Abstract
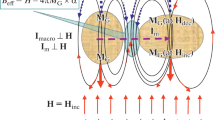
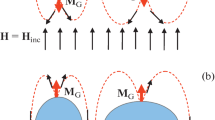
The field-cooled magnetization of high-T c superconducting ceramics measured in low magnetic fields exhibits the paramagnetic Meissner effect (PME), i.e., the diamagnetic signal initially increases with decrease in temperature but reaches a maximum at temperatureT d and later decreases with decrease in temperature. Even in some samples the signal is ultimately able to transform inversely into a paramagnetic regime once the sample is cooled below a temperatureT p as long as the applied field is sufficiently small. This PME has been observed in various high-T c cuprates and is explained by disparate aspects. An anisotropic model, in which the granular superconductors are assumed to be ideally anisotropic, was first alternatively proposed in the present work so as to theoretically account for this effect. On the other hand, an isotropic model, suitable for granular superconductors with randomly oriented grains, was proposed to deal with the samples prepared by a conventional solid-state reaction method. The anomalous magnetization behavior in the present model was demonstrated to be the superposition of the diamagnetic signal, which occurs as a result of the intragranular shielding currents, over the paramagnetic one due to the induction of the intergranular component induced by these currents where the intergranular one behaved as the efective pinning centers. The PME was demonstrated by this model to exist parasitically in granular superconductors. This intergranular effect is therefore worthy of remark when evaluating the volume fraction of superconductivity for the samples from the Meissner signal, in particular, at a low magnetic field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Krusin-Elbaum, A. P. Malozemoff, Y. Yeshurun, D. C. Cronemeyer, and F. Holtzberg,Physica C 153–155, 1460 (1988).
V. V. Alexandrov, V. V. Borisovskii, T. A. Fedotova, L. M. Fisher, N. V. Il'in, O. K. Smirnova, I. F. Voloshin, M. A. Baranov, and V. S. Gorbachev,Physica C 173, 458 (1991).
A. P. Malozemoff, L. Krusin-Elbaum, D. C. Cronemeyer, Y. Y. Eshurun, and F. Holtzberg,Phys. Rev. B 38, 6490 (1988).
K. A. Müller, M. Takashige, and J. G. Bednorz,Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 1143 (1987).
F. Seidler, P. Böhm, H. Geues, W. Braunisch, E. Braun, W. Schnelle, Z. Drzazga, N. Wild, B. Roden, H. Schmidt, D. Wohlleben, I. Felner, and Y. Wolfus,Physica C 157, 375 (1989).
S. Ruppel, G. Michaels, H. Geus, J. Kalenborn, W. Schlabitz, B. Roden, and D. Wohlleben,Physica C 174, 233 (1991).
D. Wohlleben, G. Michels, and S. Ruppel,Physica C 174, 242 (1991).
J. R. Clem,Physica C 153–155, 50 (1988).
K.-H. Muller,Physica C 159, 717 (1989).
P. Svendlindh, K. Niskanane, P. Norling, P. Nordblad, L. Lundgren, B. Lönnberg, and T. Lundström,Physica C 162–164, 1365 (1989).
W. H. Lee, Y. T. Haung, S. W. Lu, K. Chen, and P. T. Wu,Solid State Commun. 74, 97 (1990).
F. J. Blunt, A. R. Perry, A. M. Campbell, and R. S. Liu,Physica C 175, 539 (1991).
M. F. Tai, H. J. Wang, C. C. Lin, and H. L. Wang, 1992 Mater. Res. Soc. Spring Meeting, Vol. 275.
H. J. Wang and M. F. Tai, unpublished work.
W. Braunisch, N. Knauf, V. Kataev, S. Neuhausen, A. Grütz, A. Kock, B. Roden, D. Khomskii, and D. Wohlleben,Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 1908 (1992).
M. H. Tai, private communication.
S. Jin, H. M. O'Bryan, P. K. Gallagher, T. H. Teifel, R. J. Cava, R. A. Fastnacht, and G. W. Kammlott,Physica C 165, 415 (1990).
D. M. Pooke, R. G. Buckley, M. R. Presland, and J. L. Tallon,Phys. Rev. B 41, 6616 (1990).
S. C. Wu, F. H. Chen, H. S. Koo, M. F. Tai, and T. Y. Tseng, submitted to 5th International Symposium on Superconductivity.
J. Karpinski, E. Kaldis, E. Jilek, S. Rusiechi, and B. Bucher,Nature (London) 336, 660 (1988).
D. E. Morris, J. H. Nickel, J. Y. T. Wei, N. G. Asmer, J. S. Scott, V. M. Scheven, C. T. Hultgren, A. G. Markelz, J. E. Post, D. J. Heaney, D. R. Veblen, and R. M. Hazen,Phys. Rev. B 39, 7347 (1989).
D.-X. Chen, J. Nogues, and K. V. Rao,J. Appl. Phys. 64, 2533 (1988).
V. Skumryev, M. R. Koblischka, and H. Kronmlür,Physica C 184, 332 (1991).
H. Küpfer, I. Apfelstedt, R. Flokiger, C. Keller, R. Meier-Hirmer, B. Runtsch, A. Turowski, U. Wiech, and T. Wolf,Cryogenics 28, 650 (1988).
D.-X. Chen, J. Nogues, and K. V. Rao,Cryogenics 29, 800 (1989).
Y. B. Kim, C. F. Hempstead, and A. R. Strnad,Phys. Rev. Lett. 9, 306 (1962).
J. R. Clem and V. G. Kogan,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 26, 1161 (1987).
M. W. Coffey and J. R. Clem,Phys. Rev. B 45, 9872 (1992).
M. Tinkham,Introduction to Superconductivity (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1975), 113.
J. C. Martinez, J. J. Prejean, J. Karpinski, E. Kaldis, and P. Bordet,Solid State Commum. 75, 315 (1990).
W. C. Lee and D. M. Ginsberg,Phys. Rev. B 45, 7402 (1992).
T. Wada, N. Suzuki, A. Ichinose, Y. Yaegashi, H. Yamauchi, and S. Tanaka,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 29, L915 (1990).
G. Triscone, T. Graf, A. Junod, D. Sanchez, O. Brunner, D. Cattani, and J. Muller,Physica C 168, 40 (1990).
G. L. Carr, S. Perkowitz, and D. B. Tanner, inInfrared and Millimeter Waves, K. J. Button, ed. (Academic Press, London, 1985), Vol. 13, p. 171.
K. Scharnberg and D. Walker,J. Supercond. 3, 269 (1990).
F. London, inSuperfluids (Wiley, New York, 1950), Vol. 1, p. 35.
D. K. Finnemore, R. N. Shelton, J. R. Clem, R. W. McCallum, H. C. Ku, R. E. McCarley, S. C. Chen, P. Klavins, and V. Kogan,Phys. Rev. B 35, 5319 (1987).
F. H. Chen, C. W. Shih, M. F. Tai, and T. Y. Tseng, in preparation.
J. D. Jackson,Classical Electrodynamics (Wiley, New York, 1975), Ch. 5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F.H., Horng, W.C., Hsu, H.T. et al. Paramagnetic Meissner effect of high-temperature granular superconductors: Interpretation by anisotropic and isotropic models. J Supercond 8, 43–56 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00732240
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00732240