Abstract
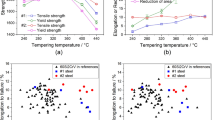
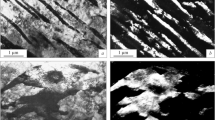
The structure, the phase composition, and the mechanical properties of high-strength austenitic steel 05S–(21–22)Cr–15Mn–8Ni–(1–2)Mo–V–N (05Kh(21–22)AG15N8MF grade) having an equilibrium nitrogen content of 0.5% (which is below the solubility limit under standard conditions) and melted in an open induction furnace are studied in the cast, hot-deformed, and heat-treated states. The steel having the same metallic base and a overequilibrium nitrogen content of 0.65–0.79% (which is above the solubility limit under standard conditions) and melted in a plasma arc furnace is also analyzed. The mechanical properties of these steel versions, including the impact toughness at low test temperatures, are compared, and their relationship with the structural-phase state of the steels is analyzed. The hot-forged steels exhibit an increase in the strength with the nitrogen concentration and a symmetrical decrease in the impact toughness. An increase in the forging reduction ratio of steel with 0.7% N is found to increase the yield strength and ultimate tensile strength but to decrease the cold resistance. The grain size and the presence of a nitride phase, which precipitates at the temperatures of the end of hot forging, exert a significant effect on the level of properties. To achieve a good combination of high strength properties and cold resistance, the nitrogen concentration in 05Kh21AG15N8MF steel should not to exceed 0.65%.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
L. G. Rigina, Ya. M. Vasil’ev, V. S. Dubov, et al., “Nitrogen alloying of steels,” Elektrometallurgiya, No. 2, 14–19 (2005).
L. G. Rigina, “Research and development of ESR and ESRD technologies for chromium–manganese nitrogen alloyed steels,” Candidate’s Dissertation in Engineering (Moscow, 2005).
H. Berns, “Alloy development and processing,” in Proceedings of Conference on High Nitrogen Steels HNS-2004 (Ostend, 2004), Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 271–281.
V. A. Malyshevskii, G. Yu. Kalinin, V. V. Tsukanov, and O. V. Fomina, “Modern low-magnetic steels for shipbuilding,” Sudostroenie, No. 5, 19–21 (2009).
Ts. Rashev, Production of Alloy Steel (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1981).
B. I. Berezhko and A. G. Ignatenko, “Quality of austenitic steel depending on the method of melting and alloying it with nitrogen,” in Proceedings of Conference on High-Nitrogen Steels (Inst. Metallofiz., Kiev, 1990), pp. 15–16.
I. P. Malkin, “Production of nitrogen-alloyed special steels,” Candidate’s Dissertation in Engineering (Moscow, 1966).
G. Stein, J. Menzel, and C. Choudhure, “Industrial manufacture of massively nitrogen-alloyed steels in pressure ERS furnace,” Steel Times, No. 3, 146–150 (1989).
Ts. Rashev, M. Venkov, I. Popov, et al., “Machines for the production of high-nitrogen steels,” in Proceedings of International and Scientific Conference High-Nitrogen Steels-89 (Varna, 1989).
B. Raj, High Nitrogen Steels and Stainless Steels. Manufacturing, Properties and Applications (Woodhead Publishing, 2004).
Ts. V. Rashev, High-Nitrogen Steels. Metallurgy under Pressure (Prof. Marine Drinov, Sofia, 1995).
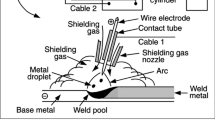
A. A. Sisev, S. G. Tsimerman, M. V. Kostina, A. I. Il’inskii, M. M. Perkas, and L. G. Rigina, “Development of an industrial technology of plasma-arc remelting of nitrogen-containing 05Kh21AG15N8MF steel,” Elektrometallurgiya, No. 12, 3–11 (2017).
S. O. Muradyan, “Structure and properties of cast corrosion-resistant nitrogen-alloyed steel,” Candidate’s Dissertation in Engineering (Moscow, 2016)
M. V. Kostina, P. Yu. Polomoshnov, V. M. Blinov, S. O. Muradyan, and V. S. Kostina, “Cold resistance of a new cast Cr–Mn–Ni–Mo–N steel with 0.5% N. Part 1,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall. 62 (11), 894–906 (2019).
Ya. S. Vishnevetskii, Free Forging (Vysshaya Shkola, Moscow, 1972).
K. H. Lo, C. H. Shek, and J. K. L. Lai, “Recent developments in stainless steels,” Mater. Sci. Eng., R 65, 39–104 (2009).
B. Hwang, T.-H. Lee, S.-J. Park, Ch.-S. Oh, and S.‑J. Kim, “Correlation of austenite stability and ductile-to-brittle transition behavior of high-nitrogen 18Cr–10Mn austenitic steels,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528 (24), 7257–7266 (2011).
Z. Yuan, Q. Dai, X. Cheng, K. Chen, and W. Xu, “Impact properties of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steels,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 475, 202–206 (2008).
S. Wang, K. Yang, Y. Shan, and L. Li, “Plastic deformation and fracture behaviors of nitrogen-alloyed austenitic stainless steels,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 490 (1–2), 95–104 (2008).
O. V. Fomina and M. V. Kostina, “Influence of the temperature–deformation HTMT parameters on the formation of excess phases in high-strength austenitic nitrogen-containing steel,” Vopr. Materialoved., No. 2 (90), 17–28 (2017).
O. V. Fomina, T. V. Vikhareva, V. B. Gribanova, and Yu. M. Markova, “Metadynamic recrystallization kinetics during thermomechanical treatment of nitrogen-containing steel,” Materialoved., No. 9, 3–11 (2018).
V. A. Malyshevskii, G. Yu. Kalinin, O. V. Fomina, T. V. Vikhareva, and A. A. Kruglova, “Formation of the structure of nitrogen-containing steel under thermal deformation and its relationship with mechanical properties,” Elektrometallurgiya, No. 9, 23–31 (2014).
O. V. Fomina and T. V. Vikhareva, “Formation of the structure of sheets made of high-strength nitrogen-containing austenitic 04Kh20N6G11M2AFB steel during multipass hot deformation,” Tyazheloe Mashinostr., No. 6, 2–8 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the Electrostal Plant for its significant practical contribution to the work on ESR and PAR steels.
Funding
This work was supported by the program of the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences RAN I.55 “The Arctic—Scientific Fundamentals of New Technologies for Exploration, Conservation, and Development” (project no. 0087-2018-0020) and was performed within the framework of state assignment no. 075-00328-21-00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by K. Shakhlevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostina, M.V., Rigina, L.G., Muradyan, S.O. et al. Properties of Austenitic, Heavily Alloyed, High-Nitrogen Steels Made by Various Casting, Special Electrometallurgy, and Hot Deformation Methods. Russ. Metall. 2022, 559–568 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029522060131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029522060131