Summary
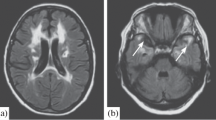
The cerebral changes are described in a woman of 54 who suffered from Binswanger's encephalopathy: there were no signs or symptoms of chronic arterial hypertension. The disease presented as dementia of about 3 years duration. Computed tomography of the brain 2. 5 years before her death showed bilateral widespread hypodense lesions in the cerebral white matter. She died of an asthmatic attack. Autopsy disclosed extensive bilateral degeneration of the central white matter, lacunes and gliosis. Severe obliterative arteriolosclerosis occurred in the meningeal vessels and those supplying the affected parts of the brain. Light microscopy showed that the most severe lesions occurred in the arterioles. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated profound extravasation of plasma proteins chiefly albumin, indicating dysfunction of the blood-brain barrier. Thus, the lesions characteristic of Binswanger's encephalopathy may develop in the absence of chronic arterial hypertension. Additional pathogenic factors, possibly genetic predisposition to vascular injury may play a role in the development of this condition.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Awad IA, Johnson PC, Spetzler RF, Hodak JA (1986) Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. II. Postmortem pathological findings. Stroke 17:1090–1097
Babikian V, Ropper AH (1987) Binswanger's disease: a review. Stroke 18:2–12
Biemond A (1970) On Binswanger's subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy and the possibility of its clinical recognition. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir 73:413–417
Binswanger O (1894) Die Abgrenzung der allgemeinen progressiven Paralyse. Klin Wochenschr 31:1103–1105, 1137–1139, 1180–1186
Caplan LR, Schoene WC (1978) Clinical features of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Neurology 28:1206–1215
Chimowitz MI, Awad IA, Furlan AJ (1989) Periventricular lesions on MRI. Curr Concepts Cerebrovasc Dis Stroke 24:7–12
Feigin I, Popoff N (1963) Neuropathological changes late in cerebral edema: the relationship of trauma, hypertensive disease and Binswanger's encephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:500–511
Ferrer I, Bella R, Serrano MT, Marti E, Guionnet N (1990) Arteriolosclerotic leucoencephalopathy in the elderly and its relation to white matter lesions in Binswanger's disease, multi-infarct encephalopathy and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci 98:37–50
Fisher CM (1989) Binswanger's encephalopathy: a review. J Neurol 236:65–79
Fukatake T, Hattori T, Kita K, Hirayama K (1985) Familial juvenile encephalopathy (Binswanger type) with alopecia and lumbago-A syndrome. Clin Neurol 25:949–955
Goto K, Ishii N, Fukasawa H (1981) Diffuse white matter disease in the geriatric population. Neuroradiology 141:687–695
Hachinski VC, Potter P, Merskey H (1987) Leukoaraiosis. Arch Neurol 44:21–23
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotinperoxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedures. H Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Huang KW, Wu L, Luo Y (1985) Binswanger's disease: progressive subcortical encephalopathy or multi-infarct dementia. Can J Neurol Sci 12:88–94
Jellinger K, Neumayer E (1964) Progressive subcorticale vasculäre Encephalopathie Binswanger, eine klinische-neuropathologische Studie. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 205:523–554
Kinkel WR, Jacobs L, Polachini I, Bates V, Heffner RR (1965) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Computed tomographic, nuclear magnetic resonance and clinical correlations. Arch Neurol 42:951–959
Kondo S, Ogasawara N, Ito T, Tsunoda T (1970) Über einen autoptischen Fall von der im ZNS lokalisierten nekrotisierenden Angitis (Periarteritis nodosa?). Adv Neurol Sci 114:274–284 (in Japanese)
Liu HM (1988) Extravasation of plasma proteins in brain trauma. Forensic Sci Int 38:285–295
Liu HM (1989) Immunohistochemical localization of intracellular plasma proteins in the human central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 78:16–21
Loizou LA, Kendall BE, Marshall J (1981) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: a clinical and radiological investigation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 44:294–304.
Loizou LA, Jefferson JM, Thomas Smith W (1982) Subcortical arterioslcerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's type) and cortical infarcts in a young normotensive patient. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:409–417
Lotz PR, Ballinger WE Jr, Quisling RG (1986) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: CT spectrum and pathological correlation. Am J Neuradiol 7:817–822
Maeda S, Nakayama H, Isaka K, Aihara Y, Nemoto S (1976) Familial unusual encephalopathy of Binswanger's type without hypertension. Folia Psychiat Neurol Jpn 30:164–177
Nemoto S (1966) Einige Beiträge zur Encephalitis subcorticalis chronica progressiva (Binswanger). Festschrift zum Zurücktritt von Professor Toshimi Ishibashi. Sendai (in Japanese), pp 51–67
Neumann MA (1947) Chronic progressive subcortical encephalopathy. J Gerontol 2:57–64
Olszewski J (1962) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: review of the literature on the so-called Binswanger's disease and presentation of two cases. World Neurol 3:359–375
Pellisser JF, Poncet M (1989) Binswanger's encephalopathy. Handb Clin Neurol 10:221–233
[Reference deleted]
Poppe W, Tennstedt A (1963) Ein Beitrag zur Encephalopathia subcorticalis Binswanger. Psychiatr Neurol (Basel) 145:27–35
Prencipe M, Marini C (1989) Leuko-Araiosis: definition and clinical correlates—An overview. Eur Neurol 29 [Suppl 2]: 27–29
Pullicino P, Eskin T, Ketonenn L (1983) Prevalence of Binswanger's disease. Lancet I:939
Revesz T, Hawkins CP, du Boulay EPGH, Barnard RO, McDonald WI (1989) Pathological findings correlated with magentic resonance imaging in subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:1337–1344
Salahuddin TS (1991) Consequences of opening the bloodbrain-barrier by carotid infusion of hyperosmolar solutions. Acta Univ Ups 297:1–44
Salahuddin TS, Kalimo H, Johansson BB, Olsson Y (1988) Observations on exudation of fibronectin, fibrinogen and albumin in the brain after carotid infusion of hyperosmolar solutions: an immunohistochemical study in the rat indicating long-lasting changes in the brain microenvironment and multifocal nerve cell injuries. Acta Neuropathol 76:1–10
Schneider R, Ringelstein EB, Zeumer H, Kiesewetter H, Jung F (1987) The role of plasma hyperviscosity in subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). J Neurol 234:67–73
Sokrab T-E O, Johansson BB, Kalimo H, Olsson Y (1988) A transient hypertensive opening of the blood-brain-barrier can lead to brain damage: extravasation of serum proteins and cellular changes in rats subjected to aortic compression. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:557–565
Sourander P, Wålinder J (1977) Hereditary multi-infarct dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 39:247–254
Tanaka M, Ikuta F, Oyake Y (1969) An autopsy case of chronic progressive subcortical encephalopathy without hypertension. Clin Neurol 9:398–405 (in Japanese)
Torack RM, Morris JC (1989) Vascular glycosaminoglycans in periventricular leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 78:492–496
Valentine AR, Moseley IF, Kendall BE (1980) White matter abnormality in cerebral atrophy: clinicoradiological correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:139–142
Yamori Y (1989) Predictive and preventive pathology of cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pathol Jpn 39:683–705
Zeumer H, Hacke W, Kollmann HL, Ringelstein EB (1982) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Exp Brain Res 5 [Suppl]:272–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council, Project No 12X-03020 and 1987 Års Stiftelse för Strokeforskning
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, K.C., Lundberg, P.O., Lilja, A. et al. Binswanger's disease in the absence of chronic arterial hypertension. Acta Neuropathol 83, 434–439 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713538
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713538