Summary
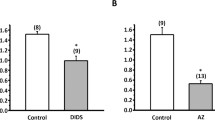
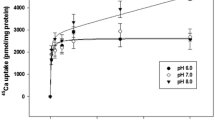
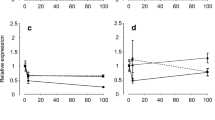
Isolated gills of the freshwater mussel,Ligumia subrostrata, accumulate Na from a pondwater bathing medium. The rate of Na transport by the isolated gill is 13.2±1.1 μmol (g dry gill·10 min)−1 which equals or exceeds the estimated Na transport rate of intact animals. Sodium influx is saturable with aV max of 13.6±1.2 μmol (g dry gill·10 min)−1 and an affinity (K s) of 0.17 mM Na/l. The isolated gills survive prolonged exposure to pondwater with a constant\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) of 890 μl O2 (g dry gill·h)−1 over a 4 h period. Sodium transport in the isolated gills is stimulated 80% above control values by 10−4 M serotonin, 60% by 0.5 mM cAMP and 60% by 12.5 μg/ml nystatin. Sodium influx is inhibited by 0.5 mM amiloride and 1 mM lithium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamford DR, Campbell E (1976) The effect of environmental factors on the absorption of L-phenylalanine by the gill ofMytilus edulis. Comp Biochem Physiol 53A:295–299
Biber TUL, Mullen TL (1980) Effect of external cation and anion substitutions on sodium transport in isolated frog skin. J Membr Biol 52:121–132
Catapane EJ, Stefano GB, Aiello E (1979) Neurophysiological correlates of the dopaminergic cilio-inhibitory mechanism ofMytilus edulis. J Exp Biol 83:315–323
Degnan KJ, Zadunaisky JA (1979) Open-circuit sodium and chloride fluxes across isolated opercular epithelia from the teleostFundalus heteroclitus. J Physiol (Lond) 294:483–495
Dietz TH (1974) Body fluid composition and aerial oxygen consumption in the freshwater mussel,Ligumia subrostrata (Say): Effects of dehydration and anoxic stress. Biol Bull 147:560–572
Dietz TH (1978) Sodium transport in the freshwater mussel,Carunculina texasensis (Lea). Am J Physiol 235:R35-R40
Dietz TH (1979) Uptake of sodium and chloride by freshwater mussels. Can J Zool 57:156–160
Dietz TH, Branton WD (1979) Chloride transport in freshwater mussels. Physiol Zool 52:520–528
Dietz TH, Findley AM (1980) Ion-stimulated ATPase activity and NaCl uptake in the gills of freshwater mussels. Can J Zool 58:917–923
Girard JP (1976) Salt excretion by the perfused head of trout adapted to sea water and its inhibition by adrenaline. J Comp Physiol 111:77–91
Graves SY, Dietz TH (1979) Prostaglandin E2 inhibition of sodium transport in the freshwater mussel. J Exp Zool 210:195–201
Graves SY, Dietz TH (1980) Diurnal rhythms of sodium transport in the freshwater mussel. Can J Zool 58:1626–1630
Handler JS, Preston AS, Rogulski J (1968) Control of glycogenolysis in the toad's urinary bladder. The effect of anaerobiosis, sodium transport and arginine vasotocin. J Biol Chem 243:1376–1383
Hynie S, Sharp GWG (1971) Adenyl cyclase in the toad bladder. Biochim Biophys Acta 230:40–51
Kuehl FA Jr (1974) Prostaglandins, cyclic nucleotides and cell function. Prostaglandins 5:325–340
Orloff J, Zusman R (1978) Role of prostaglandin E (PGE) in the modulation of the action of vasopressin on water flow in the urinary bladder of the toad and mammalian kidney. J Membr Biol (special issue) 40:297–304
Payan P, Matty AJ, Maetz J (1975) A study of the sodium pump in the perfused head preparation of the troutSalmo gairdneri in freshwater. J Comp Physiol 104:33–48
Pressman BC (1976) Biological applications of ionophores. Ann Rev Biochem 45:501–530
Prosser CL (1973) Comparative animal physiology. Saunders, Philadelphia
Robertson HA, Osborne NN (1979) Putative neurotransmitter in the annelid central nervous system: Presence of 5-hydroxytryptamine and octopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclases Comp Biochem Physiol 64C:7–14
Saintsing DG, Towle DW (1978) Na++K+-ATPase in the osmoregulating clamRangia cuneata. J Exp Zool 206:435–442
Spring J, Hanrahan J, Phillips J (1978) Hormonal control of chloride transport across locust rectum. Can J Zool 56:1879–1882
Wright SH (1979) Effect of activity of lateral cilia on transport of amino acids in gills ofMytilus californianus. J Exp Zool 209:209–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dietz, T.H., Graves, S.Y. Sodium influx in isolated gills of the freshwater mussel,Ligumia subrostrata . J Comp Physiol B 143, 185–190 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00797697
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00797697