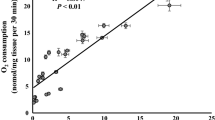
Summary
The interrelationships of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism during anaerobiosis were investigated in the ventricle of the intertidal oyster,Crassostrea gigas. While the ventricle accumulates alanine and succinate in a 2∶1 ratio during anoxia, these end products appear to arise from different precursors. Thus glucose-14C is metabolized mainly to alanine-14C (55% of glucose carbon appears in alanineversus 3% in succinate) by the anoxic ventriclein vitro while succinate-14C is the principle end product of aspartate-14C catabolism. Glutamate-14C is poorly metabolized by the anoxic ventricle, and correspondingly, while ventricular aspartate concentrations drop during anoxia, those of other amino acids do not. A metabolic scheme coupling glucose and aspartate catabolism in this facultative anaerobe is proposed. The detection of a third, as yet incompletely identified, anaerobic end product produced by the ventricle is reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M.: The anerobic tolerance of marine intertidal isopods. M.Sc. Thesis, Stanford University 1974
Bayne, B.L.: Ventilation, the heart beat, and oxygen uptake byMytilus edulis in declining oxygen tension. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.40, 1065–1085 (1971)
Brand, A.R., Roberts, D.: The cardiac response of the scallop,Pecten maximus l. to respiratory stress. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.13, 29–43 (1973)
Campbell, J.W., Bishop, S.H.: Nitrogen metabolism in molluscs. In: Comparative biochemistry of nitrogen metabolism (ed. J.W. Campbell), pp. 103–206. New York: Academic Press 1970
Chen, C., Awapara, J.: Intracellular distribution of enzymes catalyzing succinate production from glucose inRangia mantle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.30, 727–737 (1969)
Collicutt, J.M.: Anaerobic metabolism in the oyster heart. M.Sc. Thesis, University of British Columbia 1975
Crowley, G.J., Moses, V., Ullrich, J.: A versatile solvent to replace phenol in the paper chromatography of radioactive intermediary metabolites. J. Chromatog.12, 219–228 (1963)
Drummond, G.I.: Muscle metabolism. Fortschr. Zool.18, 359–429 (1966)
Dupaul, W.D., Webb, K.L.: Salinity-induced changes in the alanine and aspartic aminotransferase activity in three marine bivalve molluscs. Arch. int. Physiol. Biochem.82, 817–822 (1974)
Fields, J.H.A.: Enzymes of the citrate baanchpoint in the adductor muscle of the oyster. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia 1976a
Fields, J.H.A.: A dehydrogenase requiring alanine and pyruvate as substrates from oyster adductor muscle. Fed. Proc.35, 1687 (1976b)
Fields, J.H.A., Baldwin, J., Hochachka, P.W.: On the role of octopine dehydrogenase in cephalopod mantle muscle metabolism. Canad. J. Zool.54, 871–878 (1976)
Gäde, G., Wilps, H.: Glycogen degradation and end products of anaerobic metabolism in the fresh water bivalveAnodonta cygnea. J. comp. Physiol.104, 79–85 (1975)
Hammen, C.S.: Succinate and lactate oxidoreductases of bivalve molluses. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.50B, 407–412 (1975)
Hochachka, P.W., Fields, J., Mustafa, T.: Animal life without oxygen: basic biochemical mechanisms. Amer. Zool.13, 543–555 (1973)
Hochachka, P.W., Mustafa, T.: Invertebrate facultative anaerobiosis. Science178, 1056–1060 (1972)
Irisawa, H., Irisawa, A., Shigeto, N.: Effects of Na+ and Ca2+ on the spontaneous excitation of the bivalve heart muscle. In: Comparative physiology of the heart: Current trends (ed. F.V. McCann), pp. 176–191. Basel: Birkhäuser 1969
Kluytmans, J.H., Veenhof, P.R., Zwaan, A. de: Anaerobic production of volatile fatty acids in the sea mussel,Mytilus edulis L. J. comp. Physiol.104, 71–78 (1975)
Lowry, O.H., Passonneau J.V.: A collection of metabolite assays. In: A flexible system of enzymic analysis, pp. 146–218. New York: Academic Press 1972
Malanga, C.J., Aiello, E.L.: Succinate metabolism in the gills of the musselsModiolus demissus andMytilus edulis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.43B, 795–806 (1972)
Mustafa, T., Hochachka, P.W.: Catalytic and regulatory properties of pyruvate kinase of a marine bivalve. J. biol. Chem.246, 3196–3203 (1971)
Mustafa, T., Hochachka, P.W.: Enzymes of facultative anaerobiosis in molluscs. III. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and its role in aerobic-anaerobic transition. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.45B, 657–667 (1973)
Regnouf, F., van Thoai, N.: Octopine and lactate dehydrogenases in molluse muscles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.32, 411–416 (1970)
Snedecor, G.W., Cochran, W.G.: Statistical methods, 6th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press 1967
Stokes, T.M., Awapara, J.: Alanine and succinate as end products of glucose degradation in the clamRangia cuneata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.25, 883–892 (1968)
Thoai, N. van, Huc, C., Pho, D.B., Olomucki, A.: Octopine dehydrogenase: purification et proprietés catalytiques. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)52, 46–57 (1969)
Williamson, J.R., Corkey, B.E.: Assays of intermediates of the citric acid cycle and related compounds by fluorometric enzyme methods. Meth. Enzymol.13, 434–513 (1969)
Zwaan, A. de, Marrewijk, W. van: Anaerobic glucose degradation in the sea musselMytilus edulis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.44B, 429–439 (1973a)
Zwaan, A. de, Marrewijk, W. van: Intracellular localization of pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and “malic enzyme” and the absence of glyoxylate cycle enzyme in the sea mussel,Mytilus edulis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.44B, 1057–1066 (1973b)
Zwaan, A. de, Zandee, D.I.: The utilization of glycogen and accumulation of some intermediates during anaerobiosis inMytilus edulis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.43B, 47–54 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collicutt, J.M., Hochachka, P.W. The anaerobic oyster heart: Coupling of glucose and aspartate fermentation. J Comp Physiol B 115, 147–157 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692526
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692526