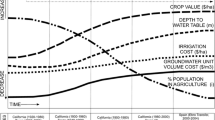
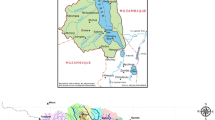
Abstract
This paper describes a technical and feasibility study of increasing groundwater usage to supplement surface water use in the Campaspe Valley in south-eastern Australia. An integrated model which simulates the surface and groundwater processes, as well as the interactions between the processes, is used to determine the sustainable long-term groundwater pumping yields. The model also provides estimates of groundwater fluxes for various management options of increasing groundwater usage. These estimates are used to assist an economic analysis to determine the relative merits of various options for the conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources. The pumping costs, value of water and tangible salinity benefits from lowering high water-tables and reducing salt load are considered in the economic analysis. The methodology is also relevant for other studies looking into the conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources throughout the Murray Basin and elsewhere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkley, A., Reid, M., and Mavrakis, M., 1991, Campaspe Valley Conjunctive Use Study, Part 2, Aquifer Pumping Test Analysis Report, Investigations Branch, Rural Water Commission of Victoria, Australia, Rep., 1991/31 (unpublished).
Chiew, F.H.S., 1990, Estimating Groundwater Recharge using an Integrated Surface and Groundwater Model, Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil and Agricultural Engineering, Univ. of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 357 pp.
Chiew, F. H. S. and McMahon, T. A., 1990, Estimating groundwater recharge using a surface watershed modelling approach,J. Hydrol. 114(3), 285–304.
Chiew, F. H. S. and McMahon, T. A., 1991a, The applicability of Morton's and Penman's evapotranspiration estimates in rainfall-runoff modelling,Wat. Resour. Bull. 27(4), 611–620.
Chiew, F. H. S. and McMahon, T. A., 1991b, Groundwater recharge from rainfall and irrigation in the Campaspe River Basin,Aust. J. Soil Res. 29(5), 651–670.
Chiew, F. H. S., McMahon, T. A., and O'Neill, I. C., 1992, Estimating groundwater recharge using an integrated surface and groundwater modelling approach.J. Hydrol. 131, 151–186.
Dudding, M., 1991, Murray Darling Basin Commission Register for Salinity Credits and Debits, Investigations Branch, Rural Water Commission of Victoria (unpublished).
Dudding, M., Chiew, F., and Brinkley, A., 1991, Campaspe Valley Conjunctive Use Study, Part 3, Technical and Economic Evaluation Report, Investigations Branch, Rural Water Commission of Victoria, Australia, Rep., 1991/33, 56 pp. (unpublished).
Evans, R. T., 1989, A Model for Determining the Quantifiable Economic Benefits of Surface Drainage, Background Paper SD2 of the Shepparton Irrigation Region Land and Water Salinity Management Plan, Economics Section, Rural Water Commission of Victoria, 107 pp. (unpublished).
McMahon, T. A., 1984, Irrigation and Groundwater Accessions. A report prepared for the Salinity Committee of the Victorian Parliament on the Proceedings of a Technical Seminar, Aust., 15 pp.
Morton, F.I., 1983, Operational estimates of actual evapotranspiration and their significance to the science and practice of hydrology,J. Hydrol. 66, 1–76.
Nolan, J., 1988, Riverine Plain Groundwater Usage Survey, Investigations Branch, Rural Water Commission of Victoria, Australia, Rep, 1988/20, 24 pp. (unpublished).
Nolan, J., Olshina., A., Carney, P., and Bartley, J., 1988, Shepparton Region Options Study: Recharge to the Deep Lead by Numerical Simulation, Department of Industry, Technology and Resources, Victoria, Australia, Rep., 88/36, 26 pp. (unpublished).
Nolan, J. and Reid, M., 1989, The Role of Deep Lead Pumping for Salinity Control and Resource Development within the Shepparton Formation, Investigations Branch, Rural Water Commission of Victoria, Australia, Rep., 1989/11 (unpublished).
Porter, J. W. and McMahon, T. A., 1976, The Monash Model: User Manual for Daily Program HYDROLOG, Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, Victoria, Australia, Res. Rep., 2/76, 41 pp.
Townley, L. R., 1992, AQUIFEM-N: A Multi-Layered Finite Element Aquifer Flow Model: User's Manual and Description, CSIRO Division of Water Resources, Perth, Western Australia.
Wilson, J. L., Townley, L. R., and Sa da Costa, A., 1979, Mathematical Development and Verification of a Finite Element Aquifer Flow Model AQUIFEM-1, Ralph M. Parsons Laboratory for Water Resources and Hydrodynamics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, U.S.A., Tech. Rep., 248, 114 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiew, F.H.S., McMahon, T.A., Dudding, M. et al. Technical and economic evaluation of the conjunctive use of surface and groundwater in the Campaspe Valley, north-central Victoria, Australia. Water Resour Manage 9, 251–275 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872487
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872487