Summary
The present investigation was undertaken to test the hypothesis that the experimentally determined degree of supersensitivity to an agonist caused by inhibition of a site of loss depends on the ratio “K m of the site of loss/ED50 of the agonist”.
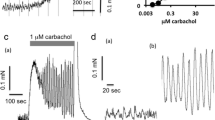
The influence of inhibition of neuronal uptake by cocaine on the α-adrenoceptor-mediated effect of noradrenaline was studied on the dog saphenous vein; the influence of inhibition of COMT by U-0521 on the β-adrenoceptor-mediated effect of isoprenaline was studied on the dog saphenous vein and on the guinea-pig trachea; the influence of inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by physostigmine on the effect of acetylcholine was studied on the guinea-pig ileum. To further extend the range of values of the ratio “K m/ED50”, several concentrations of phentolamine, propranolol or atropine were used to “increase the ED50” of the respective agonist. It was thus possible to determine the degree of supersensitivity caused by inhibition of a site of loss over a range of “K m/ED50” values of 0.02 to 2,307.
In seven situations the ratio “K m/ED50” was higher than 10. In all of these cases the supersensitivity caused by inhibition of the site of loss was maximal. In eleven situations the ratio “K m/ED50” was less than 10 and higher than 0.1 and the supersensitivity obtained was sub-maximal but was closer to the maximum, the closer the ratio was to 10. In two situations the ratio was less than 0.1 and no supersensitivity was obtained.
The results confirm the hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burn JH (1952) In: Practical pharmacology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 19
Constantine JW (1965) The spirally cut tracheal strip preparation. J Pharm Pharmacol 17:384–385
Garland LG, Marrion NV, Martin GR (1981) The extraneuronal O-methylation of3H-(±)-isoprenaline by guinea-pig tracheal rings in vitro. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 318:88–93
Graefe KH, Eckert E (1972) On the stereoselectivity of the neuronal uptake in the cat's nictitating membrane. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 275:45–68
Grohmann M, Trendelenburg U (1984) The substrate specificity of uptake2 in the rat heart. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328:164–173
Guimarães S (1982) Two adrenergic biophases in blood vessels. TIPS 3:159–161
Guimarães S, Osswald W (1969) Adrenergic receptors in the veins of the dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 5:133–140
Guimarães S, Paiva MQ (1984) Kinetics of the extraneuronal O-methylating system of the dog saphenous vein. In: Neuronal and extraneuronal events in autonomic pharmacology. Raven Press, New York, pp 131–138
Hendley ED, Snyder SH (1972) Stereoselectivity of catecholamine uptake in noradrenergic and dopaminergic peripheral organs. Eur J Pharmacol 19:56–66
Henseling M (1973) Kinetic constants for uptake and metabolism of3H-(-)-noradrenaline in rabbit aorta. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 323:12–23
Langer SZ, Trendelenburg U (1969) The effect of a saturable uptake mechanism on the slopes of dose-response curves for sympathomimetic amines and on the shift of dose-response curves produced by a competitive antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 167:117–142
Mittag TW, Ehrenpreis S, Patrick P (1971) Some properties of cholinesterase in intact guinea-pig ileum in vitro. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 191:270–278
Paiva MQ, Guimarães S (1984) The kinetic characteristics of the extraneuronal O-methylating system of the dog saphenous vein and the supersensitivity to catecholamines caused by its inhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 327:48–55
Starke K, Montel H, Wagner J (1971) Effect of phentolamine on noradrenaline uptake and release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 271:181–192
Trendelenburg U (1978) Extraneuronal uptake and metabolism of catecholamines as a site of loss. Life Sci 22:1217–1222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guimarães, S., Paiva, M.Q., Moura, D. et al. The saturability of a site of loss and the degree of supersensitivity to agonists which are substrates of this site of loss. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 329, 30–35 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695188
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695188