Abstract
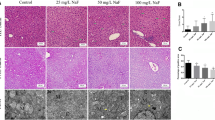
Excessive fluoride (F) exposure can lead to liver damage; moreover, recent studies found that the addition of appropriate calcium (Ca) can alleviate the symptom of skeletal fluorosis. However, whether Ca can relieve F-induced liver damage through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway has not been reported yet. Therefore, we assessed the liver morphology, serum transaminase content, liver oxidative stress-related enzymes, and apoptosis-related gene and protein expression in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats treated with 150 mg/L sodium fluoride (NaF) and different concentrations of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) for 120 days. Our results showed that NaF brought out pathological changes in liver morphology, serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels increased, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) content decreased, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content increased, suggesting that NaF caused hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress. In addition, the results of quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry showed that NaF exposure upregulated the expression of Bcl-2-associated x protein (Bax), rho-related coiled-coil kinase 1 (ROCK1), cytochrome C (Cyto-C) mRNA and protein (P < 0.01), and downregulated B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) protein and mRNA (P < 0.01), indicating that excessive F exposure activated mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in the liver. However, the addition of 1% CaCO3 to the diet significantly increased the expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 (P < 0.01), inhibited the activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway, and reduced mitochondrial damage. In summary, supplementing 1% CaCO3 in the diet can alleviate the NaF-induced liver cell damage through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Vazquez J, Pilch S, Williams MI, Cummins D (2005) Clinical efficacy of a triclosan/copolymer/NaF dentifrice and a commercially available breath-freshening dentifrice on hydrogen sulfide-forming bacteria. Oral Dis 11(Suppl 1):64–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-0825.2005.01095.x
Huang C, Zhang H, Zeng W, Ma J, Zhao S, Jiang Y, Huang C, Mao H, Liao Y (2020) Enhanced fluoride adsorption of aluminum humate and its resistance on fluoride accumulation in tea leaves. Environ Technol 41:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1498135
Prasad N, Pushpaangaeli B, Ram A, Maimanuku L (2018) Fluoride concentration in drinking water samples in Fiji. Aust N Z J Public Health 42:372–374. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-6405.12787
Tickle M, Ricketts DJN, Duncan A, O’Malley L, Donaldson PM, Clarkson JE, Black M, Boyers D, Donaldson M, Floate R, Forrest MM, Fraser A, Glenny AM, Goulao B, McDonald A, Ramsay CR, Ross C, Walsh T, Worthington HV, Young L, Bonetti DL, Gouick J, Mitchell FE, Macpherson LE, Lin YL, Pretty IA, Birch S (2019) Protocol for a randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost benefit of prescribing high dose fluoride toothpaste in preventing and treating dental caries in high-risk older adults (reflect trial). BMC Oral Health 19:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-019-0749-x
Patil MM, Lakhkar BB, Patil SS (2018) Curse of fluorosis. Indian J Pediatr 85:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-017-2574-z
Levy SM, Eichenberger-Gilmore JM, Warren JJ, Kavand G, Letuchy E, Broffitt B, Marshall TA, Burns TL, Janz KF, Pauley C, Torner JC, Phipps K (2018) Associations of fluoride intake with children’s cortical bone mineral and strength measures at age 11. J Public Health Dent 78:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphd.12286
Dure-Smith BA, Farley SM, Linkhart SG, Farley JR, Baylink DJ (1996) Calcium deficiency in fluoride-treated osteoporotic patients despite calcium supplementation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.81.1.8550763
Zigu Z, Xiaoyu W, Weiwei N, Qiuxia L, Rui Z, Wei O (2017) Effects of calcium on drinking fluorosis-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairment in the offspring of rats. Transl Neurosci 8:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1515/tnsci-2017-0026
Nóbrega DF, Leitão TJ, Cury JA, Tenuta LMA (2019) Fluoride binding to dental biofilm bacteria: synergistic effect with calcium questioned. Caries Res 53:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488598
Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang J, Manthari RK, Wang J (2018) Fluoride induces apoptosis and autophagy through the IL-17 signaling pathway in mice hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 92:3277–3289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2305-x
Han H, Sun Z, Luo G, Wang C, Wei R, Wang J (2015) Fluoride exposure changed the structure and the expressions of reproductive related genes in the hypothalamus-pituitary-testicular axis of male mice. Chemosphere 135:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.012
Wang H-W, Zhu S-Q, Liu J, Miao CY, Zhang Y, Zhou BH (2020) Fluoride-induced renal dysfunction via respiratory chain complex abnormal expression and fusion elevation in mice. Chemosphere 238:124607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124607
Ge Y, Chen L, Yin Z, Song X, Ruan T, Hua L, Liu J, Wang J, Ning H (2018) Fluoride-induced alterations of synapse-related proteins in the cerebral cortex of ICR offspring mouse brain. Chemosphere 201:874–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.167
Subramanian P, Mirunalini S, Dakshayani KB, Pandi-Perumal SR, Trakht I, Cardinali DP (2007) Prevention by melatonin of hepatocarcinogenesis in rats injected with N-nitrosodiethylamine. J Pineal Res 43:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00478.x
Perera T, Ranasinghe S, Alles N, Waduge R (2018) Effect of fluoride on major organs with the different time of exposure in rats. Environ Health Prev Med 23:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12199-018-0707-2
Chattopadhyay A, Podder S, Agarwal S, Bhattacharya S (2011) Fluoride-induced histopathology and synthesis of stress protein in liver and kidney of mice. Arch Toxicol 85:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0588-7
Zhou B, Zhao J, Liu J, Zhang JL, Li J, Wang HW (2015) Fluoride-induced oxidative stress is involved in the morphological damage and dysfunction of liver in female mice. Chemosphere 139:504–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.030
Lu Y, Luo Q, Cui H et al (2017) Sodium fluoride causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Aging (Albany NY) 9:1623–1639. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101257
Wei Q, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2018) A mini review of fluoride-induced apoptotic pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:33926–33935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3406-z
Birkinshaw RW, Czabotar PE (2017) The BCL-2 family of proteins and mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 72:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.04.001
Cao J, Chen J, Wang J, Jia R, Xue W, Luo Y, Gan X (2013) Effects of fluoride on liver apoptosis and Bcl-2, Bax protein expression in freshwater teleost, Cyprinus carpio. Chemosphere 91:1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.037
García-Sáez AJ (2012) The secrets of the Bcl-2 family. Cell Death Differ 19:1733–1740. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.105
Del Re DP, Miyamoto S, Brown JH (2007) RhoA/Rho kinase up-regulate Bax to activate a mitochondrial death pathway and induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282:8069–8078. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M604298200
Rubenstein NM, Callahan JA, Lo DH, Firestone GL (2007) Selective glucocorticoid control of Rho kinase isoforms regulate cell-cell interactions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:603–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.024
Shimokawa H, Rashid M (2007) Development of Rho-kinase inhibitors for cardiovascular medicine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2007.04.006
Xie Y, Song T, Huo M et al (2018) Fasudil alleviates hepatic fibrosis in type 1 diabetic rats: involvement of the inflammation and RhoA/ROCK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:5665–5677. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201809_15834
Yang S, Wang Z, Farquharson C, Alkasir R, Zahra M, Ren G, Han B (2011) Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis and alters bcl-2 family protein expression in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 410:910–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.094
Song GH, Gao JP, Wang CF, Chen CY, Yan XY, Guo M, Wang Y, Huang FB (2014) Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis in the kidney of rats through caspase-mediated pathways and DNA damage. J Physiol Biochem 70:857–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0354-z
Hua SG, Wang RL, Chen ZY et al (2014) Toxic effects of sodium fluoride on cell proliferation and apoptosis of Leydig cells from young mice. J Physiol Biochem 70:761–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0344-1
Wang J, Yang J, Cheng X, Xiao R, Zhao Y, Xu H, Zhu Y, Yan Z, Ommati MM, Manthari RK, Wang J (2019) Calcium alleviates fluoride-induced bone damage by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Agric Food Chem 67:10832–10843. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04295
Wang J, Xu H, Cheng X, Yang J, Yan Z, Ma H, Zhao Y, Ommati MM, Manthari RK, Wang J (2020) Calcium relieves fluoride-induced bone damage through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct 11:1155–1164. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02491c
Yang J, Zhu Y, Zhang D, Yan Z, Zhao Y, Manthari RK, Cheng X, Wang J, Wang J (2020) Effects of different doses of calcium on the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in the bone of fluorosis rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02305-6
Inkielewicz-Stępniak I (2011) Impact of fluoxetine on liver damage in rats. Pharmacol Rep 63:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70510-2
Hassan HA, Yousef MI (2009) Mitigating effects of antioxidant properties of black berry juice on sodium fluoride induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47:2332–2337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.06.023
Mohamed NE (2016) The role of calcium in ameliorating the oxidative stress of fluoride in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 170:128–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0421-5
Wang YX, Xiao X, Zhan XA (2018) Antagonistic effects of different selenium sources on growth inhibition, oxidative damage, and apoptosis induced by fluorine in broilers. Poult Sci 97:3207–3217. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey192
Feng P, Wei J, Zhang Z (2011) Intervention of selenium on chronic fluorosis-induced injury of blood antioxidant capacity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1024–1031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9087-9
Yu R-A, Xia T, Wang A-G, Chen X-M (2006) Effects of selenium and zinc on renal oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by fluoride in rats. Biomed Environ Sci 19:439–444
Sarkar SD, Maiti R, Ghosh D (2006) Management of fluoride induced testicular disorders by calcium and vitamin-E co-administration in the albino rat. Reprod Toxicol 22:606–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2006.05.001
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Wang A-G, Xia T, Chu Q-L et al (2004) Effects of fluoride on lipid peroxidation, DNA damage and apoptosis in human embryo hepatocytes. Biomed Environ Sci 17:217–222
Song GH, Huang FB, Gao JP, Liu ML, Pang WB, bin Li W, Yan XY, Huo MJ, Yang X (2015) Effects of fluoride on DNA damage and caspase-mediated apoptosis in the liver of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 166:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0265-z
Tan P-P, Zhou B-H, Zhao W-P, Jia LS, Liu J, Wang HW (2018) Mitochondria-mediated pathway regulates C2C12 cell apoptosis induced by fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res 185:440–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1265-6
Tu D, Li Y, Song HK, Toms AV, Gould CJ, Ficarro SB, Marto JA, Goode BL, Eck MJ (2011) Crystal structure of a coiled-coil domain from human ROCK I. PLoS One 6:e18080. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018080
Ark M, Ozdemir A, Polat B (2010) Ouabain-induced apoptosis and Rho kinase: a novel caspase-2 cleavage site and fragment of Rock-2. Apoptosis 15:1494–1506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0529-1
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation (Grant 31972751) and Shanxi Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant 201901D111230) and Shanxi Province Innovation Project for Graduate Students (Grant 2019SY219) and the Social Developmental Project of Jiangsu Province (BE2018715).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Hao, Z., Wang, L. et al. Dietary Calcium Alleviates Fluorine-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 271–280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02641-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02641-1