Summary
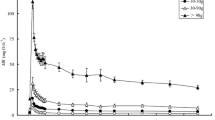
The rate of oxygen consumption (\(\dot V_{O_2 }\)) by skeletal muscle was investigated in isolated perfused hindlimbs of laboratory rats and lemmings (Lemmus). In both species,\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) increased in proportion to blood flow rate, even at flow rates 4–5 times above resting level. The slope of the line relating\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) to skeletal muscle blood flow was significantly greater in the lemming than in the rat. This may be related to the inverse relationship between body weight and metabolic rate. These data support the hypothesis that in small animals a dependent relationship exists between blood flow and skeletal muscle\(\dot V_{O_2 }\).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartunková, R., Janský, L.: Effect of cold and noradrenaline on the cardiovascular system of cold adapted rats. Physiol. Bohemoslov.20, 163–171 (1971)
Durán, W.N., Renkin, E.M.: Oxygen consumption and blood flow in resting mammalian skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.226, 173–177 (1974)
Folk, G.E., Jr., Grubb, B.: Thermogenesis of specific organs in cold acclimated rodents. Fed. Proc.37 (in press) (1978)
Grubb, B., Folk, G.E., Jr.: Effect of cold acclimation on norepinephrine stimulated oxygen consumption in muscle. J. comp. Physiol.110, 217–226 (1976)
Heroux, O., Hart, J.S., Depocas, F.: Metabolism and muscle activity of anesthetized warm and cold acclimated rats exposed to cold. J. Appl. Physiol.9, 399–403 (1956)
Holling, H.E., Verel, D.: Circulation in the elevated forearm. Clin. Sci.16, 197–213 (1957)
Holt, J.P., Rhode, E.A., Kines, H.: Ventricular volume and body weight in mammals. Am. J. Physiol.215, 704–715 (1968)
Honig, C.R., Frierson, J.L., Nelson, C.N.: O2 transport and\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) in resting muscle: significance for tissue-capillary exchange. Am. J. Physiol.220, 357–361 (1971)
Hudlická, O.: Muscle blood flow. Its relation to muscle metabolism and function. p. 112. Amsterdam: Swets & Zeitlinger B.V. 1973
Janský, L.: Participation of body organs during nonshivering heat production. In: Nonshivering thermogenesis (L. Janský ed.), pp. 159–172. Prague: Academia 1971
Kleiber, M.: The fire of life. An introduction to animal energetics, p. 212. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1961
Ross, E.: Regional blood flow in the rat. J. Appl. Physiol.21, 1273–1275 (1966)
Stainsby, W.N., Otis, A.B.: Blood flow, blood oxygen tension, oxygen uptake, and oxygen transport in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.206, 858–866 (1964)
Whalen, W.J.: Intracellular\(P_{O_2 }\): a limiting factor in cell respiration. Am. J. Physiol.211, 862–868 (1966)
Whalen, W.J., Buerk, D., Thuning, C.A.: Blood flow limited oxygen consumption in resting cat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.224, 763–768 (1973)
Zivin, J., Snarr, J.: A stable preparation for rat brain perfusion: effect of flow rate on glucose uptake. J. Appl. Physiol.32, 658–663 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grubb, B., Folk, G.E. Skeletal muscle\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) in rat and lemming: Effect of blood flow rate. J Comp Physiol B 128, 185–188 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689483
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689483