Summary
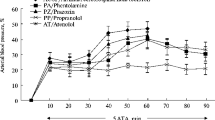
Denervation of sinocarotid zones causes a stable decrease in the saturation of the arterial blood by oxygen and a decrease of the volume of lung ventilation in cats and rabbits. Only short decrease of saturation was noted during denervation of the spleen and removal of the femoral nerves. This was due to the section of the nerves and irritation of the peritoneum. An important role is played by the reflex component in regulation of the saturation of the arterial blood by oxygen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
N. N. Beller, Biull. Eksptl. Biol. i Med. 43, No. 6, 12–18 (1957). Original Russian pagination. See C. B. Translation.
N. N. Beller, Biull. Eksptl. Biol. i Med. 45, No. 2, 42–45 (1958). Original Russian pagination. See C. B. Translation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beller, N.N. Role of interoceptors in the regulation of oxygen saturation of arterial blood. Bull Exp Biol Med 45, 309–312 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00803336
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00803336