Abstract
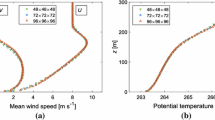
We compare the results of a local and a nonlocal scheme for vertical diffusion in the atmospheric boundary layer with observations at the 200 m tower at Cabauw. This is done for a 12 h period during daytime on 31 May 1978, which is characterised by strong insolation, clear skies, moderately strong winds and weak advection. The local diffusion scheme uses an eddy diffusivity determined independently at each point along the vertical based on local vertical gradients of wind and virtual potential temperature, similar to the usual approach in atmospheric models. The nonlocal scheme determines an eddy diffusivity profile based on a diagnosed boundary-layer height and a turbulent velocity scale. It also incorporates nonlocal (vertical) transport effects for heat and moisture. The boundary-layer diffusion schemes are forced with the locally observed fluxes for heat and moisture. The outputs of the scheme are compared with the observed mean structure along the Cabauw tower, and the radiosonde profile at a nearby location (De Bilt). Overall, the nonlocal scheme transports moisture away from the surface more rapidly than the local scheme, and deposits the moisture at higher levels. The local scheme tends to saturate the lowest model levels unrealistically in comparison with the observations. We also compare the outputs of the two diffusion schemes with the results of a transilient model simulation. Subsequently, we study the impact on the model behaviour by varying important parameters in both diffusion schemes and we investigate the sensitivity to uncertainty in the environmental conditions. Finally, we study the interaction of the diffusion schemes with a simple surface flux scheme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beljaars, A. C. M.: 1991, ‘Numerical Schemes for Parametrizations’,Proceedings of the ECMWF Seminar from 9–13 Sept. 1991, on: Numerical Methods in Atmospheric Models, Vol. II, ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, U.K., pp. 1–42.
Beljaars, A. C. M. and Holtslag, A. A. M.: 1991, ‘Flux Parameterization Over Land Surfaces for Atmospheric Models’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 30, 327–341.
Beljaars, A. C. M. and Betts, A. K.: 1992, ‘Vandations of the Boundary Layer Scheme in the ECMWF Model’,Proceedings of the ECMWF Seminar from 7–11 Sept 1992, on: Validation of Models over Europe, Vol. II, ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, U.K.
Betts, A. K., Ball, J. H., and Beljaars, A. C. M.: 1993, ‘Comparison Between the Land Surface Response of the European Centre Model and the FIFE-1987 Data’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 119, 975–1001.
Blackadar, A. K.: 1962, ‘The Vertical Distribution of Wind and Turbulent Exchange in Neutral Atmosphere’,J. Geophys. Res. 67, 3095–3103.
Bruin, H. A. R. de, and Holtslag, A. A. M.: 1982, ‘A Simple Parameterization of the Surface Fluxes of Sensible and Latent Heat During Daytime Compared with the Penman-Monteith Concept’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 21, 1610–1621.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1972, ‘Theoretical Expression for the Countergradient Vertical Heat Flux’,J. Geophys. Res. 77, 5900–5904.
Driedonks, A. G. M.: 1982, ‘Models and Observations of the Growth of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meterol. 23, 283–306.
Dyer, A. J.: 1974, ‘A Review of Flux-Profile Relationships’,Boundary-Layer Meteor. 7, 363–372.
Garratt, J. R.: 1993, ‘Sensitivity of Climate Simulations to Land-Surface and Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Treatments—A Review’,J. Climate 6, 419–449.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Nieuwstadt, F. T. M.: 1986, ‘Scaling the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 36, 201–209.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Beljaars, A. C. M.: 1989, ‘Surface Flux Parameterization Schemes: Developments and Experiences at KNMI’,Proceedings of the ECMWF Workshop on Parameterization of Fluxes Over Land Surface, ECMWF Reading UK, pp. 121–147. (Also available from KNMI as Sci. Rep. 88-06, De Bilt NL, 27 p.)
Holtslag, A. A. M., de Bruijn, E. I. F., and Pan, H.-L.: 1990, ‘A High Resolution Air Mass Transformation Model for Short-Range Weather Forecasting’,Mon. Wea. Rev. 118, 1561–1575.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Moeng, C.-H.: 1991, ‘Eddy Diffusivity and Countergradient Transport in the Convective Atmospheric Boundary Layer’,J. Atmos. Sci. 48, 1690–1698.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Boville, B. A.: 1993, ‘Local versus Nonlocal Boundary-Layer Diffusion in a Global Climate Model’,J. Climate 6, 1825–1842.
Holzworth, G. C.: 1964, ‘Estimates of Mean Maximum Mixing Depths in the Contiguous United States’,Mon. Wea. Rev. 92, 235–242.
Jarvis, P. G.: 1976, ‘The Interpretation of Leaf Water Potential and Stomatal Conductance Found in Canopies in the Field’,Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London B 273, 593–610.
Louis, J. F.: 1979, ‘A Parametric Model of Vertical Eddy Fluxes in the Atmosphere’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 187–202.
Louis, J. F., Tiedtke, M., and Geleyn, J. F.: 1982, ‘A Short History of the PBL Parameterization at ECMWF’,Proceedings of the ECMWF Workshop on Boundary-Layer Parameterization, ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, U.K., pp. 59–79.
Monna, W. A. A. and van de Vliet, J. G.: 1987, ‘Facilities for Research and Weather Observations on the 213 m Tower at Cabauw and at Remote Locations’,Scientific Report 87-5, KNMI, De Bilt. NL.
Simmons, A. J. and Strufing, R.: 1983, ‘Numerical Forecasts of Stratospheric Warming Events Using a Model with a Hybrid Vertical Coordinate’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 109, 81–111.
Stull, R. B.: 1984, ‘Transilient Turbulence Theory, Part I: The Concept of Eddy Mixing Across Finite Distances’,J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 3351–3367.
Stull, R. B. and Driedonks, A. G. M.: 1987, ‘Applications of the Transilient Turbulence Parameterization to Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Simulations’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 40, 209–239.
Troen, I. and Mahrt, L.: 1986, ‘A Simple Model of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer; Sensitivity to Surface Evaporation’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 129–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holtslag, A.A.M., Van Meijgaard, E. & De Rooy, W.C. A comparison of boundary layer diffusion schemes in unstable conditions over land. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 76, 69–95 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710891
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710891