Summary
Various procedures are available for measuring an individual's maximum oxygen capacity. Most of them, however, are time-consuming, require expensive equipment and demand maximum effort from the individuals being tested. Investigations have been made, therefore, for the purpose of finding relatively less expensive procedures which would require sub-maximum effort only. Such procedures would have a wide use in the Human Adaptability Programme of the I.B.P., when the endurance capacities of different populations in various parts of the world will be compared. It will be essential, however, for these procedures to be standardised if valid comparisons are to be made.
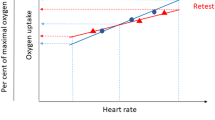
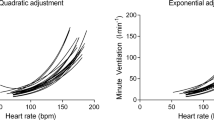
The Human Sciences Laboratory therefore measured the maximum oxygen intakes of 40 active, young men during a bicycle ergometer test, a step test and during an intermittent and a continuous treadmill test. The results obtained during the intermittent treadmill test proved to be the most accurate. It is, however, very time-consuming. The results of the continuous treadmill test are very similar to those obtained from the intermittent treadmill test, and the time required is very much shorter. It is, however, a very strenuous test. The results of the bicycle ergometer test is similar to those of the intermittent treadmill test at low levels of effort, but is significantly lower at high levels of effort. The results of the step test compared favourably with those of the intermittent treadmill test, although at low levels of effort the step test overestimates the maximum oxygen values and at high levels of effort it underestimates the values. The step test, however, has the great advantage that only sub-maximum work loads are used. It can therefore be employed without any danger for measuring the maximum oxygen intake of large groups of people and also of people of any age group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, K. Lange, A. Bolstad, Y. Løyning, andL. Irving: Physical fitness of Arctic Indians. J. appl. Physiol.15, 645–648 (1960).
Astrand, P. O.: Experimental studies of physical working capacity in relation to sex and age. Copenhagen: Munksgaard 1942.
— andI. Ryhming: A nomogram for calculation of aerobic capacity for pulse rate during submaximal work. J. appl. Physiol.7, 218–221 (1954).
Elnsner, R. W., G. W.Gardner, H.Egstrom, and J. F.Keogh: Physical working capacity of primitive peoples, p. 311. Proc. 23rd Internat. Physiol. Soc. Tokyo 1965.
Glassford, R. G., G. H. Y. Baycroft, A. W. Sedgewick, andR. B. J. MacNab: Comparison of maximal oxygen uptake values determined by predicted and actual methods. J. appl. Physiol.20, 509 (1965).
Hill, A. V., andHartley Lopton: Muscular exercise, lactic acid, and supply and utilisation of oxygen. Aust. J. Med.16, 135–171 (1923).
Maritz, J. S., J. F. Morrison, J. Peter, N. B. Strydom, andC. H. Wyndham: A practical method of estimating an individuals maximal oxygen intake. Ergonomics4, 97–122 (1961).
Taylor, H. L., E. Buskirk, andA. Henschel: Maximum oxygen intake as an objective measure of cardio-respiratory performance. J. appl. Physiol.8, 73–80 (1955).
Wyndham, C. H., N. B. Strydom, J. S. Maritz, J. F. Morrison, J. Peter, andZ. U. Potgieter: Maximum oxygen intake and maximum heart rate during strenuous work. J. appl. Physiol.14, 927–936 (1959).
— —,J. F. Morrison, J. Peter, C. G. Williams, G. A. G. Bredell, andA. Joffe: Difference between ethnic groups in physical working capacity. J. appl. Physiol.18, 361–366 (1963).
- - and C. G.Williams: A submaximal test to assess the capacity for endurance exercise. Report to Physical Fitness Sub-committee of Human Adaptability Project of I. B. P., Johannesburg, April 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wyndham, C.H., Strydom, N.B., Leary, W.P. et al. Studies of the maximum capacity of men for physical effort. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. Einschl. Arbeitsphysiol. 22, 285–295 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00698280
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00698280