Summary
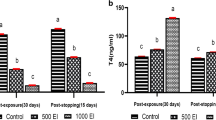
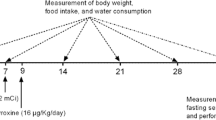
Administration of a single 1 μ C I131 dose to albino male rats provokes considerable changes in their thyroid glands and marked alterations in the physico-chemical composition of the cytoplasm and karyoplasm of the thyroid epithelium. In the first 2 days this is manifested in the dislocation of the isoelectric point of the above cellular components toward increased acidity, in the intensified neutral red sorption, in the increased mean height of follicular cells and the mean relative crude weight of the gland.
The aforementioned changes proved more pronounced in the thyroid gland previously activated by the action of 6-methylthiouracil. With the continuing 6-methylthiouracil action on the thyroid gland after radioiodine injection, the thyroid parenchyma becomes a scene of the following pathological changes: marked polymorphism of the follicular epithelium cells, large perinuclear vacuolization, a rise in the number of nuclear pycnoses and karyorrhexis and, here and there, desquamation into the follicular cavity. Thus, radioiodine affects both the unstimulated and stimulated thyroid; in the latter case the effect is considerably intensified even by small doses of radioiodine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
B. V. Aleshin and N. S. Demidenko, Arkhiv Anat., Gistol. i Émbriol.3, (1952) p. 82.
A. S. Breslavskii, Vrach. delo,11, 1009 (1951).
P. D. Gorizontov, From: The Problem of Trauma [in Russian] (Moscow, 1960) p. 113.
P. D. Gorizontov, From: The Pathological Physiology of Acute Radiation Sickness [in Russian] (Moscow, 1958) p. 5.
N. S. Demidenko, Byull. Éksper. Biol. i Med.27, 1, (1949) p. 57.
Ya. M. Kabak, Uspekhi Sovr. Biol.28, 2 (5) (1949) p. 187.
L. A. Kashchenko, Probl. Éndokrinol. i Gormonoter.1, 3 (1955) pp. 65–68.
Yu. V. Krivobok, Summaries of Reports of the Conference Devoted to the Response of the Endocrine System to Ionizing Radiation [in Russian] (Leningrad, 1956), p. 9.
Yu. V. Krivobok, Problems of Endocrinology [in Russian] (Khar'kov, 1958) p. 45.
I. A. Pigalev, From: The Biological Effects of Radiation and the Clinical Picture of Radiation Sickness [in Russian] (Moscow, 1954) p. 76.
D. D. Feller, I. L. Chaikoff,A. Taurog et al. Endocrinology45, (1949) p. 464.
R. C. Goldberg, I. L. Chaikoff, S. Lindsay et al., Ibid.46, (1950) p. 72.
F. Maloof, B. M. Dobyns and A. L. Vickery, Ibid.50 (1952) p. 612.
R. Rugh, J. Morphol.89 (1951) p. 323.
B. N. Skanse, Trans. Am. Goiter Ass. (1948) p. 103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krivobok, Y.V. The influence of radioactive iodine upon the nonstimulated and stimulated thyroid gland. Bull Exp Biol Med 51, 700–703 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00833895
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00833895