Summary
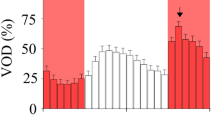
In a number of organisms which exhibit circadian rhythmicity, a continuous exposure to ethanol at moderate (0.1%) concentrations is known to cause period lengthening. In studies of the effects of ethanol on the circadian luminescence glow rhythm of the marine dinoflagellateGonyaulax, we observed that 0.1% ethanol causes instead a period shortening. We have also found that ethanol pulses cause phase shifts, with little or no after-effects on the period of the circadian rhythm which continues thereafter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT :
-
circadian time
References
Brinkmann, K.: The influence of alcohols on the circadian rhythm and metabolism ofEuglena gracilis. J. Interdiscip. Cycle Res.7, 149–170 (1976)
Bünning, E., Baltes, J.: Wirkung von Äthylalkohol auf die physiologische Uhr. Naturwissenschaften49, 19–20 (1962)
Bünning, E., Moser, I.: Light-induced phase shifts of circadian leaf movements ofPhaseolus: Comparison with the effects of potassium and ethyl alcohol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.70, 3387–3389 (1973)
Enright, J.T.: The internal clock of drunken isopods. Z. vergl. Physiol.75, 332–346 (1971)
Fogel, M., Hastings, J.W.: A substrate binding protein in theGonyaulax bioluminescence reaction. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.142, 310–321 (1971)
Guillard, R.R.L., Ryther, J.H.: Studies of marine plankton diatoms. I.Cyclotella nana Hustedt andDetonula confervacea Cleve Gran. Can. J. Microbiol.8, 229–239 (1962)
Hastings, J.W.: Unicellular clocks. Ann. Rev. Microbiol.13, 297–312 (1959)
Hastings, J.W.: Biochemical aspects of rhythms: Phase shifting by chemicals. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol.25, 131–143 (1960)
Hastings, J.W.: The biochemical basis for dinoflagellate luminescence: A molecular model for the control of flashing. In: Bioluminescence today. Herring, P.J. (ed.). London: Academic Press (in press) 1979
Hastings, J.W., Sweeney, B.M.: The luminescent reaction in extracts of the marine dinoflagellateGonyaulax polyedra. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol.49, 209–225 (1957a)
Hastings, J.W., Sweeney, B.M.: On the mechanism of temperature independence in a biological clock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.43, 804–811 (1957b)
Kastenmeier, B., Reich, V., Engelmann, W.: Effects of alcohols on the circadian petal movement rhythm ofKalanchoe and the rhythmic movement ofDesmodium. Chronobiologia4, 122 (1977)
Keller, S.: Über die Wirkung chemischer Faktoren auf die tagesperiodischen Blattbewegungen vonPhaseolus multiflorus. Z. Bot.48, 32–57 (1960)
Njus, D., Sulzman, F.M., Hastings, J.W.: Membrane model for the circadian clock. Nature248, 116–120 (1974)
Oltmanns, O.: Über den Einfluß der Temperatur auf die endogene Tagesrhythmik und die Blühinduction bei der KurztagpflanzeKalanchoe blossfeldiana. Planta54, 233–264 (1960)
Sweeney, B.M.: The potassium content ofGonyaulax polyedra and phase changes in the circadian rhythm of stimulated bioluminescence by short exposures to ethanol and valinomycin. Plant Physiol.53, 337–342 (1974)
Sweeney, B.M.: Evidence that membranes are components of circadian oscillators. In: The molecular basis of circadian rhythms Hastings, J.W., Schweiger, H.G. (eds.), pp. 267–281. Berlin: Abakon Verlagsgesellschaft, 1976
Taylor, W., Hastings, J.W.: Aldehydes phase shift theGonyaulax clock. J. Comp. Physiol.130, 359–362 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work has been supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health GM-19536 to J.W. Hastings, and by a Rackham Block Grant to Walter Taylor from the University of Michigan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, W., Van Gooch, D. & Hastings, J.W. Period shortening and phase shifting effects of ethanol on theGonyaulax glow rhythm. J Comp Physiol B 130, 355–358 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689854
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689854