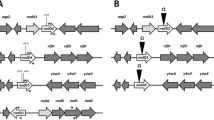
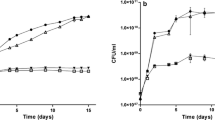
Abstract
Hybridization analysis using theRhizobium meliloti nitrogen fixation genefixN as a probe revealed the presence of a homologous DNA region in the phytopathogenic bacteriumAgrobacterium tumefaciens. Hybridization signals were also detected with total DNAs ofRhizobium leguminosarum bv.phaseoli, Rhodobacter capsulatus andEscherichia coli, but not those ofXanthomonas campestris pv.campestris andPseudomonas putida. The hybridizing fragment fromA. tumefaciens was cloned and sequenced. The predicted gene product of one of the two open reading frames identified on the sequenced fragment shows homology to FixN of differentRhizobiaceae as well as a low but significant similarity to subunit I of heme copper oxidases from various bacteria. The presence of five strictly conserved histidine residues previously implicated in forming ligands to heme and CuB in oxidases and the predicted membrane topology provide evidence that theA. tumefaciens fixN-like gene product is a component of the heme copper oxidase superfamily. The incomplete open reading frame starting only 8 nucleotides downstream of thefixN-like gene exhibits homology toRhizobium fixO. Using anuidA (GUS) gene fusion it could be shown that theA. tumefaciens fixN-like gene is preferentially expressed under microaerobic conditions. Expression of theuidA fusion is abolished inR. meliloti fixJ andfixK mutants, indicating that an Fnr-like protein is involved in transcriptional regulation of thefixN-like gene in A.tumefaciens. The presence of an upstream DNA sequence motif identical to the Fnr-consensus binding site (anaerobox) further supports this hypothesis.A. tumefaciens mutated in thefixN-like gene shows decreased TMPD-specific oxidase activity under microaerobic conditions, indicating that thefixN-like gene or operon codes for proteins involved in respiration under reduced oxygen availability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller EW, Myers, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Arnold W, Puhler A (1988) A family of high-copy-number plasmid vectors with end-label sites for rapid nucleotide sequencing. Gene 70:171–170
Batut J, Daveran-Mingot ML, David M, Jacobs J, Garnerone AM, Kahn D (1989)fixK, a gene homologous withfnr and crp fromEscherichia coli regulates nitrogen fixation genes both positively and negatively inRhizobium meliloti. EMBO J 8:1279–1286
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer inRhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Binns AN, Thomashow MF (1988) Cell biology ofAgrobacterium infection and transformation of plants. Annu Rev Microbiol 42:575–606
Bott M, Bollinger M, Hennecke H (1990) Genetic analysis of the cytochromec-aa 3 branch of theBradyrhizobium japonicum respiratory chain. Mol Microbiol 4:2147–2157
Chepuri V, Lemieux L, Au DCT, Gennis RB (1990) The sequence of thecyo operon indicates substantial structural similarities between the cytochromeo ubiquinol oxidase ofEscherichia coli and theaa 3-type family of cytochromec oxidases. J Biol Chem 265:11185–11192
Currie JA (1961) Gaseous diffusion in the aeration of aggregated soils. Soil Sci 92:40–45
David M, Daveran ML, Batut J, Dedieu A, Domergue O, Ghai J, Hertig C, Boistard P, Kahn D (1988) Cascade regulation ofnif gene expression inRhizobium meliloti. Cell 54:671–683
Garcia-Horsman JA, Barquera B, Rumbley J, Ma J, Gennis RB (1994) The superfamily of heme-copper respiratory oxidases. J Bacteriol 176:5587–5600
Graham PH (1964) The application of computer techniques to the taxonomy of the root-nodule bacteria of legumes. J Gen Microbiol 35:511–518
Hirsch AN, Wilson KJ, Jones JDG, Bang M, Walker VV, Ausubel FM (1984)Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes allowAgrobacterium tumefaciens andEscherichia coli to form pseudonodules on alfalfa. J Bacteriol 158:1133–1143
Hötte B, Rath-Arnold IR, Puhler A, Simon R (1990) Cloning and analysis of a 35.3-kilobase DNA region involved in exopolysaccharide production byXanthomonas campestris pv.campestris. J Bacteriol 172:2804–2807
Hooykaas PJJ, Klapwijk PM, Nuti MP, Schilperoort RA, Rörsch A (1977) Transfer of theAgrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid to avirulent agrobacteria and toRhizobium ex planta. J Gen Microbiol 98:477–484
Hooykaas PJJ, van Brussel AAN, den Dulk-Ras H, van Slogteren GMS, Schilperoort RA (1981) Sym plasmid ofRhizobium trifolii expressed in different rhizobial species andAgrobacterium tumefaciens. Nature 291:351–353
Hynes MF, Simon R, Pühler A (1985) The development of plasmid-free strains ofAgrobacterium tumefaciens by using incompatibility with aRhizobium meliloti plasmid to eliminate pAtC58. Plasmid 13:99–105
Hynes MF, Quandt J, O'Connell MP, Puhler A (1989) Direct selection for curing and deletion ofRhizobium plasmids using transposons carrying theBacillus subtilis sacB gene. Gene 78:111–120
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Reporter 5:387–405
Jones CW (1988) In: Anthony C (ed) Bacterial energy transduction, Academic Press, London, pp 1–82
Kahn D, Batut J, Daveran ML, Fourment J (1993) Structure and regulation of thefixNOQP operon fromRhizobium meliloti. In: Palacios R, Mora J, Newton WE (eds) New horizons in nitrogen fixation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, p 474
Kersters K, De Ley J (1984) GenusIII.Agrobacterium Conn 1942. In: Krieg NR (ed) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Williams Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 244-254
Klipp W, Reiländer H, Schlüter A, Krey R, Puhler A (1989) TheRhizobium meliloti fdxN gene encoding a ferredoxin-like protein is necessary for nitrogen fixation and is cotranscribed withnifA andnifB. Mol Gen Genet 216:293–302
Kondorosi A, Kondorosi E, Pankhurst CE, Broughton WJ, Banfalvi Z (1982) Mobilization of aRhizobium meliloti megaplasmid carrying nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes into other rhizobia andAgrobacterium. Mol Gen Genet 188:433–439
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Lemieux LJ, Calhoun MW, Thomas JW, Ingledew WJ, Gennis RB (1992) Determination of the ligands of the low spin heme of the Cytochrome o Ubiquinol Oxidase complex using site-directed mutagnesis. J Biol Chem 267:2105–2113
Lübben M, Kolmerer B, Saraste M (1992) An archaebacterial terminal oxidase combines core structures of two mitochondrial repiratory complexes. EMBO J 11:805–812
Mandon K, Kaminski PA, Elmerich C (1994) Functional analysis of thefixNOQP region ofAzorhizobium caulinodans. J Bacteriol 176:2560–2568
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Minagawa J, Mogi T, Gennis RB, Anraku Y (1992) Identification of heme and copper ligands in subunit I of the Cytochrome bo complex inEscherichia coli. J Biol Chem 267:2096–2104
Nester EW, Gordon MP, Amasino RM, Yanofsky MF (1984) Crown gall: a molecular and physiological analysis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35:387–413
Noel KD, Sanchez A, Fernandez L, Leemans J, Cevallos MA (1984)Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol 158:148–155
Pichinoty F, Mandel M, Garcia J-L (1977) Étude de six souches deAgrobacterium tumefaciens etA. radiobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol 128A:303–310
Preisig O, Anthamatten D, Hennecke H (1993) Genes for a microaerobically induced oxidase complex inBradyrhizobium japonicum are essential for a nitrogen-fixing endosymbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:3309–3313
Priefer UB (1984) Isolation of plasmid DNA. In: Puhler A, Timmis KN (eds) Advanced molecular genetics. Springer-Verlag Berlin pp 14–24
Priefer UB (1989) Genes involved in lipopolysaccharide production and symbiosis are clustered on the chromosome ofRhizobium leguminosarum biovarviciae VF39. J Bacteriol 171:6161–6168
Priefer UB, Simon R, Puhler A (1984) Cloning with cosmids. In: Puhler A, Timmis KN (eds). Advanced molecular genetics. Springer-Verlag Berlin, pp 190–201
Raitio M, Jalli T, Saraste M (1987) Isolation and analysis of the genes from cytochromec oxidase inParacoccus denitrificans. EMBO J 6:2825–2833
Sanger FS, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Saraste M, Metso T, Nakari T, Jalli T, Lauraeus M, van der Oost J (1991) TheBacillus subtilis cytochrome-c oxidase. Eur J Biochem 195:517–525
Schlüter A, Patschkowski T, Weidner S, Unden G, Hynes MF, Priefer UB (1993) Functional and regulatory characteristics of FnrN, an oxygen-responsive transcriptional activator inRhizobium leguminosarum bv.viciae. In: Palacios R, Mora J, Newton WE (eds) New horizons in nitrogen fixation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, p 493
Simon, R (1984) High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by thein vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet 196:413–420
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram negative bacteria. Bio-Technology 1:784–791
Simon R, O'Connell M, Labes M, Pühler A (1986) Plasmid vectors for the genetic analysis and manipulation of Rhizobia and other Gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol 118:640–659
Staden R (1986) The current status and partability of our sequence handling software. Nucleic Acids Res 14:217–231
Van Veen RIM, den Dulk-Ras H, Bisseling T, Schilperoort RA, Hooykaas PJJ (1988) Crown gall tumor and root nodule formation by the bacteriumPhyllobacterium myrsinacearum after the introduction of anAgrobacterium Ti plasmid or aRhizobium Sym plasmid. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 1:231–234
Vieira J, Messing J (1982) The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene 19:259–268
Yelton MM, Mulligan JT, Long SR (1987) Expression ofRhizobium meliloti nod genes inRhizobium andAgrobacterium backgrounds. J Bacteriol 169:3094–3098
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kondorosi
Dedicated to Prof. W Heumann for his 80th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlüter, A., Rüberg, S., Krämer, M. et al. A homolog of theRhizobium meliloti nitrogen fixation genefixN is involved in the production of a microaerobically induced oxidase activity in the phytopathogenic bacteriumAgrobacterium tumefaciens . Molec. Gen. Genet. 247, 206–215 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705651
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705651