Conclusions
-
1.
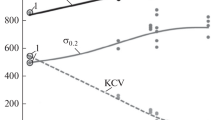
The yield of austenitic high-manganese steels can be raised by 100–250 N/mm2 as a result of disperse-carbide segregation when they are alloyed with tungsten.
-
2.
Steels with 15–20% Mn, 10% W, and more than 0.65% of C possess the best combination of mechanical properties in the initial and quenched states.
-
3.
Cold plastic deformation makes it possible to increase the yield point to 1500–1600 N/mm2 with satisfactory plasticity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
I. N. Bogachev and V. F. Egolaev, Structure and Properties of Iron-Manganese Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1973).
Y. Dastur and W. Leslie, "Mechanism of work hardening in Hadfield manganese steel," Metall. Trans.,12A, No. 5, 749–759 (1981).
Additional information
I. P. Bardin Central Scientific-Research Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 59–61, August, 1990.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kardonskii, V.M., Samoilova, O.V. High-strength austenitic steels with tungsten. Met Sci Heat Treat 32, 627–630 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700720
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700720