Summary
-
1.
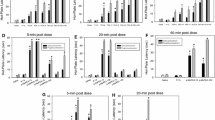
Treating rat brain homogenatesin vitro with oxymorphazone, the hydrazone derivative of oxymorphone, selectively inhibited in a long-acting manner the highaffinity (mu1) binding of a number of3H-opioids. This inhibition was not affected by extensive wash procedures which did effectively reverse classical opiates such as morphine and naloxone.
-
2.
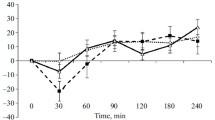
A similar, persistent inhibition of binding was observed followingin vivo administration of the drug. Both systemically and intracerebroventicularly, oxymorphazone produced a dose-dependent analgesia.
-
3.
Acutely, oxymorphazone (ED50, 0.6 mg/kg, sc) was approximately half as potent as oxymorphone (ED50, 0.3 mg/kg, sc) in the tail-flick assay.
-
4.
Administered at their ED50 doses, both compounds had the same durations of action. As the doses of drug were increased, however, the time course of oxymorphazone's analgesia became far more prolonged than that of oxymorphone.
-
5.
Following the administration of oxymorphazone (100 mg/kg), over 50% of the mice remained analgesic for greater than 24 hr, as opposed to none of the mice given oxymorphone (100 mg/kg).
-
6.
Oxymorphazone was far more potent intraventricularly (icv) than systemically. Fifty percent of the mice remained analgesic for greater than 20 hr following the injection of 40µg/mouse (icv), whereas no mice remained analgesic after 20 hr following doses of oxymorphone as high as 50µg/mouse (icv).
-
7.
These long-lasting analgesic actions of oxymorphazone could not be easily explained on pharmacokinetic grounds. Repeated administration of oxymorphazone daily for 3 days resulted in significant tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, K. J., and Cuatrecasas, P. (1979). Multiple opioid receptors.J. Biol. Chem. 2542610–2618.
Childers, S. R., and Pasternak, G. W. (1982). Naloxazone, a novel opiate antagonist: Irreversible blockade of rat brain opiate in vitro.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 293–103.
D'Amour, F. E., and Smith, D. R. (1941). A method for determining loss of pain sensation.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 7274–79.
Hahn, E. F., Carroll-Buatti, M., and Pasternak, G. W. (1982). Irreversible opiate agonists and antagonists. The 14-hydroxydihydromorphineone azines.J. Neurosci. 2572–576.
Hazum, E., Chang, K. J., Cuatrecasas, P., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Naloxazone irreversibly inhibits the high affinity binding of [125I]D-ala2-D-leu5-enkeph-alin.Life Sci. 282973–2979.
Ling, G. S. F., and Pasternak, G. W. (1983). Spinal and supraspinal opioid analgesia in the mouse: The role of subpopulations of opioid binding sites.Brain Res. 271152–156.
Ling, G. S. F., Spiegel, K., Nishimura, S., and Pasternak, G. W. (1983). Dissociation of morphine's analgesic and respiratory depressant actions.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 86487–488.
Lord, J. H., Waterfield, A. A., Hughes, J., and Kosterlitz, H. W. (1976). Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors.Nature 267495–499.
Martin, W. R., Eades, C. G., Thompson, J. A., Huppler, R. E., and Gilbert, P. (1976). The effects of morphine and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent and morphine dependent chronic spinal dog.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 197517–532.
Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Opiate, enkephalin and endorphin analgesia: Relations to a single subpopulation of opiate receptors.Neurology 311311–1315.
Pasternak, G. W., and Hahn, E. F. (1980). Long-acting opiate agonists and antagonists: 14-Hydroxydihy-dromorphinone hydrazones.J. Med. Chem. 23674–677.
Pasternak, G. W., and Snyder, S. H. (1975). Identification of novel high affinity opiate receptor binding in rat brain.Nature 253563–565.
Pasternak, G. W., Wilson, H. A., and Snyder, S. H. (1975). Differential effects of protein-modifying reagents on receptor binding of opiate agonists and antagonists.Mol. Pharmacol. 11478–484.
Pasternak, G. W., Childers, R., and Snyder, S. H. (1980a). Naloxazone, a long-acting opiate antagonist: Effects an intact animals and on opiate receptor binding in vitro.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 214455–462.
Pasternak, G. W., Childers, S. R., and Snyder, S. H. (1980b). Opiate analgesia: Evidence for mediation by a subpopulation of opiate receptors.Science 208514–516.
Pasternak, G. W., Carroll-Buatti, C., and Spiegel, K. (1981). The binding and analgesic properties of a sigma opiate, SKF10,047.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 219192–198.
Spiegel, K., Kourides, I., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Prolactin and growth hormone release by morphine in the rat: Different receptor mechanisms.Science 217745–747.
Wolozin, B. L., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 786181–6185.
Wood, P. L., and Pasternak, G. W. (1984). Specific mu2 opioid isoreceptor regulation of nigrostriatal neurons: In vivo evidence with naloxonazine.Neurosci. Lett. (in press).
Wood, P. L., Richard, J. W., and Thakur, M. (1982). Mu opiate isoreceptors: Differentiation with kappa agonists.Life Sci. 312313–2317.
Zhang, A. Z., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981a). Opiates and enkephalins: A common binding site mediates their analgesic actions in rats.Life Sci. 29843–851.
Zhang, A. Z., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981b). Ontogeny of opioid pharmacology and receptors: High and low affinity site differences.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 7329–40.
Zhang, A. Z., Chang, J. K., and Pasternak, G. W. (1981). The actions of naloxazone on the binding and analgesic properties of morphiceptin (NH2Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-CONH2), a selective mu receptor ligand.Life Sci. 282829–2836.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, G.S.F., Galetta, S. & Pasternak, G.W. Oxymorphazone: A long-acting opiate analgesic. Cell Mol Neurobiol 4, 1–13 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710938
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710938