Summary
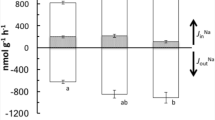
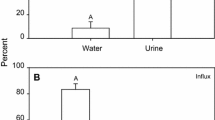
Measurements of the transepithelial potential (Vint-Vext) across the gills of Brown Trout,Salmo trutta, were made in solutions of a range of pH and calcium concentrations. The potential was strongly dependent on external pH, being negative in neutral solutions but positive in acid solutions. The addition of calcium to the external medium produced a positive shift in potential in all but very acid media (pH 4.0–3.5), where very little change was seen. The gill membrane appears to act as a hydrogen electrode having a very high permeability to H+ ions, and the potential behaves as a diffusion potential. The presence of calcium reduced the permeability to both H+ and Na+ ions but even at a calcium concentration of 8.0 mM/l the permeability ratio ΦH+/ΦNa+ was still more than 900. The transepithelial potential is shown to be diffusional in origin and is discussed in terms of the relative permeability of the gill to H+, Na+ and Cl− ions. Sodium fluxes across the gills were measured and provide the basis for a theoretical consideration of Na+, Cl− and H+ fluxes across the gills in neutral and acid solutions. The positive potential at low pH largely accounts for the increased loss of sodium from fish in these conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cuthbert, A.W., Maetz, J.: Effects of Ca++ and Mg++ on sodium fluxes through the gills ofCarassius auratus. J. Physiol. (Lond.)221, 633–643 (1972)
Dively, J.L., Mudge, J.E., Neff, W.H., Anthony, A.: Blood PO2, PCO2 and pH changes in brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) exposed to sublethal levels of acidity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.57A, 347–351 (1977)
Eddy, F.B.: The effect of calcium on gill potentials and on sodium and chloride fluxes in the goldfish,Carassius auratus. J. comp. Physiol.96, 131–142 (1975)
Eddy, F.B.: Acid-base balance in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdnerii) subjected to acid stress. J. exp. Biol.64, 159–171 (1976)
Gilbert, D.L., Lowenberg, W.E.: The effect of pH on the resting membrane potential of frog sartorius muscle. J. cell. comp. Physiol.63, 359–364 (1964)
Goldman, D.E.: Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes. J. gen. Physiol.27, 37–60 (1943)
Hargis, J.R.: Ventilation and metabolic rate of young rainbow trout exposed to sublethal environmental pH. J. exp. Zool.196, 39–44 (1975)
Hodgkin, A.L., Horowicz, P.: The influence of K+ and Cl− on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)148, 127–160 (1959)
House, C.R., Maetz, J.: On the electrical gradient across the gill of the sea water-adapted eel. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.47A, 917–924 (1974)
Isaia, J., Masoni, A.: The effects of calcium and magnesium on water and ionic permeabilities in the sea water-adapted eel,Anguilla anguilla. J. comp. Physiol.109, 221–233 (1976)
Kerstetter, T.H., Kirschner, L.B., Rafuse, D.D.: On the mechanism of Na+ transport by the irrigated gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdnerii). J. gen. Physiol.56, 342–359 (1970)
Kitasato, H.: Influence of H+ on the membrane potential and ion fluxes ofNitella. J. gen. Physiol.52, 60–87 (1968)
Leivestad, H., Muniz, I.P.: Fish kill at low pH in a Norwegian River. Nature259, 391–392 (1976)
Maetz, J.: Na+/NH +4 , Na+/H+ exchanges and NH3 movement across the gill ofCarassius auratus. J. exp. Biol.58, 255–275 (1973)
Maetz, J.: Origine de la différence de potentiel eléctrique transbranchiale chez le poisson rougeCarassius auratus. Importance de l'ion Ca++. C.R. Acad. Sc. Paris279, 1277–1280 (1974)
Maetz, J., Payan, P., de Renzis, G.: Controversial aspects of ionic uptake in freshwater animals. In: Perspectives in experimental biology, Vol. 1 (ed. Spencer Davies). London: Pergamon 1976
Oduleye, S.O.: The effects of calcium and prolactin on water and electrolyte regulation in the brown trout (Salmo trutta). Ph. D. thesis, University of Lancaster (1973)
Packer, R.K., Dunson, W.A.: Effects of low environmental pH on blood pH and Na+ balance of brook trout. J. exp. Zool.174, 65–72 (1970)
Packer, R.K., Dunson, W.A.: Anoxia and sodium loss associated with the death of brook trout at low pH. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.41A, 17–26 (1972)
Pequeux, A.: Effects of pH changes on the frog skin electrical potential difference and on the potential variations induced by high hydrostatic pressures Comp. Biochem. Physiol.55A, 103–108 (1976)
Potts, W.T.W., Eddy, F.B.: Gill potentials and sodium fluxes in the flounder,Platichthys flesus. J. comp. Physiol.87, 29–48 (1973)
Rahn, H., Baumgardner, F.W.: Temperature and acid-base regulation in fish. Resp. Physiol.14, 171–182 (1972)
Shaw, J.: Absorbtion of sodium ions by the crayfishAstacus pallipes L. III. Effect of other cations in the external solution. J. exp. Biol.37, 548–556 (1960)
Ussing, H.H.: Active ion transport through the isolated frog skin in the light of tracer studies. Acta Physiol. Scand.17, 1–37 (1949)
Woodbury, J.W., White, S.H., Weakly, J.N.: High membrane permeability of frog skeletal muscle. Abstracts, XXIV Int. Cong. Physiol. Sci., p. 472. Bethesda, MD: Federation of American societies for Experimental Biology 1968
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McWilliams, P.G., Potts, W.T.W. The effects of pH and calcium concentrations on gill potentials in the Brown Trout,Salmo trutta . J Comp Physiol B 126, 277–286 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688938
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688938