Summary
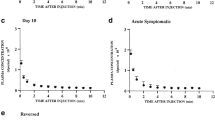
Rats maintained on a thiamine-deficient diet for 38 days lost weight and showed neurological symptoms. The PA value, representing the permeability of the blood-brain barrier to14C-sucrose, was significantly increased whether urethane or ethanol was used as anaesthetic. This increase was prevented by giving rats on the same diet injections of thiamine twice weekly. Barrier function was normalised by injecting thiamine into deficient rats for just 3 days before biopsy. The brains of the thiamine-deficient rats were stained by the Fink-Heimer method but showed no degenerating axons except for silver grains in the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb.
Other rats were maintained on the same diet for 38 days and additionally exposed to ethanol vapour for 16 h per day. This resulted in a similar loss of weight but a greater leakage of the blood-brain barrier. The latter was normalised by a thiamine injection only 24 h before biopsy, but was not reduced by withdrawal of ethanol for 3 days before biopsy. Axonal degeneration was present in the olfactory glomeruli. However, no lesions or extravasated blood cells were seen in any brains, there was no change in brain water indicative of oedema and no degeneration in retina, distal peripheral nerves or leg muscles. The relation of these and other experimental findings to alcohol-related brain damage is considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Itokawa Y (1977) Effect of ethanol administration on thiamine metabolism and transketolase activity in rats. Int J Vitamin Nutrit 47:307–314
Anker RL, Cragg BG (1974) Development of the extrinsic connections of the visual cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol 154:29–42
Collins GH, Converse WK (1970) Cerebellar degeneration in thiamine-deficient rats. Am J Pathol 58:219–232
Dreyfus PM (1961) The quantitative histochemical distribution of thiamine in deficient rat brain. J Neurochem 8:139–145
Fink RP, Heimer L (1967) Two methods for selective impregnation of degenerating axons and their synaptic endings in the central nervous system. Brain Res 4:369–374
Gray GM (1978) Intestinal disaccharidase deficiencies and glucosegalactose malabsorption. In: Stanbury JB, Wijngaarden JB, Fredrickson DS (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1526–1536
Graziadei PPC, Monti-Graziadei CA (1978) Continuous nerve cell renewal in the olfactory system. In: Jacobson M (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol IX: Development of sensory systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 55–83
Haller RG (1980) Alcoholism and neurologic disorders. In: Rosenberg RN (ed) The science and practice of clinical medicine, vol 5: Neurology. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 569–588
Harper C (1979) Wernicke's encephalopathy: a more common disease than realised. A neuropathological study of 51 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 42:226–231
Horton JC, Hedley-Whyte T (1979) Protein movement across the blood-brain barrier in hypervolemia. Brain Res 169:610–614
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Norenberg MD (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination: relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science 211:1068–1070
Majumdar SK, Shaw GK, Thompson AD (1981) Vitamin utilization status in chronic alcoholics. Int J Vitamin Nutrit Res 51:54–58
Ohno K, Pettigrew KD, Rapoport SI (1978) Lower limits of cerebrovascular permeability to nonelectrolytes in the conscious rat. Am J Physiol 235:299–307
Pardridge WM, Oldendorf WH (1977) Transport of metabolic substrates through the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 28:5–12
Pekkanen L (1980) Effects of thiamine deprivation and antagonism on voluntary ethanol intake in rats. J Nutrit 110:937–944
Phillips SC (1981) Does ethanol damage the blood-brain barrier? J Neurol Sci 50:81–87
Phillips SC, Cragg BG (1982a) Weakening of the blood-brain barrier by alcohol-related stresses in the rat. J Neurol Sci 54:271–278
Phillips SC, Cragg BG (1982b) A change in the susceptibility of rat cerebellar Purkinje cells to alcohol, during foetal, neonatal and adult life. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 8:217–231
Phillips SC, Cragg BG, Singh SC (1981) The short-term toxicity of ethanol to neurons in rat cerebral cortex tested by topical application, and a note on a problem in estimating ethanol concentration in tissues. J Neurol Sci 49:353–361
Prickett CO (1934) The effect of deficiency of vitamin B1 upon the central and peripheral nervous systems of the rat. Am J Physiol 107:459–470
Rindi G, Patrini C, Comincioli V, Reggiani C (1980) Thiamine content and turnover rates of some rat nervous regions, using labelled thiamine as a tracer. Brain Res 181:369–380
Robertson DM, Manz HJ (1971) Effect of thiamine deficiency on the competence of the blood-brain barrier to albumin labelled with fluorescent dyes. Am J Pathol 63:393–399
Smith WT (1976) Nutritional deficiencies and disorders. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 3rd edn. Year Book Med Publ, Chicago, pp 194–201
Victor M, Adams RD, Collins GH (1971) The Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Davis, Philadelphia
Victor M, Ferrendelli JA (1970) The nutritional and metabolic diseases of the cerebellun Clinical pathological aspects. In: Fields WS, Willis WD (eds) The cerebellum in health and disease. Green, Missouri, pp 412–449
Watenabe I, Tomita T, Hung KS, Iwasaki Y (1981) Edematous necrosis in thiamine-deficient encephalopathy of the mouse. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 40:454–471
Warnock LG, Burkhalter VJ (1968) Evidence of malfunctioning blood-brain barrier in experimental thiamine deficiency in rats. J Nutrit 94:256–260
Woolley DW, White AGC (1943) Production of thiamine deficiency disease by the feeding of a pyridine analogue of thiamine. J Biol Chem 149:285–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Australian Associated Brewers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips, S.C., Cragg, B.G. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in thiamine-deficient, alcohol-treated rats. Acta Neuropathol 62, 235–241 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691858
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691858