Summary
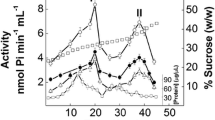
The naupliar stage ofArtemia salina has been found to contain large amounts of an ATPase which requires the presence of Mg++, is stimulated by Na+ and K+, and is sensitive to ouabain. Upon cell fractionation, sixty percent of the Na+K-activated ATPase activity was present in a heavy membrane fraction which accompanied mitochondria, and twenty percent of the activity was found in the microsomal fraction. Separation of the heavy membranes containing the Na+K-activated ATPase from mitochondria was accomplished by sucrose density gradient centrifugation.
Kinetic characterization of the Na+K-activated ATPase was examined with both mitochondrial and microsomal preparations. No significant differences were observed between the two preparations. Maximal enzyme activity occurred at pH 7.2 and a temperature of 45 ° C. Half maximal inhibition of enzymatic activity occurred with ouabain concentration of 8 × 10−6 M. Half maximal activation of the enzyme by ATP and MgCl2 occurred at 8 × 10−4 and 1 × 10−3 M, respectively, with an optimal Mg++/ATP ratio of 2.0. NaCl and KC1 (or NH4C1) were required for activity, with half maximal activation at 1 × 10−2 and 9 × 10−3 M (or 2.1 × 10−2 M), respectively. The optimal Na+/K+ ratio was 4.0, although enzymatic activity occurred through a wide range of ratios. In contrast, survival of nauplii was reduced in media in which the Na+/K+ ratio was less than 10.
Anatomical localization of the enzyme in nauplii indicated that the abdominal region contained 44% of the total Na+K-activated ATPase activity, while the cephalothoracic region contained 54% of the total activity. Isolated larval salt glands contained 10% or less of the total activity. In contrast, the adult leg segments containing the salt-transporting organs showed 54% of the total Na+K-activated ATPase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, R. W.: Biochemical aspects of active transport. Ann. Rev. Biochem.36 727–756 (1967)
Augenfeld, J. M.: The role of Na+-K+-activated, ouabain-sensitive ATPase in the response ofArtemia salina L. to salinity changes. Life Sci.8, 973–978 (1969)
Bonting, S. L.: Sodium-potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase and cation transport. In: Bittar, E. E. (ed.), Membranes and ion transport, vol. I., p. 257. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1970
Conte, F. P., Hootman, S. R., Harris, P. J.: Neck organ ofArtemia salina nauplii. A larval salt gland. J. comp. Physiol.80, 239–246 (1972)
Copeland, D. E.: A mitochondrial pump in the cells of the anal papillae of mosquito larvae. J. Cell Biol.23, 253–263 (1964)
Copeland, D. E.: A study of salt-secreting cells in the brine shrimp (Artemia salina). Protoplasma (Wien)63, 363–384 (1967)
Croghan, P. C.: The osmotic and ionic regulations ofArtemia salina (L.). J. exp. Biol.35, 219–233 (1958a)
Croghan, P. C.: The mechanism of osmotic regulation inArtemia salina (L.): the physiology of the branchiae. J. exp. Biol.35, 234–242 (1958b)
Dejdar, E.: Die Korrelationen zwischen Kiemensäcken und Nackenschild bei Phyllopoden. (Versuch einer Analyse mit Hilfe elektiver Vitalfärbung). Z. wiss. Zool.136, 422–452 (1930)
Ernst, S. A.: Transport adenosine triphosphatase cytochemistry. II. Cytochemical localization of ouabain-sensitive potassium-dependent phosphatase activity in the secretory epithelium of the avian salt gland. J. Histochem. Cytochem.20, 23–38 (1972)
Ernst, S. A., Goertemiller, C. C., Jr., Ellis, R. A.: The effect of salt regimens on the development of (Na++K+)-dependent ATPase activity during the growth of salt glands of ducklings. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)135, 682–692 (1967)
Ernster, L., Zvetterstrom, R., Lindberg, O.: A method for the determination of tracer phosphate in biological material. Acta chem. scand.4, 942–947 (1950)
Ewing, R. D., Peterson, G. L., Conte, F. P.: Larval salt gland ofArtemia salina nauplii. Effects of inhibitors on survival at various salinities. J. comp. Physiol.80, 247–254 (1972)
Finamore, F. J., Clegg, J. S.: Biochemical morphogenesis in the brine shrimp. In: Padilla, G. M., Whitson, G. L., and Cameron, I. L. (eds.), The cell cycle: Gene-enzyme interactions, p. 249–278. New York: Academic Press 1969
Hokin, L. E., Dahl, J. L., Deupress, J. D., Dixon, J. F., Hackney, J. F., Perdue, J. F.: Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. X. Purification of the enzyme from the rectal gland ofSqualus acanthias. J. biol. Chem.248, 2593–2605 (1973)
Hootman, S. R., Harris, P. J., Conte, F. P.: Surface specialization of the larval salt gland inArtemia salina, nauplii. J. comp. Physiol.79, 97–104 (1972)
Jorgensen, P. L., Skou, J. C., Solomonson, L. P.: Purification and characterization of (Na++K+)-ATPase. II. Preparation by zonal centrifugation of highly active (Na++K+)-ATPase from the outer medulla of rabbit kidneys. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)233, 381–394 (1971)
Katz, A. I., Epstein, F. H.: Physiological role of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the transport of cations across biological membranes. New Engl. J. Med.278, 253–261 (1968)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951)
Maetz, J., Garcia Romeu, F.: The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a fresh-water fish,Carassius auratus. II. Evidence for NH4 +/Na+ and HCO3 −/C1− exchanges. J. gen. Physiol.47, 1209–1227 (1964)
Philpott, C. W., Copeland, D. E.: Fine structure of chloride cells from three species ofFundulus. J. Cell Biol.18, 389–404 (1963)
Skou, J. C.: Enzymatic basis for active transport of Na+ and K+ across cell membranes. Physiol. Rev.45, 596–617 (1965)
Smith, P. G.: The ionic relations ofArtemia salina (L.). I. Measurements of electrical potential difference and resistances. J. exp. Biol.51, 727–738 (1969a)
Smith, P. G.: The ionic relations ofArtemia salina L. II. Fluxes of sodium, chloride and water. J. exp. Biol.51, 739–757 (1969b)
Thuet, P., Motais, R., Maetz, J.: Les méchanismes de l'euryhalinité chez le crustacé des salinesArtemia salina L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.26, 793–818 (1968)
Uesugi, S., Dulak, N. C., Dixon, I. F., Hexum, T. D., Dahl, J. L., Perdue, J. F., Hokin, L. E.: Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatases. VI. Large scale partial purification and properties of a lubrol-solubilized bovine brain enzyme. J. biol. Chem.246, 531–543 (1971)
Wharton, D. C., Tzagoloff, A.: Cytochrome oxidase from beef heart mitochondria. In: Estabrook, R. W. (ed.), Methods in enzymology, vol. X, Oxidation and phosphorylation, p. 245–250. New York: Academic Press 1967
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
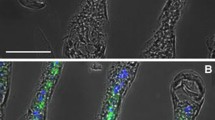
This work was supported by AEC Grant RLO 2227-T13-5. The authors wish to express their gratitude to S. R. Hootman for preparation of the electron micrographs presented in Fig. 2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ewing, R.D., Peterson, G.L. & Conte, F.P. Larval salt gland ofArtemia salina nauplii. J. Comp. Physiol. 88, 217–234 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00697956
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00697956