Abstract
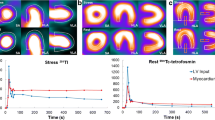
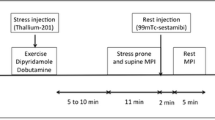
Nineteen patients with angina were recruited in this study for comparison of two 1-day protocols (stress-4 h rest and rest-4-h stress) and a 2-day protocol of technetium-99m tetrofosmin single-photon emission tomography (SPET). All of them underwent coronary angiography before or after the study. Exercise stress-rest study and rest-stress study were performed on two consecutive days. Delayed imaging was performed before the rest injection on the 2nd day. The stress study on the 1 st day and rest study on the 2nd day were considered as a 2-day protocol. The 1-day stress-rest protocol had a sensitivity of 100% (18/18) and an accuracy of 100% (19/19) in diagnosing ischaemic heart disease. The 1-day rest-stress protocol had a sensitivity of 94.4% (17/18) and an accuracy of 94.7% (18/19). These differences were not statistically significant (P=0.5 for sensitivity and accuracy). There was also no statistically significant difference between the two protocols in the diagnosis of ischaemic heart disease in individual artery territories. For the left descending artery, sensitivity was 88.2% (15/17) vs 76.5% (13/17) (P=0.48) for the stress-rest and rest-stress studies respectively. For the left circumflex artery, sensitivity was 90% (9/10) vs 80% (8/10) (P=1) and specificity was 66.7% (6/9) vs 77.8% (7/9) (P=1) respectively. For the right coronary artery, the sensitivity was 100% (16/16) vs 94% (15/16) (P=1) respectively, while the specificity was 33.3% (1/3) in both studies. Three hundred and forty-two myocardial segments were analysed. The stress-rest and 2-day protocols showed no statistically significant difference in the overall identification of segments with reversible ischaemia (48/141 segments vs 48/141 segments) or in respect of individual artery territories. There was also no significant difference in the identification of reversible ischaemic segments between the rest-stress and 2-day protocols (48/141 segments vs 34/135 segments,P=0.14). Abdominal activity was seen in 36 studies and interpretation was affected in five of them. Five patients with 24-h delayed images were evaluated and 24 segments with washout were identified. It is concluded that99mTc-tetrofosmin is a valuable new tracer in the investigation of ischaemic heart disease. The 1-day stress-rest protocol is as good as the 1-day rest-stress protocol in diagnosing coronary heart disease. The 1-day protocols and the 2-day protocol display no difference in identifying segments with reversible ischaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones AG, Abrams JM, Davison A, et al. Biological studies of a new class of technetium complexes: the hexakis(alkylisonitrile)technetium (I) cations.Int J Nucl Med Biol 1984; 11: 225–234.
Van Train KF, Garcia EV, Maddahi J, et al. Multicenter trial validation for quantitative analysis of same-day rest-stress technetium-99m-sestamibi myocardial tomograms.J Nucl Med 1993; 35: 609–618.
Bisi G, Sciagra R, Santoro GM, et al. Evaluation of coronary disease extent using99mTcm-sestamibi: comparison of dipyridamole versus exercise and of planar versus tomographic imaging.Nucl Med Commun 1993; 14: 946–954.
Taillefer R. Same day injection of Tc-99m methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (MIBI) for myocardial tomographic imaging: comparison between rest-stress and stress-rest injection sequences.Eur J Nucl Med 1989; 15: 113–124.
Dondi M, Tartagi F, Coccolini S, et al. Clinical evaluation of four study protocols with99mTc-methoxyisobutylisonitrile and SPELT for detecting diseased coronary vessels.J Nucl Biol Med 1991; 35: 76–81.
Higley B, Smith FW, Smith T, et al. Technetium-99m-1,2-bis [bis (2-ethoxyethyl) phosphino] ethane: human biodistribution, dosimetry and safety of a new myocardial perfusion imaging agent.J Nucl Med 1990; 34: 30–38.
Tamaki N, Tonekura Y, Mukai T, et al. Stress thallium-201 transaxial emission computed tomography: quantitative versus qualitative analysis for evaluation of coronary heart disease.J Am Coll Cardiol 1994; 4: 1213–1221.
DePasquale EE, Nody AC, DePuey EG, et al. Quantitative rotational thallium-201 tomography for identifying and localizing coronary heart disease.Circulation 1988; 77: 316–327
West DJ, Najm YC, Mistry R, et al. the localization of myocardial ischaemia with technetium-99m methoxy isobutyl isonitrile and single photon emission computed tomography.Br J Radiol 1989; 62: 303–313.
Inoue Y, Machida K, Honda N, et al. Clearance of99mTc-tet-rofosmin from the myocardium and the adjacent organs.Jpn J Nucl Med 1993; 30: 313–316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Au Yong, T.K., Chambers, J., Maisey, M.N. et al. Technetium-99m tetrofosmin myocardial perfusion scan: comparison of 1-day and 2-day protocols. Eur J Nucl Med 23, 320–325 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00837631
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00837631