Summary
-
1.
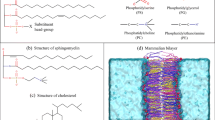
Gangliosides are neuraminic acid-containing glycolipids preferently localized in nervous membranes and showing physicochemical peculiarities, e.g., drastically changing amphiphilic properties by Ca2+ binding. On account of this they are favorite compounds to act as modulators of membraneous organization and functions during synaptic transmission. Lipid monolayers are suitable experimental systems for the study of the surface behavior of amphipatic molecules and therefore are useful to interpret membraneous organization.
-
2.
The surface pressure/area isotherms of monolayers of different individual gangliosides (GM1, GD1a, GD1b, GT1b) of an artificial reconstituted and a natural ganglioside mixture from bovine brain and of ganglioside mixtures from different brain parts of summer- and winter-adapted dsungarian hamsters were compared at three temperatures (11, 20, and 37°C) with egg phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylserine (PS) monolayers. The monolayers were formed in a Teflon trough on a triethanolamine/HCl-buffered (pH 7.4) subphase, in some cases containing different amounts of CaCl2.
-
3.
The surface pressure/area isotherms of ganglioside monolayers, in contrast to phospholipids, generally showed slowly rising slopes, with transitions from the liquidexpanded to the liquid-condensed state at a surface pressure of 20–30 mN/m. Ganglioside monolayers, in particular from GD1a or GT1b versus GD1b or from mixtures from summer- versus winter-adapted hamster brain, were differently affected by temperature and/or by Ca2+. PS monolayers were slightly condensed only by Ca2+. PC monolayers, however, were influenced neither by temperature nor by Ca2+. In mixed monolayers of the unpolar natural lipid cholesterol (Ch) and the disialoganglioside GD1a, intermolecular interactions were indicated.
-
4.
Ganglioside monolayers, in contrast to phospholipids, were shown to be easily modulated by temperature and/or Ca2+ ions, thus enabling gangliosides to act as possible membrane modulators, e.g., during synaptic transmission. In particular, the differences concerning the influences of temperature and/or Ca2+ on the surface behavior of ganglioside mixtures from the brain of summer- compared with winteradapted hamsters are correlated with other physiologically relevant data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach, D., and Sela, B. -A. (1980). A differential scanning calorimeter study of the interactions of gangliosides with peanut lectin, serotonin and daunomycin.Biochim Biophys. Acta 506186–191.
Bach, D., Miller, J. R., and Sela, B. -A. (1982). Calorimetric studies on various gangliosides and ganglioside-lipid interactions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 686233–239.
Baret, J. F., Bois, A. G., Dupin, J. J., and Firpo, J. L. (1982). The liquid-expanded and the liquid condensed phases in amphiphile monolayers are separated by a second-order phase transition.J. Colloid Interface Sci. 86370–376.
Behr, J. -P., and Lehn, J. -M. (1973). The binding of divalent cations by purified gangliosides.FEBS Lett. 31297–300.
Bertoli, E., Masserini, M., Sonnino, S. Ghidoni, R., Cestaro, B., and Tettamanti, G. (1981). Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on the fluidity and surface dynamics of egg phosphatidyl choline vesicles containing gangliosides.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 467196–202.
Breckenridge, W. C., Gombos, G., and Morgan, J. G. (1972). The lipid composition of adult rat brain synaptosomal plasma membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 226695–707.
Bunow, M. R., and Bunow, B. (1979). Phase behaviour of ganglioside-lecithin mixtures. Relation of dispersions of gangliosides in membranes.Biophys. J. 27325–337.
Chaudhury, M. K., and Ohki, S. (1981). Correlation between membrane expansion and temperature induced membrane fusion.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 642365–374.
Conrad, M. J., and Singer, S. J. (1979). Evidence for a large internal pressure in biological membranes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 765202–5206.
Corti, M., Degiorgio, V., Ghidoni, R., and Sonnino, S. (1982). Micellar properties of gangliosides. InSolution Behaviour of Surfactants, Vol. 1 (Mittal, K. L., and Fendler, E. J., Eds.), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 573–594.
Cossins, A. R. (1977). Adaptation of biological membranes to temperature. The effect of temperature acclimation of goldfish upon the viscosity of synaptosomal membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 470395–411.
Curatolo, W., Small, D. M., and Shipley, G. G. (1977). Phase behaviour and structural characteristics of hydrated bovine brain gangliosides.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 46811–20.
Delmelle, M., Dufrane, S. P., Brasseur, R., and Ruysschaert, J. M. (1980). Clustering of gangliosides in phospholipid bilayers.FEBS Lett. 12111–14.
Feinstein, M. B., Fernandez, S. M., and Shaàfi, R. J. (1975). Fluidity of natural membranes and phosphatidylserine and ganglioside dispersions. Effects of local anesthetics, cholesterol and protein.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 413354–370.
Felgner, P. L., Thompson, T. E., Barenholz, Y., and Lichtenberg, D. (1983). Kinetics of transfer of gangliosides from their micelles to dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles.Biochemistry 221670–1674.
Gaines, G. L. (1966). Insoluble monolayers at liquid-gas interfaces. InInterscience Monographs on Physical Chemistry (Prigogine, I., Ed.), Interscience, New York, pp. 281–300.
Ganesan, M. G., Schwinke, D. L., and Weiner, N. (1982). Effect of Ca2+ on thermotropic properties of saturated phosphatidylcholine liposomes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 686245–248.
Gershfeld, N. L. (1982). The liquid condensed/liquid expanded transition in lipid films: A critical analysis of the film balance experiment.J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 8528–40.
Grüniger, H., Möbius, D., and Meyer, H. (1983). Enhanced light reflection by dye monolayers at the air-water interface.J. Chem. Phys. 793710–3716.
Harris, P. L., and Thornton, E. R. (1978). Carbon-13 and proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of gangliosides.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1006738–6745.
Hayashi, K., and Katagiri, A. (1974). Studies on the interaction between gangliosides, protein and divalent cations.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 337107–117.
Hayashi, K., Mühleisen, M., Probst, W., and Rahmann, H. (1984). Binding of Ca2+ to phosphoinositols, phosphatidylserines and gangliosides.Chem. Phys. Lipids 34317–322.
Hilbig, R., Rösner, H., Merz, G., and Segler-Stahl, K. (1982). Developmental profiles of gangliosides in mouse and rat cerebral cortex.Roux Arch. Dev. Biol. 191281–284.
Hinz, H. -J., Körner, O., and Nicolau, C. (1981). Influence of gangliosides GM1 and GD1a on structural and thermotropic properties of sonicated small 1,2-dipalmitoyl-L-α-phosphatidylcholine vesicles.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 643 557–571.
Hui, S. W., Boni, L. T., Stewart, T. P., and Isac, T. (1983). Identification of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylcholine in calcium-induced phase separated domains.Biochemistry 223511–3516.
Iwamori, M., and Nagai, Y. (1978). A new chromatographic approach to the resolution of individual gangliosides.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 528257–267.
Jacques, L. W., Brown, E. B., Barret, J. M., Brey, W. S., and Weltner, W. (1977). Sialic acid. A calcium-binding carbohydrate.J. Biol. Chem. 2524533–4539.
Jacques, L. W., Riesco, B. F., and Weltner, W. (1980). N.M.R. spectroscopy and calcium binding of sialic acids: N-Glycolyl-neuraminic acid and periodate-oxidized N-acetyl neuraminic acid.Carbohydrate Res. 8321–32.
Krnjevic, K. (1974). Chemical nature of synaptic transmission in vertebrates.Physiol. Rev. 54418–507.
Kuhn, H., Möbius, D., and Bücher, H. (1972). Spectroscopy of monolayer assemblies. InPhysical Methods of Chemistry (Weissberger, A., and Rossiter, B., Eds.), Wiley, New York, Vol. 1, Pt. 3B, pp. 577–702.
Lee, P. M., and Grant, C. W. M. (1980). Ganglioside headgroup disorder as a sequel to lectin binding.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 951299–1305.
Lee, P. M., Ketis, N. V., Barber, K. R., and Grant, C. W. M. (1980). Ganglioside headgroup dynamics.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 601302–314.
Lichtenberg, D., and Schmidt, C. F. (1981). Molecular packing and stability in the gel phase of curved phosphatidyl choline vesicles.Lipids 16555–557.
Lundberg, B. (1982). A surface film study of the lateral packing of phosphadityl choline and cholesterol.Chem. Phys. Lipids 3123–32.
Maggio, B., Cumar, F. A., and Caputto, R. (1978a). Surface behaviour of gangliosides and related glycosphingolipids.Biochem. J. 171559–565.
Maggio, B., Cumar, F. A., and Caputto, R. (1978b). Interactions of gangliosides with phospholipids and glycosphingolipids in mixed monolayers.Biochem. J. 1751113–1118.
Maggio, B., Cumar, F. A., and Caputto, R. (1980). Configuration and interactions of the polar head group in gangliosides.Biochem. J. 189435–440.
Maggio, B., Cumar, F. A., and Caputto, R. (1981). Molecular behaviour of glycosphingolipids in interfaces. Possible participation in some properties of nerve membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 65069–87.
Morgan, J. G., Tettamanti, G., and Gombos, G. (1976). Biochemical evidence on the role of gangliosides in nerve endings.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 71137–150.
Mühleisen, M., Probst, W., Wiegandt, H., and Rahmann, H. (1979). In vitro studies on the influence of cations, neurotransmitters and tubocurarine on calcium-ganglioside-interactions.Life Sci. 25791–796.
Mühleisen, M., Probst, W., Hagashi, K., and Rahmann, H. (1983). Calcium binding to liposomes composed of negatively charged lipid moieties.Jap. J. Exp. Med. 53103–107.
Nir, S., and Andersen, M. (1977). Van der Waals interactions between cell surfaces.J. Membr. Biol. 311–18.
Papahadjopoulos, D. (1968). Surface properties of acide phospholipids: Interaction of monolayers and hydrated liquid crystals with uni- and bi-valent metal ions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 163240–254.
Papahadjopoulos, D., and Poste, G. (1975). Calcium induced phase separation and fusion in phospholipid membranes.Biophys. J. 15945–948.
Portis, A. R., Newton, C., Pangborn, W., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1979). Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: Evidence for an intermembrane Ca2+-phospholipid complex, synergism with Mg2+, and inhibition by spectrin.Biochemistry 18780–790.
Probst, W., and Rahmann, H. (1980). Influence of temperature changes on the ability of gangliosides to complex with Ca2+.J. Therm. Biol. 5243–247.
Probst, W., Rösner, H., Wiegandt, H., and Rahmann, H. (1979). Das Komplexationsvermögen von Gangliosiden für Ca2+. I. Einfluβ mono- und divalenter Kationen sowie von Acetylcholin.Hoppe-Seyler Z. Physiol. Chem. 360979–986.
Riquelme, G., Jaimovich, E., Lingsch, C., and Behn, C. (1982). Lipid monolayer expansion by calcium chlorotetracyline at the air/water interface and, as inferred from cell shape changes, in the human erythrocyte membrane.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 689219–229.
Rahmann, H. (1976). Possible functional role of gangliosides. In Ganglioside function: Biochemical and pharmacological implications.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 71151–161.
Rahmann, H. (1983a). Possible functional role of brain gangliosides in adaptive neuronal processes. InNeural Transmission, Learning and Memory (Caputto, R., and Marsau, C. A., Eds.), Raven Press, New York, pp. 159–177.
Rahmann, H. (1983b). Functional implication of gangliosides in synaptic transmission. Neurochem. Int.5539–547.
Rahmann, H., Rösner, H., and Breer, H. (1976). A functional model of sialoglycomacromolecules in synaptic transmission and memory formation.J. Theor. Biol. 57231–237.
Rahmann, H., Probst, W., and Mühleisen, M. (1982). Gangliosides and synaptic transmission.Jap. J. Exp. Med. 52275–286.
Reaves, T. A., and Hayward, J. N. (1979). Hypothalamic and extra hypothalamic thermoregulatory centers. InBody Temperature (Lomax, P., and Schönbaum, E., Eds.), Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 39–70.
Reckhaus, W., and Rahmann, H. (1983). Long-term thermal adaptation of evoked potentials in fish brain.J. Therm. Biol. 8456–457.
Rösner, H. (1980). A new thin-layer chromatographic approach for separation of multisialogangliosides. Novel gangliosides fractions in the embryonic chicken brain.Anal. Biochem. 109437–442.
Seimiya, T., Aschida, M., Muramutsu, T., Hara, I., and Hayashi, M. (1978a). Temperature dependent ionic structure of phospholipid monolayers.Chem. Phys. Lipids 22221–226.
Seimiya, T., Ashida, M., Hayashi, M., Muramutsu, T., and Hara I. (1978b). Hydrogen bond among the ionic groups of ampholytic phospholipid.Chem. Phys. Lipids 2169–76.
Sester, U., Probst, W., and Rahmann H. (1984). Einfluβ unterschiedlicher Akklimationstemperaturen auf die Ultrastruktur neuronaler Synapsen von Buntbarschen (Tilapia mariae; Cichlidae, Teleostei).J. Hirnforsch. (in press).
Sillerud, L. O., Prestegard, J. H., Yu, R. K., Schafer, D. E., and Königsberg, W. H. (1978). Assignment of the (13) C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of aqueous ganglioside GM1 micelles.Biochemistry 172619–2628.
Sillerud, L. O., Schafer, D. E., Yu, R. K., and Königsberg, W. O. (1979). Calorimetric properties of mixtures of ganglioside GM1 and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine.J. Biol. Chem. 25410876–10880.
Sharom, F. J., and Grant, C. W. M. (1977). A ganglioside spin label: ganglioside head group interactions.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 741039–1045.
Sharom, F. J., and Grant, C. W. M. (1978). A model for ganglioside behaviour in cell membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 507280–293.
Sonnino, S., Ghidoni, R., Tettamanti, G., Marx, J., Hilbig, R., and Rahmann, H. (1984). Nervous system ganglioside composition of normothermic and hibernating dormice (Glis glis).Neurochem. Int. (in press).
Svennerholm, L. (1963). Chromatographic separation of human brain gangliosides.J. Neurochem. 1055–61.
Svennerholm, L., and Fredman, P. (1980). A procedure for the quantitative isolation of brain gangliosides.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 61797–109.
Träuble, H. (1977). Membrane electrostatics. InStructure of Biological Membranes (Abrahamsson, S., and Pascher, I., Eds.), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 509–550.
Uchida, T., Nagai, Y., Kawasaki, Y., and Wakayama, N. (1981). Fluorospectroscopic studies of various ganglioside and ganglioside lecithin dispersions. Steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence measurements with 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene.Biochemistry 20162–169.
Watanabe, K., Hakomori, S., Powell, M. E., and Yokota, M. (1980). The amphipathic membrane proteins associated with gangliosides. The Paul-Bunnell antigen is one of the gangliophilic proteins.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 92638–646.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Probst, W., Möbius, D. & Rahmann, H. Modulatory effects of different temperatures and Ca2+ concentrations on gangliosides and phospholipids in monolayers at air/water interfaces and their possible functional role. Cell Mol Neurobiol 4, 157–176 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711002
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711002