Summary
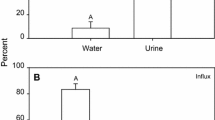
The levels of Na+, K+ ATPase were measured in gills fromPlatichthys flesus adapted to seawater and freshwater using a variety of experimental techniques. Na+, K+ ATPase was assayed directly in crude gill homogenates,3H-ouabain binding was determined in isolated, perfused gills and ouabainsensitive oxygen consumption measured in sliced gill filaments. These experimental approaches all failed to show any difference in Na+, K+ ATPase activity or in enzyme turnover rate in gills from seawateradapted and freshwater-adaptedPlatichthys. The results are discussed in terms of the marine origin of the flounder and the energetic demands of ion regulation in euryhaline fish.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson A, Gatemby AO, Lowe AG (1973) The determination of inorganic orthophosphate in biological systems. Biochim Biophys Acta 320:195–204
Baker PF, Willis JS (1972) Binding of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to intact cells. J Physiol 224:441–462
Brading AF, Widdicombe JH (1974) An estimate of sodium/potassium pump activity, and the number of pump sites in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli, using3H ouabain. J Physiol 238:235–249
Butler DG, Carmichael FJ (1972) (Na+−K+)-ATPase activity in eel (Anguilla rostrata) gills in relation to changes in environmental salinity: Rôle of adrenocortical steroids. Gen Comp Endocrinol 19:421–427
Dawson MA, Gould E, Thuberg FP, Calabrese A (1977) Physiological response of juvenile striped bass,Morone saxatilis to low levels of cadmium and mercry. Chesapeake Sci 18:353–359
Eddy FB (1975) Effect of calcium on gill potentials and on sodium and chloride fluxes in the goldfishCarassius auratus. J Comp Physiol 96:131–142
Epstein FH, Katz AI, Pickford GE (1967) Sodium and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of gills. Rôle in adaptation of teleosts to salt water. Science NY 156:1234–1247
Evans DH (1979) Ionic and osmotic regulation in fish. In: Maloiy GMO (ed) Comparative physiology of osmoregulation in animals. Academic Press, New York, pp 305–390
Forrest JN, Cohen AD, Schon DA, Epstein FH (1973) Na transport and Na+−K+-ATPase in gills during adaptation to seawater: effect of cortisol. Am J Physiol 224:709–713
Giles MA, Vanstone WE (1976) Changes in ouabain sensitive adenosine triphosphatase activity in gills of coho salmon (Oncorhyncus kisutch) during parr-smolt transformation. J Fish Res Board Can 33:54–62
Ho S-M, Chan DKO (1980) Branchial ATPases and ionic transport in the eel,Anguilla japonica I. Na+−K+-ATPase. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] 66:255–260
Jampol LM, Epstein FH (1970) Sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase and osmotic regulation by fishes. Am J Physiol 218:607–611
Johnson SL, Ewing RD, Lichatowich JA (1977) Characterization of gill (Na+−K+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from Chinook salmon,Oncorhynchus tschwytscha. J Exp Zool 199:345–354
Kamiya M, Utida S (1968) Changes in activity of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in gills during adaptation of the japanese eel to seawater. Comp Biochem Physiol 26:675–685
Karnaky KJ, Kinter LB, Kinter WB, Stirling CE (1976) Teleost chloride cell II. Autoradiographic localisation of gill Na+, K+ ATPase in killifishFundulus heteroclitus adapted to low and high salinity environments. J Cell Biol 70:157–171
Kirschner LB (1969) ATPase activity in gills of euryhaline fish. Comp Biochem Phsyiol 29:871–874
Lassere P (1971) Increase of (Na+ K+)-dependent ATPase activity in gills and kidneys of two euryhaline marine teleosts,Crenimugil labrosus (Risso, 1826) andDicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758), during adaptation to freshwater. Life Sci 10:113–119
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maetz J (1971) Fish gills: mechanisms of salt transfer in freshwater and scawater. Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 262:209–249
Maetz J, Bornancin M (1975) Biochemical and biophysical aspects of salt excretion by chloride cells in teleosts. Fortschr Zool 23:322–362
Mashiter KE (1976) Chloride transport and enzyme levels in flounder gills. Ph D thesis, University of Lancaster
Pfeiler E, Kirschner LB (1972) Studies on gill ATPase of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Biochem Biophys Acta 282:301–310
Potts WTW (1977) Fish gills. In: Gupta BL, Moreton RB, Oschman JL, Wall BJ (eds) Transport of ions and water in animals. Academic Press, New York London, pp 453–480
Potts WTW, Fletcher CR, Eddy FB (1973) An analysis of the sodium and chloride fluxes in the flounder,Platichthys flesus. J Comp Physiol 87:21–28
Sargent JR, Thompson AJ (1974) The nature and properties of the inducible sodium-plus-potassium ion dependent adenosine triphosphatase in the gills of eels (Anguilla anguilla) adapted to freshwater and seawater. Biochem J 144:69–75
Shuttleworth TJ (1978) The effect of adrenaline on potentials in the isolated gills of the flounder (Platichthys flesus L.). J Comp Physiol 124:129–136
Shuttleworth TJ, Freeman RFH (1973) The role of the gills in seawater adaptation inAnguilla dieffenbachii. J Comp Physiol 86:293–313
Shuttleworth TJ, Potts WTW, Harris JN (1974) Bioelectric potentials in the gills of the flounderPlatichthys flesus. J Comp Physiol 94:321–329
Silva P, Solomon R, Spokes K, Epstein FH (1977) Ouabain inhibition of gill Na-K-ATPase: relationship to active chloride transport. J Exp Zool 199:419–426
Somero GN, Yancey PH, Chow TJ, Snyder CB (1977) Lead effects on tissue and whole organism respiration of the estuarine teleost fish,Gillichthys mirabilis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 6:349–354
Stuenkel EL, Hillyard SD (1980) Effects of temperature and salinity on gill Na+, K+ ATPase activity in the pupfish,Cyprinodon salinus. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 67:179–182
Towle DW, Gilman ME, Hempel JD (1977) Rapid modulation of gill Na and K dependent ATPase activity during acclimation of the killifishFundulus heteroclitus to salinity change. J Exp Zool 202:179–186
Utida S, Hirano T (1973) Effects of changes in environmental salinity on salt and water movement in the intestine and gills of the eel,Anguilla japonica. In: Chavin W (ed) Response of fish to environmental changes. Thomas, Springfield, pp 240–267
Utida S, Kamiya M, Shirai N (1971) Relationship between the activity of Na, K-activated adenosine triphosphatase and the number of chloride cells in eel gills with special reference to seawater adaptation. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 38:443–447
Zaugg WS, McLain LR (1971) Gill sampling as a method of following biochemical changes: ATPase activities altered by ouabain injection and salt water adaptation. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] 38:501–506
Doneen BA (1981) Effects of adaptation to seawater, 170% seawater and to freshwater on activities and subcellular distribution of branchial Na+−K+-ATPase, low- and high-affinity Ca++-ATPase, and ouabain-insensitive ATPase inGillichthys mirabilis. J Comp Physiol 145:51–62
Gallis J-L, Lassere P, Belloc F (1979) Freshwater adaptation in the euryhaline teleostChelon labrosus. 1. Effects of adaptation, prolactin, cortisol and actinomycin D on plasma osmotic balance and (Na+−K+) ATPase in gill and kidney. Gen Comp Endocrinol 38:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stagg, R.M., Shuttleworth, T.J. Na+, K+ ATPase, quabain binding and quabain-sensitive oxygen consumption in gills fromPlatichthys flesus adapted to seawater and freshwater. J Comp Physiol B 147, 93–99 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689296
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689296