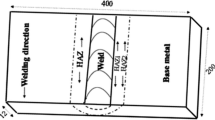
Conclusions
-
1.
Carbon increases the stability of the austenite in the transition zone; in welded samples of base metal containing 0.01 and 0.18% C the austenite in the base metal decomposes with formation of a structure corresponding to that resulting from quenching.
-
2.
Carbides are formed from austenite and alloyed martensite in the transition zone during isothermal heating at temperatures ensuring high diffusional mobility of carbon atoms and carbide-forming elements. The precipitation of carbon from the austenite and martensite lattices during crystallization of the carbide phase favors pearlitic and intermediate transformation of these phases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Yu. N. Gotal'skii, Avtomaticheskaya svarka (1961), No. 8.
B. I. Bruk, Radioactive Isotopes in Metallurgy and Welding [in Russian], Sudpromgiz (1959).
E. V. Panchenko, Yu. A. Skakov, K. V. Popov, B. I. Krimer, P. P. Arsent'ev, Ya. D. Khorin, Metallographic Laboratories [in Russian], Moscow, Metallurgizdat (1957).
E. Houdremont, Special Steels and Alloys, Vol. 1 [Russian translation], Moscow, Metallurgizdat (1959).
V. S. Mes'kin, Fundamentals of Alloying Steel [in Russian], Metallurgizdat (1959).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 6, pp. 48–50, June, 1964
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yarkovoi, V.S., Ivanov, V.D. Structure of the transition zone in weld seams of different steels welded together. Met Sci Heat Treat 6, 382–384 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00775337
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00775337