Summary
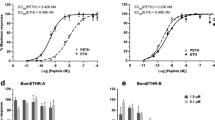
Head segments and brains were extirpated from embryos of the tobacco hornworm,Manduca sexta, extracted and the resulting extracts assayed for prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) activity on prothoracic glands from day 3 fifth instar larvae and day 0 pupae. Dose-response curves were generated and indicated the presence of PTTH activity in embryonic brains and head segments, suggesting a role(s) for this neurohormone during embryogenesis. Maximal PTTH activity was found in brains from embryos 117 h post-oviposition, just prior to hatching, but activity was also noted in head segments as early as 24 h postoviposition. These data on PTTH and those on ecdysteroids and juvenile hormones in embryos suggest that these 3 classes of hormones which control insect post-embryonic development, may also be involved in the regulation of developmental processes in the embryo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollenbacher WE, Granger NA (1985) Endocrinology of the prothoracicotropic hormone. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 7. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 109–151
Bollenbacher WE, Agui N, Granger NA, Gilbert LI (1979) In vitro activation of insect prothoracic glands by the prothoracicotropic hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5148–5152
Bollenbacher WE, O'Brien M, Katahira E, Gilbert LI (1983) A kinetic analysis of the action of the insect prothoracicotropic hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol 32:27–46
Bollenbacher WE, Katahira E, O'Brien M, Gilbert LI, Thomas M, Agui N, Baumhover A (1984) The insect prothoracicotropic hormone: Evidence for two molecular forms. Science 224:1243–1245
Chen J-H, Fugo H, Nakajima M, Nagasawa H, Suzuki A (1986) The presence of neurohormonal activities in embryos of the silkworm,Bombyx mori. J Seric Sci Jpn 55:54–59
Dorn A (1985) Neurosecretion in the insect embryo. Proc Arthropod Embryol Jpn 1984:1–16
Dorn A, Bishoff ST, Gilbert LI (1987) An incremental analysis of the embryonic development of the tobacco hornworm,Manduca sexta. Int J Invert Reprod Dev 11:137–158
Gilbert LI, Schneiderman HA (1961) The content of juvenile hormone and lipid in Lepidoptera: Sexual differences and developmental changes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 1:453–472
Gilbert LI, Goodman W, Bollenbacher WE, Agui N, Granger NA, Sedlak BJ (1980) Hormones controlling insect metamorphosis. Rec Prog Hormone Res 36:401–449
Hoffmann JA, Lagueux M (1985) Endocrine aspects of embryonic development in insects. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 1. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 435–460
Horn DHS, Bergamasco R (1985) Chemistry of ecdysteroids. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 7. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 185–248
Jones BM (1953) Activity in the incretory centres ofLocusta pardalina during embryogenesis: Function of the prothoracic glands. Nature (Lond) 172:551
O'Brien M, Granger NA, Agui N, Gilbert LI, Bollenbacher WE (1986) Prothoracicotropic hormone in the developing brain of the tobacco hornworm,Manduca sexta: Relative amounts of two molecular forms. J Insect Physiol 32:719–725
Riddiford LM (1985) Hormone action at the cellular level. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 8. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 37–84
Schooley DA, Baker FC (1985) Juvenile hormone biosynthesis. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 7. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 363–389
Truman JW, Taghert PH, Copenhaver PF, Tublitz NJ, Schwartz LM (1981) Eclosion hormone may control all ecdyses in insects. Nature (Lond) 291:70–71
Vince R, Gilbert LI (1977) Juvenile hormone esterase activity in precisely timed larvae and pharate pupae ofManduca sexta. Insect Biochem 7:115–120
Warren JT, Smith WA, Gilbert LI (1984) Simplification of the ecdysteroid radioimmunoassay by the use of protein A fromStaphylococcus aureus. Experientia 40:393–394
Warren JT, Steiner B, Dorn A, Pak M, Gilbert LI (1986) Metabolism of ecdysteroids during the embryogenesis ofManduca sexta. J Liquid Chromatog 9:1759–1782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorn, A., Gilbert, L.I. & Bollenbacher, W.E. Prothoracicotropic hormone activity in the embryonic brain of the tobacco hornworm,Manduca sexta . J Comp Physiol B 157, 279–283 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693354
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693354