Summary
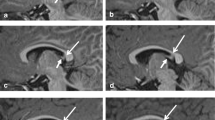
Two neonates are presented with intrauterine necrosis of the brain stem. In one the necrosis and calcification were multifocal and extended from the thalamus to the medulla oblongata. In the other the process was limited to the medulla, but was associated with severe hypoplasia of the nuclei pontis. In both cases the cerebellum was hypoplastic and immature for the gestational age. The connection between the two lesions remains obscure, and two hypotheses are discussed. One hypothesis ascribes the delay in cerebellar development to subliminal damage caused by the same insult that produced the brain-stem lesions, the other considers the possible effects of partial deafferentation on the maturation of the cerebellum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RD, Prod'hom LS, Rabinowicz T (1977) Intrauterine brain death. Neuraxial reticular core necrosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 40:41–49
Bankl H, Jellinger K (1967) Zentralnervöse Schäden nach fetaler Kohlenoxydvergiftung. Beitr Pathol Anat Allg Pathol 135: 350–376
Colmant HJ, Wever H (1963) Pränatale Kohlenoxydvergiftung mit “Organtod” des Zentralnervensystems. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 204:271–287
Corner MA, Schade JP (1967) Developmental patterns in the central nervous system of birds. IV. Cellular and molecular bases of functional activity. In: Bernhard CG, Schade JP (eds) Developmental neurology. Progress in brain research, vol 26. Elsevier, Amsterdam London New York, pp 237–250
Dambska M, Dydyk L, Szretter T, Wozniewicz J, Myers RE (1976) Topography of lesions in newborn and infant brains following cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Damage to brain stem and hemispheres. Biol Neonate 29:194–206
Essick CR (1912) The development of the nuclei pontis and the nucleus arcuatus in man. Am J Anat 13:25–54
Gilles FH (1969) Hypotensive brain stem necrosis. Selective symmetrical necrosis of tegmental neuronal aggregates following cardiac arrest. Arch Pathol 88:32–41
Gilles FH, Nag D (1971) Vulnerability of human spinal cord in transient cardiac arrest. Neurology 21:833–839
Gutmann E (1964) Neurotrophic relations in the regeneration process. In: Singer M, Schade JP (eds) Mechanisms of neural regeneration. Progress in brain research, vol 13. Elsevier, Amsterdam London New York, pp. 72–112
Hamburger V, Wenger E, Oppenheim R (1966) Motility in the chick embryo in the absence of sensory input. J Exp Zool 162:133–160
Janzer RC, Friede RL (1980) Hypotensive brain stem necrosis or cardiac arrest encephalopathy? Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 50:53–56
Leech RW, Alvord EC Jr (1977) Anoxic ischemic encephalopathy in the human neonatal period. Arch Neurol 34: 109–113
Myers RE (1973) Two classes of dysergic brain abnormality and their condition of occurrence. Arch Neurol 29:394–399
Myers RE, Yamaguchi S (1977) Nervous system effects of cardiac arrest in monkeys. Arch Neurol 34:65–74
Norman MG (1972) Antenatal neuronal loss and gliosis of the reticular formation thalamus and hypothalamus. A report of three cases. Neurology 22:910–916
Rakić P, Sidman RL (1970) Histogenesis of cortical layers in human cerebellum, particularly the lamia dissecans. J Comp Neurol 139:473–500
Schneider H, Ballowitz L, Schachinger H, Hanefeld F, Droszus JU (1975) Anoxic encephalopathy with predominant involvement of basal ganglia, brain stem and spinal cord in the perinatal period. Report on seven newborns. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 32:287–298
Schneider H, Dralle J, Ebhardt G (1973) Läsionen des Rückenmarks nach temporärem Kreislaufstillstand. Z Neurol 204:165–178
Sidman RL, Rakić P (1973) Neuronal migration with special reference to developing human brain: a review. Brain Res 62:1–35
Thakkar N, O'Neil W, Duvally L, Liu C, Ambler M (1977) Möbius syndrome due to brain stem tegmental necrosis. Arch Neurol 34:124–126
Towfighi J, Marks K, Palmer E, Vannucci R (1979) Möbius syndrome. Neuropathologic observations. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 48:11–17
Wilson ER, Mirra SS, Schwartz JF (1982) Congenital diencephalic and brain stem damage; neuropathologic study of three cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 57:70–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gessaga, E.C., Herrick, M.K. & Urich, H. Necrosis of the fetal brain stem with cerebellar hypoplasia. Acta Neuropathol 69, 326–331 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688312
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688312