Abstract
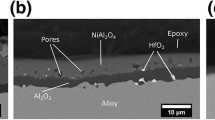
A commercial superalloy, MP35N, which was modified by adding various amounts of Al up to 10 wt.%, has been studied over the temperature range of 600–900°C in 0.01 atm sulfur vapor. The Al-modified alloys contained a second phase whose amount increased with increasing Al. The sulfidation rate followed the parabolic rate law and decreased with increasing Al content. An activation energy of 46 kcal/mol was obtained for MP35N, MP35N-5Al, and MP35N-7Al, while a value of 56 kcal/mol was found for MP35N-10Al at 700–800°C. Triplex sulfide scales formed on MP35N, consisting of an outer layer of solid solution (Co, Ni) 3S4,an intermediate layer of Cr 2S3,and a complex, heterophasic inner layer of mostly MoS 2.The Al-modified alloys also formed an outer scale of (Co, Ni) 3S4,and an inner layer containing a mixture of CoCr 2S4 and Al 2S3.An internal-sulfidation zone containing an Al-rich sulfide was formed in the substrate. Only a moderate beneficial effect of Al additions to MP35N was observed at 600°C. The observation of the location of platinum markers suggests that cobalt, nickel, chromium, and aluminum diffuse outward to form the major part of scale, and sulfur diffuses inward to produce an internal-sulfidation zone. Transport processes in the internal-sulfidation zone governed the sulfidation rate of the alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. V. Carter, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 31, 341 (1989).
M. F. Chen and D. L. Douglass,Oxid. Met. 32, 185 (1989).
B. Gleeson and D. L. Douglass,Mat. Sci. Eng. A120, 39 (1989).
M. F. Chen and D. L. Douglass,Oxid. Met. 33, 103 (1990).
B. Gleeson, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. (in press).
G. Wang, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 35, 279 (1991).
B. Gleeson, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. 31, 209 (1989).
M. J. Ferrante and R. A. McCune,U.S. Bur. Mines RI, 8526 (1981).
K. N. Strafford and P. K. Datta,Mat. Sci. Tech. 5, 765 (1989).
A. Bruckman,Corros. Sci. 7, 51 (1967).
T. Biegun, A. Bruckman, and S. Mrowec,Oxid. Met. 12, 152 (1978).
T. Biegun and A. Bruckman,Bull. Ac. Pol. Chem. 29, 69 (1981).
M. Robbinset al., J. Solid State Chem. 9, 170 (1974).
P. C. Donohue,J. Solid State Chem. 2, 6 (1970).
G. Wang, D. L. Douglass, and F. Gesmundo,Oxid. Met. (in press).
K. N. Strafford,J. Less-Common Metals 21, 305 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shing, C., Douglass, D.L. & Gesmundo, F. Sulfidation behavior of Al-modified MP35N alloys. Oxid Met 35, 295–315 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00738291
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00738291