Summary
Freshwater eel gills are notorious for their limited ability to pump chloride. As a result there is a considerable discrepancy between the Na+ and Cl− plasma levels, and plasma HCO3 − and blood pH are relatively high in this species.
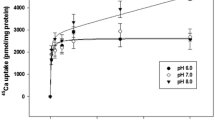
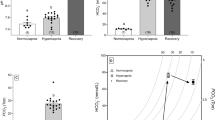
When eels are kept in tanks aerated with pure oxygen, significant alterations in blood acid-base balance, an increase in plasma pCO2 and a decrease in blood pH, are observed. In fish studied after 3 weeks hyperoxia, the decrease in blood pH is compensated by an increase in plasma HCO3 −. Such fish exhibit a Cl− influx 5 times higher than that observed in normoxic fish. This Cl− influx is readily inhibited by addition of SCN− to the external medium.
An anion-stimulated ATPase activated by HCO3 − and by Cl− and inhibited by SCN− was recently described in membrane fractions of the gills ofCarassius auratus, a fish noted for its high Cl− pumping rate. This enzyme is also found in the gills of the eel. While the maximal rates of enzyme activation by HCO3 − and by Cl− are similar inCarassius andAnguilla, the affinity of the enzyme for Cl− is 25 times higher inCarassius. In the microsomal fraction of the hyperoxic eel gills, the maximal anionstimulated ATPase activity remains unchanged but HCO3 − affinity decreases by 50%, while Cl− affinity increases 5 times. Thus some characteristics of this ATPase seem to be closely related to the Cl− pump activity exhibited by the gill in fresh water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornancin, M., De Renzis, G.: A sensitive automated method for ATPase kinetics. Anal. Biochem.75, 374–381 (1976)
Clark, B., Porteous, J.W.: Determination of succinic acid by an enzymatic method. Biochem. J.93, 21c-22c (1964)
Cameron, J.N.: Branchial ion uptake in arctic Grayling: resting values and effects of acid-base disturbance. J. exp. Biol.64, 711–725 (1976)
Dejours, P.: Problems of control of breathing in fishes. In: Comparative physiology: locomotion, respiration, transport and blood (ed. L. Bolis, K. Schmidt-Nielsen, S.H.P. Maddrell), pp. 117–133. Amsterdam and New York: North Holland/American Elsevier 1973
De Renzis, G.: The branchial chloride pump in the goldfishCarassius auratus: relationship between Cl−/HCO3 − and Cl−/Cl− exchanges and the effect of thiocyanate. J. exp. Biol.63, 587–602 (1975)
De Renzis, G., Bornancin, M.: A Cl−/HCO3 − ATPase in the gills ofCarassius auratus. Its inhibition by thiocyanate. Biochem. Biophys. Acta467, 192–207 (1977)
De Renzis, G., Maetz, J.: Studies on the mechanism of chloride absorption by the goldfish gill. Relation with acid-base regulation. J. exp. Biol.59, 339–358 (1973)
Epstein, F.H., Katz, A.I., Pickford, P.E.: Sodium and potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase of gills: role in adaptation of teleosts to salt water. Science156, 1245–1247 (1967)
Epstein, F.H., Maetz, J., De Renzis, G.: Active transport of chloride by the teleost gill: inhibition by thiocyanate. Am. J. Physiol.224, 1295–1299 (1973)
Farrell, A.P., Lutz, P.L.: Apparent anion imbalance in the fresh water adapted eel. J. comp. Physiol.102, 159–166 (1975)
Garcia Romeu, F., Motais, R.: Mise en évidence d'échanges Na+/NH4 + chez l'anguille d'eau douce. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.17, 1201–1204 (1966)
Hughes, G. M.: Comparative physiology of vertebrate respiration. London: Heinemann 1963
Kerstetter, T.H., Kirschner, L.B.: Active chloride transport by the gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. exp. Biol.56, 263–272 (1972)
Kerstetter, T.H., Kirschner, L.B.: HCO3 −-dependent ATPase activity in the gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.48B, 581–589 (1974)
Kirsch, R.: Plasma chloride and sodium and chloride space in the european eel,Anguilla anguilla L. J. exp. Biol.57, 113–131 (1972a)
Kirsch, R.: The kinetics of peripheral exchanges of water and electrolytes in the silver eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) in fresh water and in sea water. J. exp. Biol.57, 489–512 (1972b)
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951)
Maetz, J.: Fish gills: mechanisms of salt transfer in fresh water and sea water. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London,B 262, 209–251 (1971)
Maetz, J., Bornancin, M.: Biochemical and biophysical aspects of salt secretion by chloride cells in teleosts. Fortschr. Zool.23, 322–362 (1975)
Maetz, J., Garcia Romeu, F.: The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a fresh water fish,Carassius auratus. II. Evidence of NH4 +/Na+ and HCO3 −/Cl− exchanges. J. gen. Physiol.47, 1209–1227 (1964)
Maetz, J., Mayer, N., Chartier-Baraduc, M.M.: Labalance minérale du sodium chezAnguilla anguilla en eau de mer, en eau douce et au cours du transfert d'un milieu à l'autre. Effects de l'hypophysectomie et de la prolactine. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol.8, 177–188 (1967)
Motais, R.: Les méchanismes d'échanges ioniques branchiaux chez les téléostéens. Ann. Inst. oceanog. Monaco45, 1–84 (1967)
Shaw, J.: The control of the salt balance in the crustacea. Symposia Exp Biol.18, 237–254 (1964)
Truchot, J.P.: Blood acid-base changes during experimental emersion and reimmersion of the shore crabCarcinus maenas (L.). Resp. Physiol.23, 351–360 (1975a)
Truchot, J.P.: Changements de l'état acide-base du sang en fonction de l'oxygénation de l'eau chez le crabeCarcinus maenas. J. Physiol. (Paris)70, 583–592 (1975b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bornancin, M., De Renzis, G. & Maetz, J. Branchial Cl transport, anion-stimulated ATPase and acid-base balance inAnguilla anguilla adapted to freshwater: Effects of hyperoxia. J Comp Physiol B 117, 313–322 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691557
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691557