Conclusions
-
1.
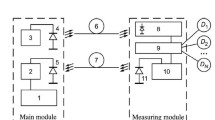
The compensating converter with the photodiode makes it possible to attain higher accuracy of measurements of quantities of illumination engineering than in measurements making use of direct conversion methods; the design of the primary converter is rather simple but dependable in operation.
-
2.
In order to increase the accuracy of a converter of this type, measures must be taken to restrict the range of temperatures at which the photodiode is operated to the interval in which the condition r≪R0 is satisfied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Effects in Semiconductors [in Russian], Fizmatgiz, Moscow (1963).
P. P. Ornatskii, Automatic Measuring Instruments [in Russian], Tekhnika, Kiev (1965).
V. A. Gorokhov, Semiconductor Devices and Their Applications [in Russian], No. 10, Sovet-skoe Radio, Moscow (1963).
L. A. Sinitskii (editor), Measuring Converters for Direct Current [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1965).
Additional information
Translated from Izmeritel'naya Tekhnika, No. 5, pp. 21–23, May, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shostak, V.A. Compensating converter with photodiode. Meas Tech 17, 674–677 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00812383
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00812383