Abstract
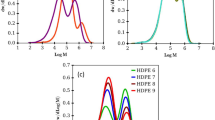
By comparing the relaxation spectra respectively calculated on the basis of the iterative and approximation methods, it is confirmed that the latter may be used to describe the viscoelastic properties of polyethylene melts. A method is proposed for identifying the form of the frequency relaxation spectrum by three characteristic numerical quantities. The effect of the molecular-mass, the molecular-mass distribution, and the long-chain branching characteristics on the form of the frequency relaxation spectrum is considered. The question of the geometrical similarity of the relaxation spectrum is discussed, and it is shown that, in general, these spectra are not linearly similar. The asymmetry of the spectrum depends solely on the index representing the rate of fall of the dynamic viscosity with increasing frequency of deformation. Methods of determining the characteristic relaxation time without constructing a frequency relaxation spectrum are proposed; ways of determining the characteristic relaxation time from experimental data are indicated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. J. Stawerman and F. Schwartzl, "Nonlinear deformation behavior of high polymers," in: Physics of High Polymers, Vol. 4, Berlin (1956), pp. 126–158.
A. N. Moltkov, Yu. S. Zelenev, and G. M. Bartenev, "Comparative analysis of the relaxation spectra of polymers of various classes," Mekh. Polim., No. 3, 445–449 (1968).
N. I. Gol'dberg, Mechanical Behavior of Polymer Materials [in Russian], Moscow (1970).
I. P. Briedis and L. A. Faitel'son, "Rheology and molecular structure of polyethylene melts. 1. Identification of melts by reference to mechanical properties," Mekh. Polim., No. 3, 523–532 (1975).
B. Gross, Mathematical Structure of the Theories of Viscoelasticity, Paris (1953), p. 74.
J. D. Ferry, Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 2nd ed., Wiley (1970).
B. Hlavaček and V. Kotrba, "Numerical iterations for the calculation of the relaxation spectrum from dynamic measurements," Rheologica Acta,6, 288 (1967).
É. É. Yakobson, "Iterative method of determining the spectrum of relaxation times from the components of the complex shear modulus," Mekh. Polim., No. 6, 1069–1076 (1975).
R. H. Schroff and M. Shida, "Effect of long-chain branching on the relation between steady-flow and dynamic viscosity of polyethylene melts," J. Polym. Sci., Pt. A, No. 8, 1917–1925 (1970).
I. P. Briedis and L. A. Faitel'son, "Rheology and molecular structure of polyethylene melts. 2. Influence of molecular structure on the viscoelastic characteristics," Mekh. Polim., No. 1, 120–127 (1976).
I. Labaig, P. Monge, and J. Bednarich, Steady-flow and dynamic viscoelastic properties of branched polyethylene," Polymer,14, No. 8, 384–386 (1973).
K. S. Cole and R. H. Cole, "Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics. 1. Alternating-current characteristics," J. Chem. Phys.,9, 341–351 (1941).
Additional information
For communication 2, see [10].
Institute of Polymer Mechanics, Academy of Sciences of the Latvian SSR, Riga. Translated from Mekhanika Polimerov, No. 2, pp. 322–330, March–April, 1976.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briedis, I.P., Faitel'son, L.A. Rheology and molecular structure of a polyethylene melt. 3. Relaxation spectra and characteristic relaxation time. Polymer Mechanics 12, 278–286 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00856466
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00856466