalcin in rats by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem 122: 65–68, 1993
Long RM, Moore L: Cytosolic calcium after carbon tetrachloride, 1,1-dichloroethylene, and phenylephrine exposure. Studies in rat hepatocytes with phosphorylasea and quin 2. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 1215–1221, 1987
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall E: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–273, 1951
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pirotal role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 19–27, 1980
Waisman DM, Salimath BP, Anderson MJ: Isolation and characterization of CAB-63, a novel calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem 260: 1652–1660, 1985
Fliegel L, Burns K, MacLennan DH, Reithmeier RAF, Michalak M: Molecular cloning of the high affinity calcium-binding protein (calreticulin) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 264: 21522–21528, 1989
Simokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Expression of hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA is mediated through Ca2+/calmodulin in rat liver. FEBS Lett 316: 79–84, 1993
Simokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett 327: 251–255, 1993
Fujita T, Shirasawa T, Uchida K, Maruyama N: Isolation of cDNA clone encoding rat senesence marker protein-30 (SMP30) and its tissue distribution. Biochim Biophys Acta 1132: 297–305, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isogai, M., Shimokawa, N. & Yamaguchi, M. Hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin is released into the serum of rats administered orally carbon tetrachloride. Mol Cell Biochem 131, 173–179 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925954
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925954