Abstract
A simple, semi-analytic method is developed for obtaining the orbits of galaxies undergoing fast collisions in which the galaxies are represented by Plummer models. The results are found to agree fairly well with those of N-body simulations.
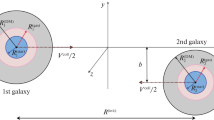
A simple formula for obtaining the angle of deflection is deduced. The maximum angle of deflection is 180° forV p/V esc(p)=1.00, about 36° forV p/V esc(p)=1.50, and about 18° forV p/V esc(p)=2.00, whereV p is the velocity at closest approachp, andV esc(p) is the parabolic velocity of escape atp. The angle of deflection of a pair of colliding elliptical galaxies without halos is about twice that for a pair of galaxies with halos for the same relative velocity at infinite separation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarseth, S. J.: 1966,Mon. Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 132, 35.
Aarseth, S. J. and Fall, S. M.: 1980,Astrophys. J. 236, 43.
Ahmed, F.: 1979,Astrophys. and Spa. Sci. 60, 493.
Ahmed, F. and Alladin, S. M.: 1981,Bull. Astron. Soc. India. 9, 40.
Alladin, S. M.: 1965,Astrophys. J. 141, 768.
Alladin, S. M. and Narasimhan, K. S. V. S.: 1982,Phys. Reports. 92, 339.
Binney, J. and Tremaine, S.: 1987,Galactic Dynamics, Princeton University Press, p. 455.
Chandrasekhar, S.: 1943,Principles of Stellar Dynamics, Dover Publications, Inc. New York, p. 239.
Goldstein, H.: 1950,Classical Mechanics, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co. Cambridge, Mass. p. 58.
Laubert, A.: 1974,Astron. Astrophys. 33, 231.
Limber, D. N.: 1961,Astrophys. J. 134, 537.
Miller, R. H. and Smith, B. F.: 1980,Astrophys. J. 235, 421.
Narasimhan, K. S. V. S. and Alladin, S. M.: 1986,Astrophys. and Spa. Sci. 128, 307.
Narasimha, Rao, M., Narasimhan, K. S. V. S., and Alladin, S. M.: 1990,Journal of Pure and Applied Physics 2, 1.
Narasimha, Rao, M. and Narasimhan, K. S. V. S.: 1992,Astrophys. and Spa. Sci. 194, 245.
Sastry, K. S. and Alladin, S. M.: 1977,Astrophys. and Spa. Sci. 46, 285.
Spitzer, L.: 1958,Astrophys. J. 127, 17.
Toomre, A.: 1977,The Evolution of Galaxies and Stellar Populations, B. M. Tinsley and R. B. Larson (eds.), Yale University Observatory, p. 401.
Zwicky, F.: 1959,Handbuch der Physik,53, Springer Verlag, Berlin, p. 373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narasimha Rao, M., Alladin, S.M. & Narasimhan, K.S.V.S. Orbits of colliding galaxies. Celestial Mech Dyn Astr 58, 65–80 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692118